SLUSEM9A September 2022 – June 2024 UCC21755-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Power Ratings
- 5.6 Insulation Specifications
- 5.7 Safety Limiting Values
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.9 Switching Characteristics
- 5.10 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 5.11 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Power Supply
- 7.3.2 Driver Stage
- 7.3.3 VCC and VDD Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.4 Active Pulldown
- 7.3.5 Short Circuit Clamping
- 7.3.6 Internal Active Miller Clamp
- 7.3.7 Desaturation (DESAT) Protection
- 7.3.8 Soft Turn-Off
- 7.3.9 Fault (FLT), Reset and Enable (RST/EN)
- 7.3.10 Isolated Analog to PWM Signal Function
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Input Filters for IN+, IN-, and RST/EN
- 8.2.2.2 PWM Interlock of IN+ and IN-
- 8.2.2.3 FLT, RDY, and RST/EN Pin Circuitry
- 8.2.2.4 RST/EN Pin Control
- 8.2.2.5 Turn-On and Turn-Off Gate Resistors
- 8.2.2.6 Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection
- 8.2.2.7 Isolated Analog Signal Sensing
- 8.2.2.8 Higher Output Current Using an External Current Buffer
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 PWM Interlock of IN+ and IN-
The device features the PWM interlock for IN+ and IN- pins, which can be used to prevent the phase leg shoot through issue. As shown in Table 7-1, the output is logic low while both IN+ and IN- are logic high. When only IN+ is used, IN- can be tied to GND. To utilize the PWM interlock function, the PWM signal of the other switch in the phase leg can be sent to the IN- pin. As shown in Figure 8-2, the PWM_T is the PWM signal to top side switch, the PWM_B is the PWM signal to bottom side switch. For the top side gate driver, the PWM_T signal is given to the IN+ pin, while the PWM_B signal is given to the IN- pin; for the bottom side gate driver, the PWM_B signal is given to the IN+ pin, while PWM_T signal is given to the IN- pin. When both PWM_T and PWM_B signals are high, the outputs of both gate drivers are logic low to prevent the shoot through condition.
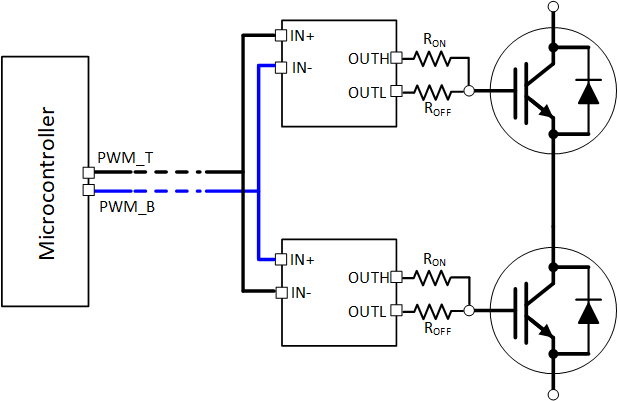 Figure 8-2 PWM Interlock for a Half Bridge
Figure 8-2 PWM Interlock for a Half Bridge