ZHCSBE0C August 2013 – August 2015 UCC27517A
PRODUCTION DATA.
8 Specifications
8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)(3)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | VDD | –0.3 | 20 | V |
| OUT voltage | DC | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V |
| Repetitive pulse less than 200 ns(5) | –2 | VDD + 0.3 | ||
| Output continuous current | IOUT_DC (source/sink) | 0.3 | A | |
| Output pulsed current (0.5 µs) | IOUT_pulsed(source/sink) | 4 | ||
| Input voltage | IN+, IN-(4) | –6 | 20 | V |
| Operating virtual junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Lead temperature | Soldering, 10 sec. | 300 | °C | |
| Reflow | 260 | |||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages are with respect to GND unless otherwise noted. Currents are positive into, negative out of the specified terminal. See Packaging Section of the datasheet for thermal limitations and considerations of packages.
(3) These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper device-handling procedures.
(4) Maximum voltage on input pins is not restricted by the voltage on the VDD pin.
(5) Values are verified by characterization on bench.
8.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±4000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VDD | 4.5 | 12 | 18 | V |
| Operating junction temperature | –40 | 140 | °C | |
| Input voltage, IN+ and IN- | 0 | 18 | V |
8.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1)(2) | UCC27517A | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBV (SOT-23) | |||
| 5 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 217.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 85.8 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 44 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 4 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 43.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | n/a | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
(2) Under identical power dissipation conditions, the DRS package will allow to maintain a lower die temperature than the DBV. θJA metric should be used for comparison of power dissipation capability between different packages (Refer to the Application Information section).
