ZHCSAY5D march 2013 – april 2021 UCD3138064
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Functional Block Diagram
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Options
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings #GUID-DB56AA00-A5E9-4426-9853-ACC9CCD10656/SLUSB727999
- 8.2 Handling Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 8.6 Timing Characteristics
- 8.7 PMBus/SMBus/I2C Timing
- 8.8 Power On Reset (POR) / Brown Out Reset (BOR)
- 8.9 Typical Clock Gating Power Savings
- 8.10 Typical Characteristics
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 System Module
- 9.3.2 Peripherals
- 9.3.3 Automatic Mode Switching
- 9.3.4 DPWMC, Edge Generation, Intramux
- 9.3.5 Filter
- 9.3.6 Communication Ports
- 9.3.7 Real Time Clock
- 9.3.8 Timers
- 9.3.9 General Purpose ADC12
- 9.3.10 Miscellaneous Analog
- 9.3.11 Brownout
- 9.3.12 Global I/O
- 9.3.13 Temperature Sensor Control
- 9.3.14 I/O Mux Control
- 9.3.15 Current Sharing Control
- 9.3.16 Temperature Reference
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Memory
-
10Applications and
Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
9.3.2.1.3 DPWM Events
Each DPWM can control the following timing events:
- Sample Trigger Count–This register defines where the error voltage is sampled by the EADC in relationship to the DPWM period. The programmed value set in the register should be one fourth of the value calculated based on the DPWM clock. As the DCLK (DCLK = 62.5 MHz max) controlling the circuitry runs at one fourth of the DPWM clock (PCLK = 250MHz max). When this sample trigger count is equal to the DPWM Counter, it initiates a front end calculation by triggering the EADC, resulting in a CLA calculation, and a DPWM update. Over-sampling can be set for 2, 4 or 8 times the sampling rate.
- Phase Trigger Count–count offset for slaving another DPWM (Multi-Phase/Interleaved operation).
- Period–low resolution switching period count. (count of PCLK cycles)
- Event 1–count offset for rising DPWM A event. (PCLK cycles)
- Event 2–DPWM count for falling DPWM A event that sets the duty ratio. Last 4 bits of the register are for high resolution control. Upper 14 bits are the number of PCLK cycle counts.
- Event 3–DPWM count for rising DPWM B event. Last 4 bits of the register are for high resolution control. Upper 14 bits are the number of PCLK cycle counts.
- Event 4–DPWM count for falling DPWM B event. Last 4 bits of the register are for high resolution control. Upper 14 bits are the number of PCLK cycle counts.
- Cycle Adjust–Constant offset for Event 2 and Event 4 adjustments.
Basic comparisons between the programmed registers and the DPWM counter can create the desired edge placements in the DPWM. High resolution edge capability is available on Events 2, 3 and 4.
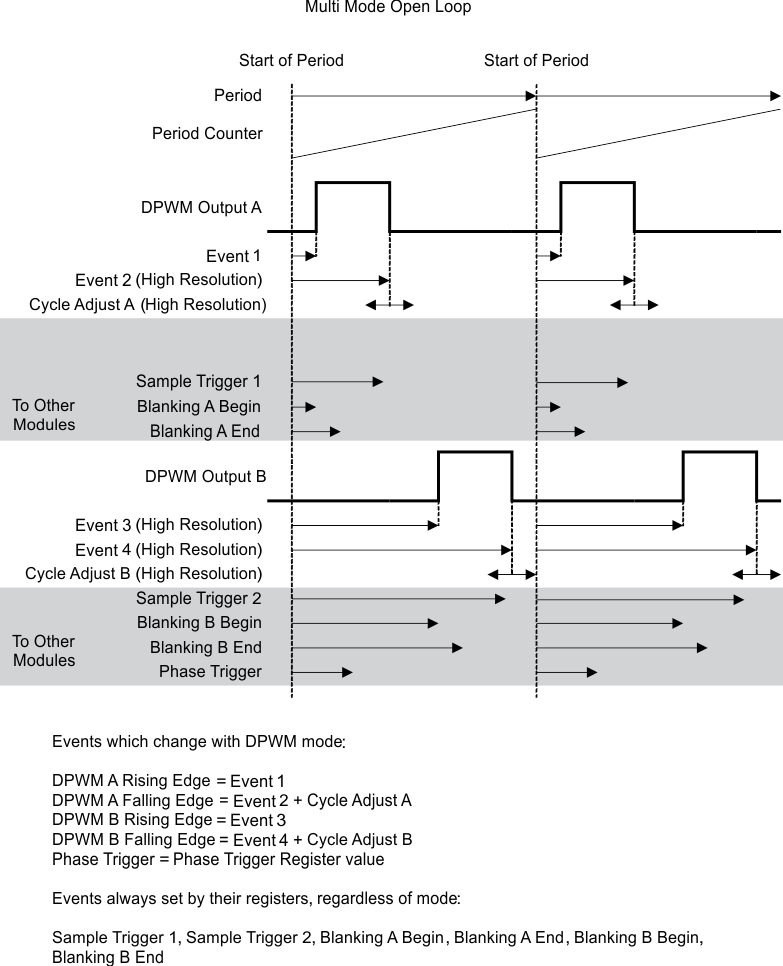 Figure 9-3 Multi Mode Open Loop
Figure 9-3 Multi Mode Open LoopFigure 9-3 is for multi-mode, open loop. Open loop means that the DPWM is controlled entirely by its own registers, not by the filter output. In other words, the power supply control loop is not closed.
The Sample Trigger signals are used to trigger the Front End to sample input signals. The Blanking signals are used to blank fault measurements during noisy events, such as FET turn on and turn off. Additional DPWM modes are described below.