ZHCSLS0B July 2022 – April 2024 TPS929240-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Device Bias and Power
- 6.3.2 Constant Current Output
- 6.3.3 PWM Dimming
- 6.3.4 FAIL-SAFE State Operation
- 6.3.5 On-Chip, 8-Bit, Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 6.3.6
Diagnostic and Protection in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.1 VBAT Undervoltage Lockout Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.2 Low-Supply Warning Diagnostics in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.3 Supply Undervoltage Diagnostics in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.4 Reference Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.5 Pre-Thermal Warning in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.6 Overtemperature Protection in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.7 Overtemperature Shutdown in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.8 LED Open-Circuit Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.9 LED Short-Circuit Diagnostics in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.10 Single-LED Short-Circuit Detection in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.11 EEPROM CRC Error in NORMAL state
- 6.3.6.12 Communication Loss Diagnostic in NORMAL State
- 6.3.6.13 Fault Masking in NORMAL state
- 53
- 6.3.7
Diagnostic and Protection in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.1 Supply Undervoltage Lockout Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.2 Low-Supply Warning Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.3 Supply Undervoltage Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE State
- 6.3.7.4 Reference Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE states
- 6.3.7.5 Pre-Thermal Warning in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.6 Overtemperature Protection in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.7 Overtemperature Shutdown in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.8 LED Open-Circuit Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.9 LED Short-Circuit Diagnostics in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.10 Single-LED Short-Circuit Detection in FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.7.11 EEPROM CRC Error in FAIL-SAFE State
- 6.3.7.12 Fault Masking in FAIL-SAFE state
- Diagnostics Table in FAIL-SAFE State
- 6.3.8 OFAF Setup In FAIL-SAFE state
- 6.3.9 ERR Output
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6 Register Maps
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DCP|38
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DCP|38
订购信息
6.5.1.1 Protocol Overview
The FlexWire is a UART-based protocol supported by most microcontroller units (MCU). Each frame contains multiple bytes started with a synchronization byte. The synchronization byte allows LED drivers to synchronize with master MCU frequency, therefore saving the extra cost on high precision oscillators that are commonly used in UART / CAN interfaces. Each byte has 1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity check. The LSB data follows the start bit as the below figure describes. The FlexWire supports adaptive communication frequency ranging from 10kHz to 1MHz. The protocol supports master-slave with star-connected topology.
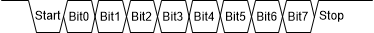 Figure 6-10 One Byte Data Structure
Figure 6-10 One Byte Data StructureThe FlexWire is designed robust for automotive environment. After the slave device receives a communication frame, it firstly verifies its CRC byte. When CRC is verified, the slave device sends out response frame and clears the watchdog timer. In addition, if one communication frame is interrupted in the middle without any bus toggling for a period longer than timeout timer t(DBWTIMER), the TPS929240-Q1 resets the communication and waits for next communication starting from synchronization byte. It is also required for idle period between bytes within t(DBWTIMER). The timeout timer t(DBWTIMER) is programmable by configuration register DBWTIMER. TI recommends using a longer timeout setting for low baud rate communication to avoid unintended timeout and using a shorter timeout setting for high baud rate communication.
If communication CRC check fails, the TPS929240-Q1 ignores the message without sending the feedback. The master does not receive any feedback if the communication is unsuccessful. In this case, the communication can be reset by keeping communication bus idle for t(DBWTIMER), which forces the TPS929240-Q1 to clear its cache and be ready for new communication.
FlexWire supports both write and readback. Both write or readback communication supports burst mode for high throughput and single-byte mode. Figure 6-11 describes the frame structure of a typical single-byte write action. The master frame consists of SYNC, DEV_ADDR, REG_ADDR, DATA and CRC bytes. After CRC is verified, the slave immediately feeds back ACK byte. Figure 6-12 describes the frame structure of a typical single-byte readback action. The master frame consists of SYNC, DEV_ADDR, REG_ADDR, and CRC bytes. After CRC is verified, the slave immediately feeds back DATA and ACK bytes.
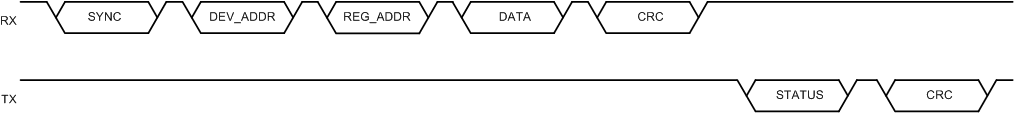 Figure 6-11 Single-Byte Write Command with Status
Feedback
Figure 6-11 Single-Byte Write Command with Status
Feedback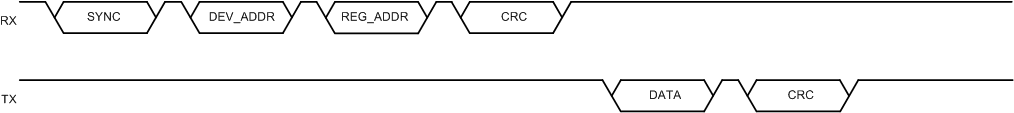 Figure 6-12 Single-Byte Readback Command
Figure 6-12 Single-Byte Readback Command| BYTE NAME | LENGTH (byte) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| SYNC | 1 | Synchronization byte from master |
| DEV_ADDR | 1 | Device address bit, r/w, broadcast, burst mode |
| REG_ADDR | 1 | Register address |
| DATA_N | Variable (1, 4, 16, 24) | N-th byte data content |
| CRC | 1 | Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for DEV_ADDR, REG_ADDR and all DATA bytes |
| STATUS | 1 | Acknowledgment (Return FLAG_ERR register value) |