8.5 Electrical Characteristics
VDD = 12 V, TA = TJ = –40°C to 140°C, 1-µF capacitor from VDD to GND. Currents are positive into, negative out of the specified terminal.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITION | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIAS CURRENTS | |||||||
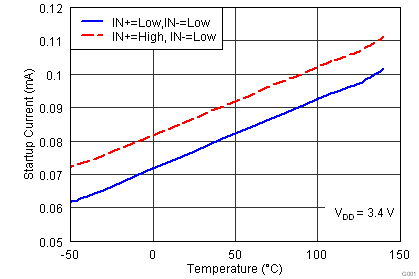
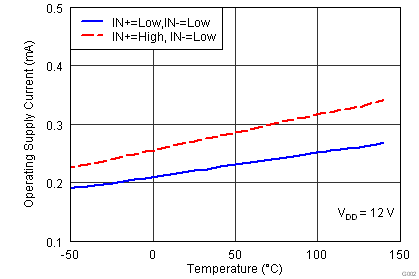
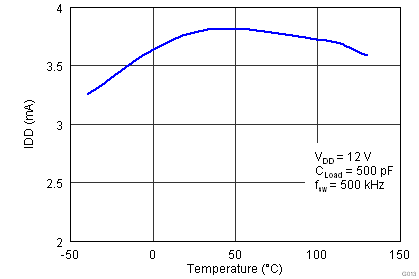
| IDD(off) | Startup current | VDD = 3.4 V | IN+ = VDD, IN- = GND | 40 | 100 | 160 | µA |
| IN+ = IN- = GND or IN+ = IN- = VDD | 25 | 75 | 145 | ||||
| IN+ = GND, IN- = VDD | 20 | 60 | 115 | ||||
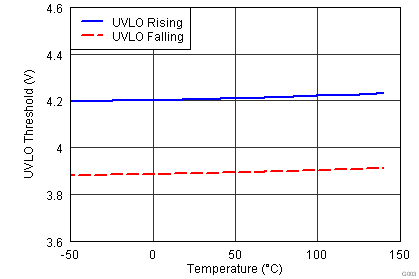
| UNDER VOLTAGE LOCKOUT (UVLO) | |||||||
| VON | Supply start threshold | TA = 25°C | 3.91 | 4.20 | 4.5 | V | |
| TA = -40°C to 140°C | 3.70 | 4.20 | 4.65 | ||||
| VOFF | Minimum operating voltage after supply start | 3.45 | 3.9 | 4.35 | V | ||
| VDD_H | Supply voltage hysteresis | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | V | ||
| INPUTS (IN+, IN-) | |||||||
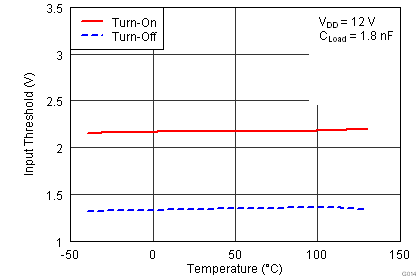
| VIN_H | Input signal high threshold | Output high for IN+ pin, Output low for IN- pin | 2.2 | 2.4 | V | ||
| VIN_L | Input signal low threshold | Output low for IN+ pin, Output high for IN- pin | 1.0 | 1.2 | V | ||
| VIN_HYS | Input signal hysteresis | 1.0 | V | ||||
| SOURCE/SINK CURRENT | |||||||
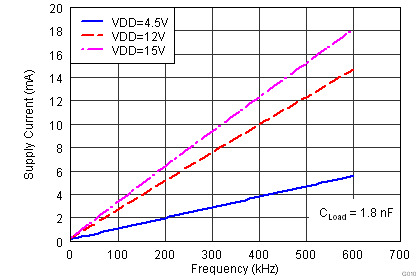
| ISRC/SNK | Source/sink peak current(1) | CLOAD = 0.22 µF, FSW = 1 kHz | ±4 | A | |||
| OUTPUTS (OUT) | |||||||
| VDD-VOH | High output voltage | VDD = 12 V IOUT = -10 mA |
50 | 90 | mV | ||
| VDD = 4.5 V IOUT = -10 mA |
60 | 130 | |||||
| VOL | Low output voltage | VDD = 12 IOUT = 10 mA |
5 | 10 | mV | ||
| VDD = 4.5 V IOUT = 10 mA |
6 | 12 | |||||
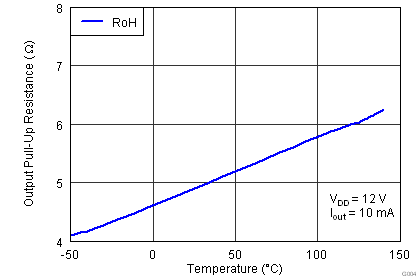
| ROH | Output pullup resistance(2) | VDD = 12 V IOUT = -10 mA |
5.0 | 7.5 | Ω | ||
| VDD = 4.5 V IOUT = -10 mA |
5.0 | 11.0 | |||||
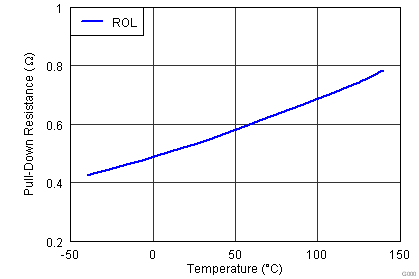
| ROL | Output pulldown resistance | VDD = 12 V IOUT = 10 mA |
0.5 | 1.0 | Ω | ||
| VDD = 4.5 V IOUT = 10 mA |
0.6 | 1.2 | |||||
(1) Ensured by Design.
(2) ROH represents on-resistance of P-Channel MOSFET in pull-up structure of the UCC27517A's output stage.
8.6 Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
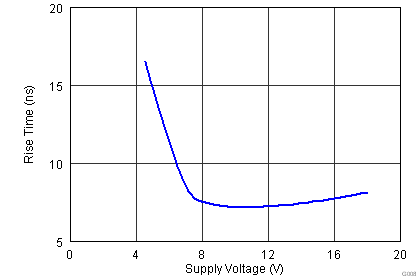
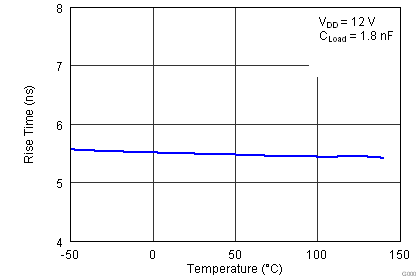
| tR | Rise time(1) | VDD = 12 V CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
8 | 12 | ns | |
| VDD = 4.5 V CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
16 | 22 | ||||
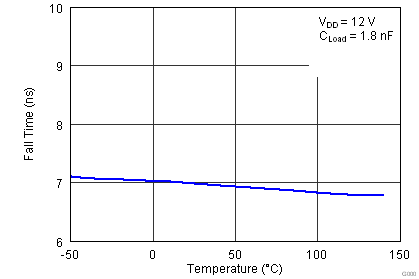
| tF | Fall time(1) | VDD = 12 V CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
7 | 11 | ns | |
| VDD=4.5V CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
7 | 11 | ||||
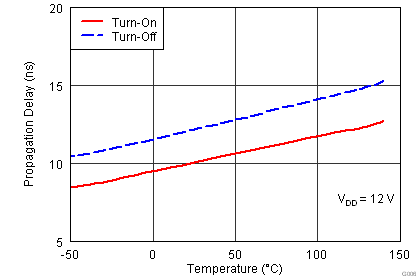
| tD1 | IN+ to output propagation delay(1) | VDD = 12 V 5-V input pulse CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
4 | 13 | 23 | ns |
| VDD = 4.5 V 5-V input pulse CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
4 | 13 | 26 | |||
| tD2 | IN- to output propagation delay(1) | VDD = 12 V CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
4 | 13 | 23 | ns |
| VDD = 4.5 V CLOAD = 1.8 nF |
4 | 19 | 30 | |||
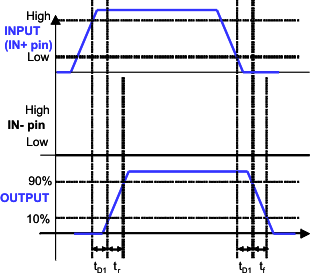 Figure 1. Non-Inverting Configuration
Figure 1. Non-Inverting Configuration(PWM Input to IN+ pin (IN- pin tied to GND))
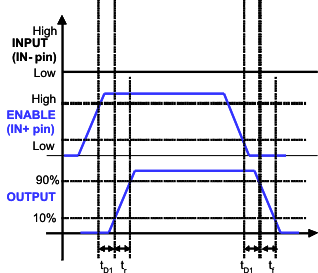 Figure 3. Enable and Disable Function Using IN+ Pin
Figure 3. Enable and Disable Function Using IN+ Pin (Enable and disable signal applied to IN+ pin, PWM input to IN- pin)
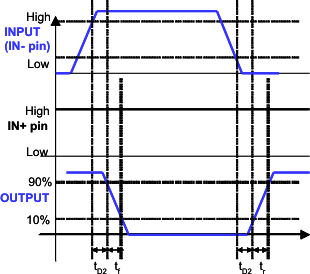 Figure 2. Inverting Configuration
Figure 2. Inverting Configuration(PWM input to IN- pin (IN+ pin tied to VDD))
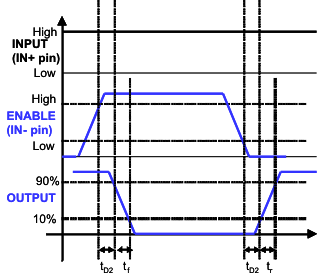 Figure 4. Enable and Disable Function Using IN- Pin
Figure 4. Enable and Disable Function Using IN- Pin(Enable and disable signal applied to IN- pin, PWM input to IN+ pin)
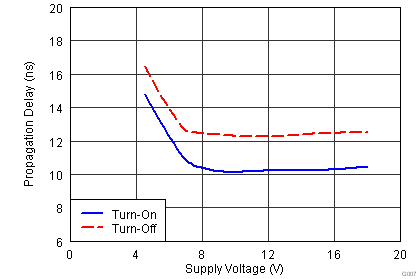
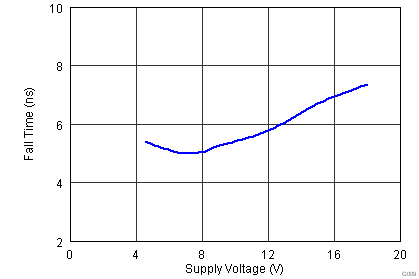
8.7 Typical Characteristics