ZHCS266F June 2011 – May 2017 TRF7960A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Characteristics
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5Specifications
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.2 Power Supplies
- 6.3 Supply Arrangements
- 6.4 Supply Regulator Settings
- 6.5 Power Modes
- 6.6 Receiver – Analog Section
- 6.7 Receiver – Digital Section
- 6.8 Oscillator Section
- 6.9 Transmitter - Analog Section
- 6.10 Transmitter - Digital Section
- 6.11 Transmitter – External Power Amplifier or Subcarrier Detector
- 6.12 Communication Interface
- 6.13
Direct Commands from MCU to Reader
- 6.13.1 Command Codes
- 6.13.2 Reset FIFO (0x0F)
- 6.13.3 Transmission With CRC (0x11)
- 6.13.4 Transmission Without CRC (0x10)
- 6.13.5 Delayed Transmission With CRC (0x13)
- 6.13.6 Delayed Transmission Without CRC (0x12)
- 6.13.7 Transmit Next Time Slot (0x14)
- 6.13.8 Block Receiver (0x16)
- 6.13.9 Enable Receiver (0x17)
- 6.13.10 Test Internal RF (RSSI at RX Input With TX On) (0x18)
- 6.13.11 Test External RF (RSSI at RX Input With TX Off) (0x19)
- 6.13.12 Register Preset
- 6.14
Register Description
- 6.14.1
Register Overview
- 6.14.1.1 Main Configuration Registers
- 6.14.1.2
Protocol Subsetting Registers
- 6.14.1.2.1 ISO14443B TX Options Register (0x02)
- 6.14.1.2.2 ISO14443A High-Bit-Rate and Parity Options Register (0x03)
- 6.14.1.2.3 TX Timer High Byte Control Register (0x04)
- 6.14.1.2.4 TX Timer Low Byte Control Register (0x05)
- 6.14.1.2.5 TX Pulse Length Control Register (0x06)
- 6.14.1.2.6 RX No Response Wait Time Register (0x07)
- 6.14.1.2.7 RX Wait Time Register (0x08)
- 6.14.1.2.8 Modulator and SYS_CLK Control Register (0x09)
- 6.14.1.2.9 RX Special Setting Register (0x0A)
- 6.14.1.2.10 Regulator and I/O Control Register (0x0B)
- 6.14.1.3 Status Registers
- 6.14.1.4 Test Registers
- 6.14.1.5 FIFO Control Registers
- 6.14.1
Register Overview
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8器件和文档支持
- 9机械、封装和可订购信息
6.12.2 FIFO Operation
The FIFO is a 12-byte register at address 0x1F with byte storage locations 0 to 11. FIFO data is loaded in a cyclical manner and can be cleared by a reset command (0x0F, see Figure 6-9 showing this Direct Command).
Associated with the FIFO are two counters and three FIFO status flags. The first counter is a 4-bit FIFO byte counter (bits B0 to B3 in register 0x1C) that keeps track of the number of bytes loaded into the FIFO. If the number of bytes in the FIFO is n, the register value is n – 1 (number of bytes in FIFO register). If 8 bytes are in the FIFO, the FIFO counter (bits B0 to B3 in register 0x1C) has the value 7.
A second counter (12 bits wide) indicates the number of bytes being transmitted (registers 0x1D and 0x1E) in a data frame. An extension to the transmission-byte counter is a 4-bit broken-byte counter also provided in register 0x1E (bits B0 to B3). Together these counters make up the TX length value that determines when the reader generates the EOF byte.
FIFO status flags are as follows:
- FIFO overflow (bit B4 of register 0x1C): Indicates that the FIFO was loaded too soon
- FIFO level too low (bit B5 of register 0x1C): Indicates that only three bytes are left to be transmitted (Can be used during transmission.)
- FIFO level high (bit B6 of register 0x1C): Indicates that nine bytes are already loaded into the FIFO (Can be used during reception to generate a FIFO reception IRQ. This is to notify the MCU to service the reader in time to ensure a continuous data stream.)
During transmission, the FIFO is checked for an almost-empty condition, and during reception for an almost-full condition. The maximum number of bytes that can be loaded into the FIFO in a single sequence is 12 bytes.
NOTE
The number of bytes in a frame, transmitted or received, can be greater than 12 bytes.
