ZHCSKB4C September 2019 – December 2024 TPSM82810 , TPSM82813
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- VCA|13
- SIL|14
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
8.4.5 Soft Start / Tracking (SS/TR)
The internal soft-start circuitry controls the output voltage slope during start-up. This control avoids excessive inrush current and makes sure of a controlled output voltage rise time. This control also prevents unwanted voltage drops from high impedance power sources or batteries. When EN is set high, the device starts switching after a delay of about 200μs. Then VOUT rises with a slope controlled by an external capacitor connected to the SS/TR pin.
A capacitor connected from SS/TR to GND is charged with 2.5µA by an internal current source during soft start until the capacitor reaches the reference voltage of 0.6V. After reaching 0.6V, the SS/TR pin voltage is clamped internally while the SS/TR pin voltage keeps rising to a maximum of about 3.3V. The capacitance required to set a certain ramp-time (tramp) is:
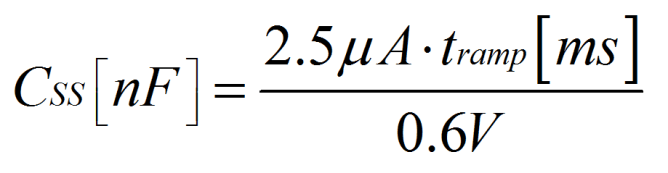
Leaving the SS/TR pin un-connected provides the fastest start-up ramp of 150µs typically. If the device is set to shutdown (EN = GND), undervoltage lockout, or thermal shutdown, an internal resistor pulls the SS/TR pin to GND tomake sure of a proper low level. Returning from those states causes a new start-up sequence.
A voltage applied at the SS/TR pin can also be used to track a controller voltage. The output voltage follows this voltage in both directions up and down in forced PWM mode. In PFM mode, the output voltage decreases based on the load current. An external voltage applied on SS/TR is internally clamped to the feedback voltage (0.6V). TI recommends to set the final value of the external voltage on SS/TR to be slightly above 0.6V to make sure the device operates with the internal reference voltage when the power-up sequencing is finished. See Section 9.3.1.