ZHCSKB9Q December 1999 – October 2019 UCC1895 , UCC2895 , UCC3895
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 ADS (Adaptive Delay Set)
- 7.3.2 CS (Current Sense)
- 7.3.3 CT (Oscillator Timing Capacitor)
- 7.3.4 DELAB and DELCD (Delay Programming Between Complementary Outputs)
- 7.3.5 EAOUT, EAP, and EAN (Error Amplifier)
- 7.3.6 OUTA, OUTB, OUTC, and OUTD (Output MOSFET Drivers)
- 7.3.7 PGND (Power Ground)
- 7.3.8 RAMP (Inverting Input of the PWM Comparator)
- 7.3.9 REF (Voltage Reference)
- 7.3.10 RT (Oscillator Timing Resistor)
- 7.3.11 GND (Analog Ground)
- 7.3.12 SS/DISB (Soft Start/Disable)
- 7.3.13 SYNC (Oscillator Synchronization)
- 7.3.14 VDD (Chip Supply)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Power Loss Budget
- 8.2.2.2 Preliminary Transformer Calculations (T1)
- 8.2.2.3 QA, QB, QC, QD FET Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Selecting LS
- 8.2.2.5 Selecting Diodes DB and DC
- 8.2.2.6 Output Inductor Selection (LOUT)
- 8.2.2.7 Output Capacitance (COUT)
- 8.2.2.8 Select Rectifier Diodes
- 8.2.2.9 Input Capacitance (CIN)
- 8.2.2.10 Current Sense Network (CT, RCS, RR, DA)
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
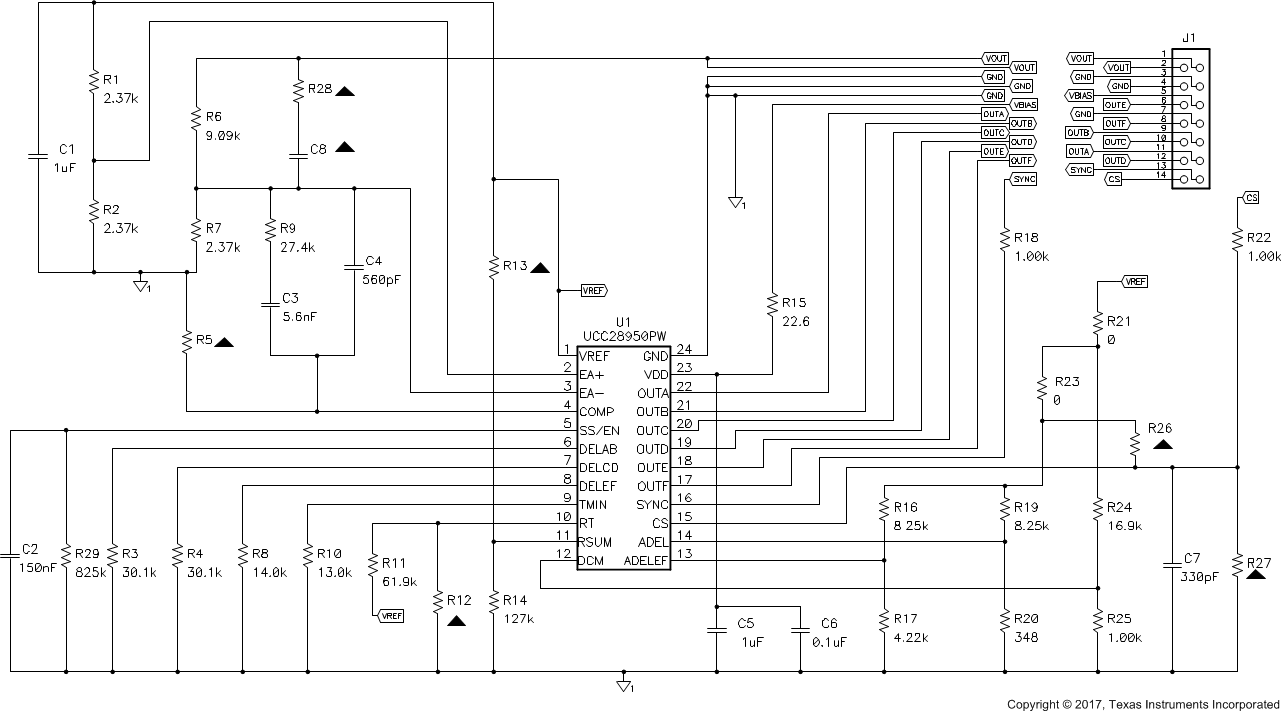
8.2.2.10.6 Setting the Slope Compensation
Slope compensation is necessary to stabilise a converter operating in peak current mode at duty cycles greater than 50%. The optimum slope compensation ramp should be half the inductor current ramp downslope during the off time. This slope is calculated as follows:
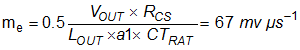
The magnetizing current of the power transformer provides part of the compensating ramp and is calculated as follows. The VIN x DTYP factor takes account of the fact that the slope of the magnetizing current is less at lower input voltages.
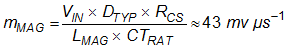
The added slope compensation ramp is then:
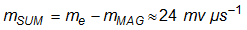
The resistor RSC sets the added slope compensation ramp, mSUM and is chosen as follows:
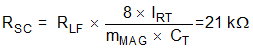
A small AC coupling capacitor is used in the emitter of Q1 to eliminate the need for offset biasing circuitry. CC = 1 nF.
The resistor REL is a DC load resistor for the emitter of Q1. It should have the same value as RSC.
A small capacitor at the RAMP pin input helps suppress high frequency noise, we set CRAMP = 56 pF. Transistor Q1 is a small signal NPN type.
In peak current mode control the RAMP pin receives the current sense signal, plus the slope compensation ramp, through the 510-Ω resistor RRCS. The 10-kΩ resistor RRB provides approximately 250-mV offset bias. The value of this resistor may be adjusted up or down to alter the point at which the internal no load comparator trips.
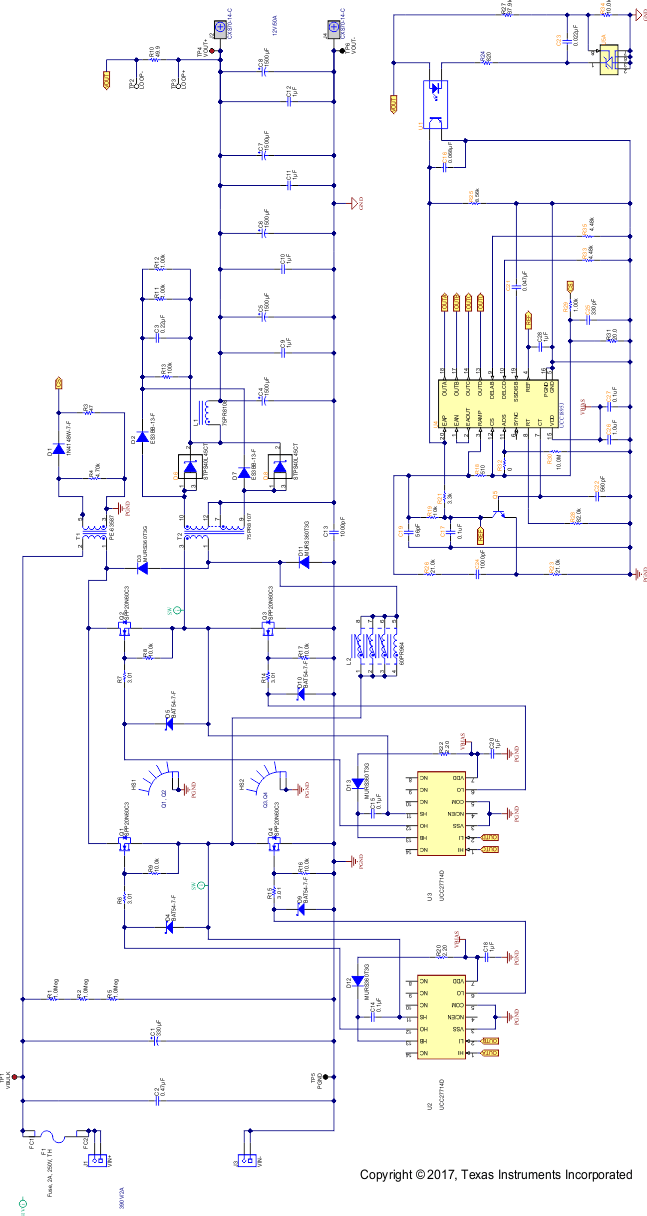 Figure 24. Power Stage Schematic
Figure 24. Power Stage Schematic