During transmission, the MCU loads the TRF7960A FIFO (or, during reception, the MCU removes data from the FIFO), and the FIFO counter counts the number of bytes being loaded into the FIFO. Meanwhile, the byte counter keeps track of the number of bytes being transmitted. An interrupt request is generated if the number of bytes in the FIFO is less than 3 or greater than 9, so that MCU can send new data or remove the data as necessary. The MCU also checks the number of data bytes to be sent, so as to not surpass the value defined in TX length bytes. The MCU also signals the transmit logic when the last byte of data is sent or was removed from the FIFO during reception. Transmission starts automatically after the first byte is written into FIFO.
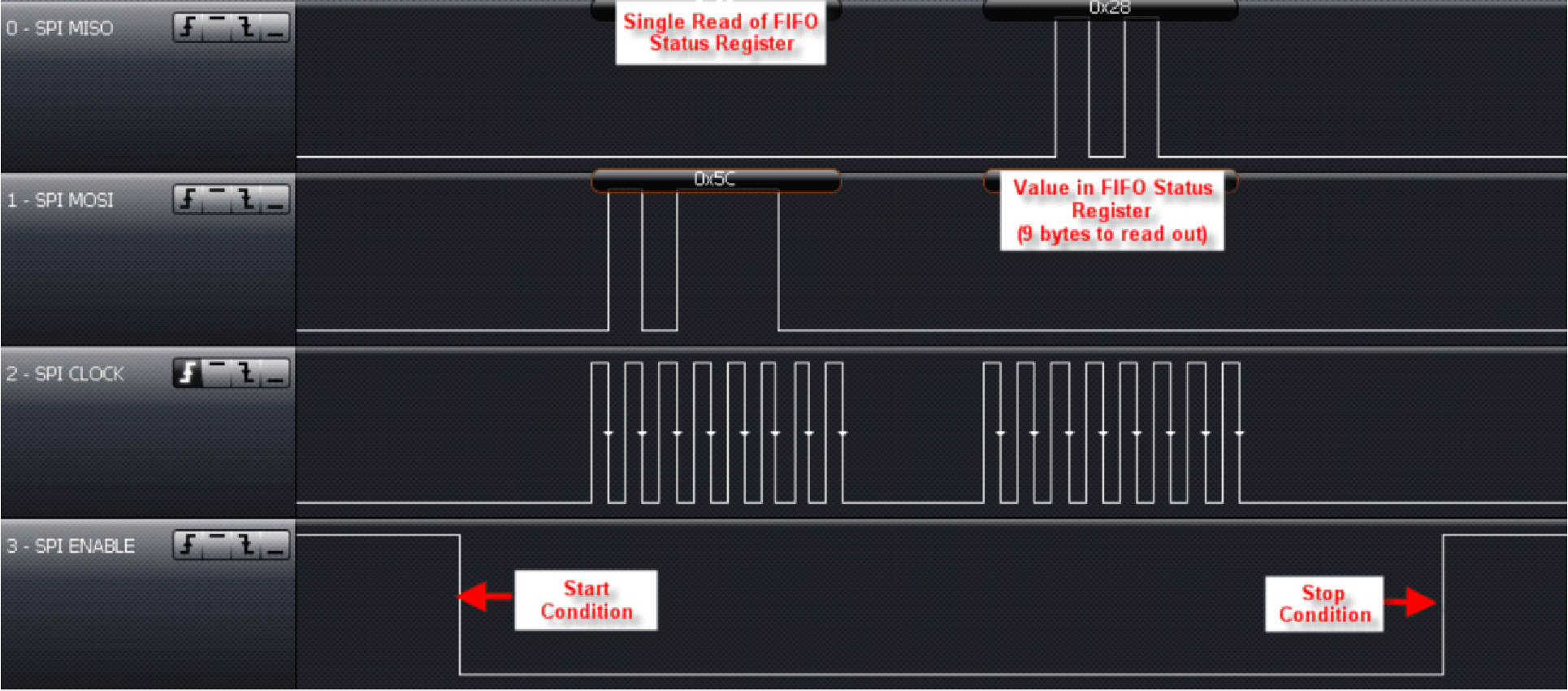 Figure 6-10 Checking the FIFO Status Register (Using SPI With SS Mode)
Figure 6-10 Checking the FIFO Status Register (Using SPI With SS Mode)