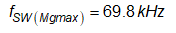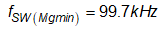ZHCSJY8E june 2019 – february 2021 UCC256402 , UCC256403 , UCC256404
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 High Voltage Start-Up
- 7.4.2 X-Capacitor Discharge
- 7.4.3 Burst Mode Control
- 7.4.4
System State Machine
-
Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 LLC Power Stage Requirements
- 8.2.2.2 LLC Gain Range
- 8.2.2.3 Select Ln and Qe
- 8.2.2.4 Determine Equivalent Load Resistance
- 8.2.2.5 Determine Component Parameters for LLC Resonant Circuit
- 8.2.2.6 LLC Primary-Side Currents
- 8.2.2.7 LLC Secondary-Side Currents
- 8.2.2.8 LLC Transformer
- 8.2.2.9 LLC Resonant Inductor
- 8.2.2.10 LLC Resonant Capacitor
- 8.2.2.11 LLC Primary-Side MOSFETs
- 8.2.2.12 LLC Rectifier Diodes
- 8.2.2.13 LLC Output Capacitors
- 8.2.2.14 HV Pin Series Resistors
- 8.2.2.15 BLK Pin Voltage Divider
- 8.2.2.16 ISNS Pin Differentiator
- 8.2.2.17 VCR Pin Capacitor Divider
- 8.2.2.18 BW Pin Voltage Divider
- 8.2.2.19 Soft Start and Burst Mode Programming
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
-
Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
8.2.2.5 Determine Component Parameters for LLC Resonant Circuit
Before determining the resonant tank component parameters, a nominal switching frequency (resonant frequency) should be selected. In this design, 100 kHz is selected as the resonant frequency.
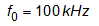
The resonant tank parameters can be calculated as the following:
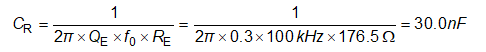
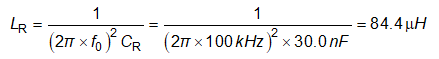
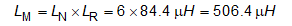
After the preliminary parameters are selected, find the closest actual component value that is available, re-check the gain curve with the selected parameters, and then run time domain simulation to verify the circuit operation.
The following resonant tank parameters are:
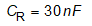
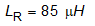
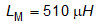
Based on the final resonant tank parameters, the resonant frequency can be calculated:
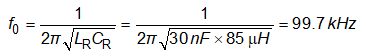
Based on the new LLC gain curve, the normalized switching frequency at maximum and minimum gain are given by:
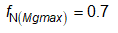
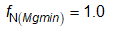
The maximum and minimum switching frequencies are: