ZHCSIB2B December 2017 – October 2019 UCC28064A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Principles of Operation
- 8.3.2 Natural Interleaving
- 8.3.3 On-Time Control, Maximum Frequency Limiting, Restart Timer and Input Voltage Feed-Forward compensation
- 8.3.4 Distortion Reduction
- 8.3.5 Zero-Current Detection and Valley Switching
- 8.3.6 Phase Management and Light-Load Operation
- 8.3.7 Burst Mode Operation
- 8.3.8 External Disable
- 8.3.9 Improved Error Amplifier
- 8.3.10 Soft Start
- 8.3.11 Brownout Protection
- 8.3.12 Line Dropout Detection
- 8.3.13 VREF
- 8.3.14 VCC
- 8.3.15
System Level Protections
- 8.3.15.1 Failsafe OVP - Output Over-voltage Protection
- 8.3.15.2 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.15.3 Open-Loop Protection
- 8.3.15.4 VCC Undervoltage Lock-Out (UVLO) Protection
- 8.3.15.5 Phase-Fail Protection
- 8.3.15.6 CS - Open, TSET - Open and Short Protection
- 8.3.15.7 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.15.8 Fault Logic Diagram
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.2.2 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.3 ZCD Resistor Selection RZA, RZB
- 9.2.2.4 HVSEN
- 9.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 Selecting RS For Peak Current Limiting
- 9.2.2.7 Power Semiconductor Selection (Q1, Q2, D1, D2)
- 9.2.2.8 Brownout Protection
- 9.2.2.9 Converter Timing
- 9.2.2.10 Programming VOUT
- 9.2.2.11 Voltage Loop Compensation
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Package Option Addendum
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.11 Brownout Protection
As the power line RMS voltage decreases, RMS input current must increase to maintain a constant output voltage for a specific load. Brownout protection helps prevent excess system thermal stress (due to the higher RMS input current) from exceeding a safe operating level. Power-line voltage is sensed at VINAC pin. When the VINAC fails to exceed the brownout threshold for the brownout filter time (tBODLY), a brownout condition is detected and both gate drive outputs are turned off. During brownout, COMP is actively pulled low and soft-start condition is initiated. When VINAC rises above the brownout threshold, the power stage soft-starts as COMP rises with controlled current.
The brownout threshold and its hysteresis are set by the voltage-divider ratio and resistor values. Brownout protection is based on VINAC peak voltage; the threshold and hysteresis are also based on the line peak voltage. Hysteresis is provided by a 2-μA current-sink (IBOHYS) enabled whenever Brownout protection is activated. As soon as the Brownout protection is activated an additional timer is started that counts the tBORST time. During this time the device is forced to stay in a Brownout condition. So, during tBORST time, the device is not allowed to switch, COMP is pulled low and the 2-uA current sink (IBOHYS) is active regardless of the voltage on VINAC pin. After tBORST is elapsed the device can exit from Brownout condition only if VINAC pin exceeds VBOTHR threshold. When the device operates in burst mode, several blocks inside the IC are turned off to reduce IC current consumption. The Brownout management block is also turned off. Each time the system stops switching, because of burst mode, the Brownout filter timer is reset. So if the system is operating in burst mode, the Brownout protection, generally is not triggered. The main purpose of Brownout is to avoid excess system thermal stress. When the system is operating in burst-mode the load is low enough to avoid thermal stress. The peak VINAC voltage can be easily translated into an RMS value. Example resistor values for the voltage divider are 8.61 MΩ ±1% from the rectified input voltage to VINAC and 133 kΩ ±1% from VINAC to ground. These resistors set the typical thresholds for RMS line voltages, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Brownout Thresholds (For Conditions Stated in the Text)
| THRESHOLD | AC-LINE VOLTAGE (RMS) |
|---|---|
| Falling | 67 V |
| Rising | 81 V |
Equation 13 and Equation 14 can be used to calculate the VINAC divider-resistors values based on desired brownout and brown-in voltage levels. VAC_OK is the desired RMS turnon voltage, VAC_BO is the desired RMS turnoff brownout voltage, and VLOSS is total series voltage drop due to wiring, EMI-filter, and bridge-rectifier impedances at VAC_BO. VBOTHR, and IBOHYS are found in the data-tables of this datasheet.

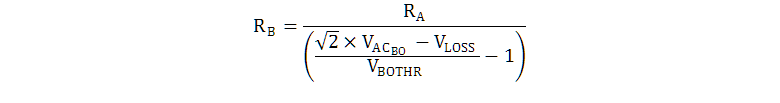
When standard values for the VINAC divider-resistors RA and RB are selected, the actual turn-on and brownout threshold RMS voltages for the ac-line can be back-calculated with Equation 15 and Equation 16:
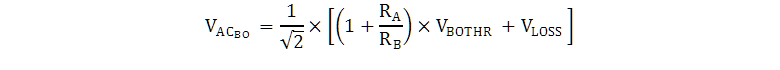
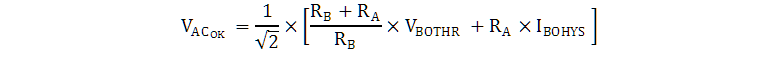
An example of the timing for the brownout function is illustrated in Figure 28.