ZHCSC62D March 2014 – December 2017 UCC28630 , UCC28631 , UCC28632 , UCC28633 , UCC28634
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 High-Voltage Current Source Start-Up Operation
- 8.3.2 AC Input UVLO / Brownout Protection
- 8.3.3 Active X-Capacitor Discharge (UCC28630 and UCC28633 only)
- 8.3.4 Magnetic Input and Output Voltage Sensing
- 8.3.5 Fixed-Point Magnetic Sense Sampling Error Sources
- 8.3.6 Magnetic Sense Resistor Network Calculations
- 8.3.7 Magnetic Sensing: Power Stage Design Constraints
- 8.3.8 Magnetic Sense Voltage Control Loop
- 8.3.9 Peak Current Mode Control
- 8.3.10 IPEAK Adjust vs. Line
- 8.3.11 Primary-Side Constant-Current Limit (CC Mode)
- 8.3.12 Primary-Side Overload Timer (UCC28630 only)
- 8.3.13 Overload Timer Adjustment (UCC28630 only)
- 8.3.14 CC-Mode IOUT(lim) Adjustment
- 8.3.15 Fault Protections
- 8.3.16 Pin-Fault Detection and Protection
- 8.3.17 Over-Temperature Protection
- 8.3.18 External Fault Input
- 8.3.19 External SD Pin Wake Input (except UCC28633)
- 8.3.20 External Wake Input at VSENSE Pin (UCC28633 Only)
- 8.3.21 Mode Control and Switching Frequency Modulation
- 8.3.22 Frequency Dither For EMI (except UCC28632)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Applications and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Notebook Adapter, 19.5 V, 65 W
- 9.2.2 UCC28630 Application Schematic
- 9.2.3 Design Requirements
- 9.2.4
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.4.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.4.2 Input Bulk Capacitance and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 9.2.4.3 Transformer Turn Ratio
- 9.2.4.4 Transformer Magnetizing Inductance
- 9.2.4.5 Current Sense Resistor RCS
- 9.2.4.6 Transformer Constraint Verification
- 9.2.4.7 Transformer Selection and Design
- 9.2.4.8 Slope Compensation Verification
- 9.2.4.9 Power MOSFET and Output Rectifier Selection
- 9.2.4.10 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.4.11 Calculation of CC Mode Limit Point
- 9.2.4.12 VDD Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.4.13 Magnetic Sense Resistor Network Selection
- 9.2.4.14 Output LED Pre-Load Resistor Calculation
- 9.2.5 External Wake Pulse Calculation at VSENSE Pin (UCC28633 Only)
- 9.2.6 Energy Star Average Efficiency and Standby Power
- 9.2.7 Application Performance Plots
- 9.3 Dos and Don'ts
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.18 External Fault Input
An external fault input signal may be applied to the controller SD (shutdown) pin. This signal forces the controller into fault mode. To trigger the fault, the voltage on this pin should be pulled below the fault trip threshold. A typical application is shown in Figure 37, where this pin is used to shut down the controller in the event of an over-temperature event as detected by a NTC (negative temperature coefficient) thermistor. The device pulls up the SD pin internally using a current source. As temperature rises, the external NTC resistance decreases, reducing the voltage on the pin. When the pin voltage drops to the fault trip threshold, the controller enters fault mode. The fault response (latching or recovery) depends on the device variant, per Table 4.
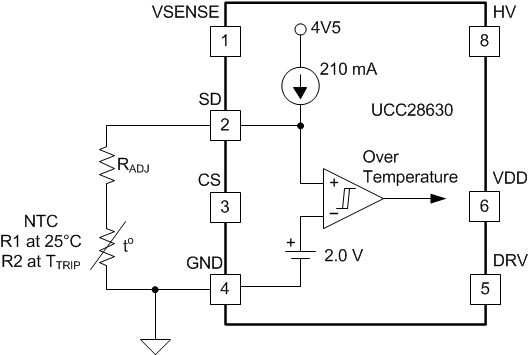 Figure 37. Fault Interface to SD Pin
Figure 37. Fault Interface to SD Pin The required trip resistance can be calculated from the internal trip voltage and pull-up current source. Nominally, this is 9.5 kΩ. Choose the NTC should so that it can achieve this value of resistance at the desired hot-spot trip temperature. If the NTC resistance is too low at the required trip temperature, connect a standard chip resistor in series to bring the total resistance up to 9.5 kΩ.
The device internally filters the SD pin with persistence delay as listed in Table 4. An external filter capacitor is not normally necessary. However, if an application uses an external filter capacitor, the value should be limited to 1 nF maximum. A larger value may impact the useful life of the controller.