SLUSCZ1 May 2017 TPS92518-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 General Operation
- 8.3.2 Important System Considerations: Off-Timer and Maximum Peak Threshold Values
- 8.3.3 Shunt FET or Matrix dimming: Maximum Off-timer Calculation
- 8.3.4 VIN and the VCC Internal Regulators
- 8.3.5 Output Enable Control Logic
- 8.3.6 BOOT Capacitor and BOOT UVLO
- 8.3.7 Drop-out Operation
- 8.3.8 Analog and PWM Dimming
- 8.3.9 VIN and CSPx Pin Configuration
- 8.3.10 Enable and Undervoltage Lock-out Configuration
- 8.3.11 Voltage Sampling and DAC Operation
- 8.3.12 Device Functional Modes
- 8.4 Serial Interface
- 8.5
Registers
- 8.5.1 CONTROL Register (Address = 00h) [reset = 00h]
- 8.5.2 STATUS (FAULT) Register (Address = 01h) [reset = 10h]
- 8.5.3 THERM_WARN_LMT Register (Address = 02h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.4 LED1_PKTH_DAC Register (Address = 03h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.5 LED2_PKTH_DAC Register (Address = 04h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.6 LED1_TOFF_DAC Register (Address = 05h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.7 LED2_TOFF_DAC Register (Address = 06h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.8 LED1_MAXOFF_DAC Register (Address = 07h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.9 LED2_MAXOFF_DAC Register (Address = 08h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.5.10 VTHERM Register (Address = 09h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.11 LED1_MOST_RECENT Register (Address = 0Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.12 LED1_LAST_ON Register (Address = 0Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.13 LED1_LAST_OFF Register (Address = 0Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.14 LED2_MOST_RECENT Register (Address = 0Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.15 LED2_LAST_ON Register (Address = 0Eh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.16 LED2_LAST_OFF Register (Address = 0Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.5.17 Reset Register (Address = 10h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6 Programming
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.8.4.2 ANALOG:
Another impact on linearity can occur when analog dimming (LEDx_PKTH_DAC threshold adjustment) and the inductor current becomes discontinuous. Discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) occurs when the inductor current reaches 0 A each off-time. When the device enters DCM, the output current is no longer the peak current minus half the ripple current (as shown in Figure 16) and is no longer a linear relationship between the LEDx_PKTH_DAC value and the average output current. The linear range can be extended by lowering the ripple, ΔIL-PP to extend the natural linear region of operation.
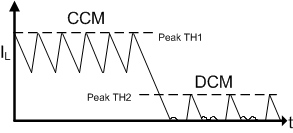 Figure 29. Analog Dimming Limitation
Figure 29. Analog Dimming Limitation
Another approach can be used by first analyzing the system operation. The point at which DCM is entered can be calculated as well as the average current value when in DCM. The micro-controller writing the LEDx_PKTH_DAC values can simply write alternate values in the DCM area to ensure net linear response to the LED average current. See DCM Current Calculationfor information on calculating the average current when in DCM.