ZHCSJE0 September 2018 UCD90320U
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Rail Monitoring Configuration
- 8.4.2 GPI Configuration
- 8.4.3 Rail Sequence Configuration
- 8.4.4 Fault Responses Configuration
- 8.4.5 GPO Configuration
- 8.4.6 Margining Configuration
- 8.4.7 Pin Selected Rail States Configuration
- 8.4.8 Watchdog Timer
- 8.4.9 System Reset Function
- 8.4.10 Cascading Multiple Devices
- 8.4.11 Rail Monitoring
- 8.4.12 Status Monitoring
- 8.4.13 Data and Error Logging to EEPROM Memory
- 8.4.14 Black Box First Fault Logging
- 8.4.15 PMBus Address Selection
- 8.4.16 ADC Reference
- 8.4.17 Device Reset
- 8.4.18 Brownout
- 8.4.19 Internal Fault Management
- 8.4.20 Single Event Upset
- 8.5 Device Configuration and Programming
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.4.9 System Reset Function
The system reset function can generate a programmable system reset signal through a GPIO pin. The system reset signal is de-asserted when the selected rail voltages reach their respective Power Good On thresholds and the selected GPIs are asserted, plus a programmable delay time. These are the available options for the system-reset delay times.
- 0 ms
- 1 ms
- 2 ms
- 4 ms
- 8 ms
- 16 ms
- 32 ms
- 64 ms
- 128 ms
- 256 ms
- 512 ms
- 1.02 s
- 2.05 s
- 4.10s
- 8.19 s
- 16.38 s
- 32.8 s
The System Reset signal can be asserted immediately when any of the selected rail voltage falls below Power Good Off threshold, or any selected GPI is de-asserted. Alternatively, the System Reset signal can be configured as a pulse once Power Good On is achieved. An example in Figure 26 illustrates the difference of the two configurations. The pulse width can be configured between 0.001 s to 32.256 s. See the UCD90320U Sequencer and System Health Controller PMBus Command Reference for pulse width configuration details.
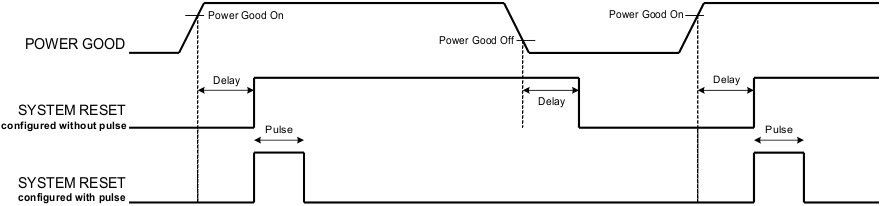 Figure 26. System Reset With and Without Pulse Setting (Active Low)
Figure 26. System Reset With and Without Pulse Setting (Active Low) The System Reset signal can also integrate watchdog timer. An example is shown in Figure 27. In Figure 27, the first delay on System Reset is for the initial reset release that would enable the CPU once all necessary voltage rails are Power Good. The watchdog is configured with a Start Time and a Reset Time. If these times expire and timeout occurs, it means that the CPU providing the WDI signal is not operating. The System Reset signal is then toggled either using a Delay or GPI Tracking Release Delay to determine if the CPU recovers.
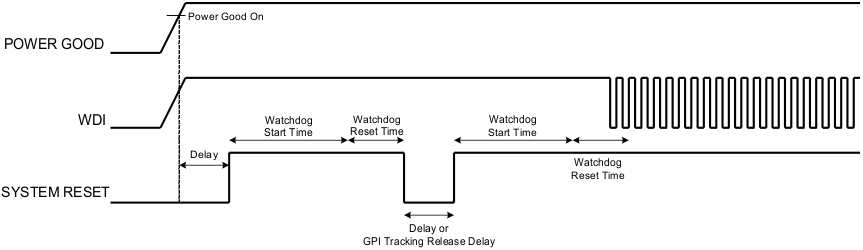 Figure 27. System Reset With Watchdog
Figure 27. System Reset With Watchdog The default state of the system reset pin (RESET) is assert. When the system reset function is configured in-circuit through PMBus commands during normal operation, the (RESET) pin is briefly asserted by default, even if conditions for de-assert are present. This is because the firmware requires a finite time to examine the de-assert conditions.