ZHCSNG6 November 2021 UCC28781-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Detailed Pin Description
- 7.3.1 BUR Pin (Programmable Burst Mode)
- 7.3.2 FB Pin (Feedback Pin)
- 7.3.3 REF Pin (Internal 5-V Bias)
- 7.3.4 VDD Pin (Device Bias Supply)
- 7.3.5 P13 and SWS Pins
- 7.3.6 S13 Pin
- 7.3.7 IPC Pin (Intelligent Power Control Pin)
- 7.3.8 RUN Pin (Driver and Bias Source for Isolator)
- 7.3.9 PWMH and AGND Pins
- 7.3.10 PWML and PGND Pins
- 7.3.11 SET Pin
- 7.3.12 RTZ Pin (Sets Delay for Transition Time to Zero)
- 7.3.13 RDM Pin (Sets Synthesized Demagnetization Time for ZVS Tuning)
- 7.3.14 XCD Pin
- 7.3.15 CS, VS, and FLT Pins
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Adaptive ZVS Control with Auto-Tuning
- 7.4.2 Dead-Time Optimization
- 7.4.3 EMI Dither and Dither Fading Function
- 7.4.4 Control Law Across Entire Load Range
- 7.4.5 Adaptive Amplitude Modulation (AAM)
- 7.4.6 Adaptive Burst Mode (ABM)
- 7.4.7 Low Power Mode (LPM)
- 7.4.8 First Standby Power Mode (SBP1)
- 7.4.9 Second Standby Power Mode (SBP2)
- 7.4.10 Startup Sequence
- 7.4.11 Survival Mode of VDD (INT_STOP)
- 7.4.12
System Fault Protections
- 7.4.12.1 Brown-In and Brown-Out
- 7.4.12.2 Output Over-Voltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.4.12.3 Input Over Voltage Protection (IOVP)
- 7.4.12.4 Over-Temperature Protection (OTP) on FLT Pin
- 7.4.12.5 Over-Temperature Protection (OTP) on CS Pin
- 7.4.12.6 Programmable Over-Power Protection (OPP)
- 7.4.12.7 Peak Power Limit (PPL)
- 7.4.12.8 Output Short-Circuit Protection (SCP)
- 7.4.12.9 Over-Current Protection (OCP)
- 7.4.12.10 External Shutdown
- 7.4.12.11 Internal Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4.13 Pin Open/Short Protections
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application Circuit
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements for a 60-W, 15-V ZVSF Bias Supply Application with a DC Input
- 8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.7 Low Power Mode (LPM)
As NSW drops to two in ABM and the condition of fBUR less than fBUR(LR) is qualified under two consecutive burst periods, the controller enters into LPM mode and disables PWMH. The purpose of LPM is to provide a soft peak current transition between VCST(BUR) and VCST(MIN). LPM fixes NSW at two and sets fBUR equal to fLPM of 25 kHz. In LPM mode, VCST is controlled to regulate the output voltage. At the start of each burst packet, after RUN pulls high, tD(RUN-PWML) is used to wake up both the isolated gate driver and the controller. With PWMH disabled, the two PWML pulses turn on QL close to valley-switching by sensing ZCD. When ZCD is detected again at the end of the second pulse, the RUN pin goes low and the controller enters its low-power wait state. For LPM mode with the SET pin connected to REF, the minimum on-time of PWML can be further reduced to tON(MIN), to allow the peak magnetizing current to be reduced below the level limited by tCSLEB of the peak current loop. In this condition, operation of the LPM control loop is changed from a current-mode control to a voltage-mode control, so the on-time adjustment of PWML is not limited to tCSLEB. With this feature, before fBUR starts to fall below fLPM and enters the audible frequency range of SBP mode, the peak current is low enough to limit the magnitude of audible excitation.
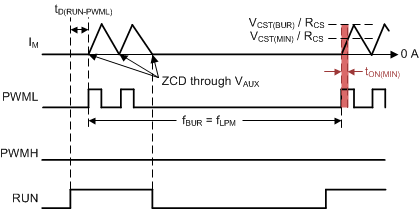 Figure 7-32 PWM Pattern in LPM
Figure 7-32 PWM Pattern in LPM