ZHCSV99C February 1997 – October 2024 XTR105
PRODUCTION DATA
7.1.3 2-Wire and 3-Wire RTD Connections
In Figure 7-1, the RTD can be located remotely simply by extending the two connections to the RTD. With this remote 2-wire connection to the RTD, line resistance introduces error. This error can be partially corrected by adjusting the values of RZ, RG, and RLIN1.
A better method for remotely located RTDs is the 3-wire RTD connection (see Figure 6-3). This circuit offers improved accuracy. RZ’s current is routed through a third wire to the RTD. Assuming line resistance is equal in RTD lines 1 and 2, this produces a small common-mode voltage that is rejected by the XTR105. A second resistor, RLIN2, is required for linearization.
Note that although the 2-wire and 3-wire RTD connection circuits are very similar, the gain-setting resistor, RG, has slightly different equations:
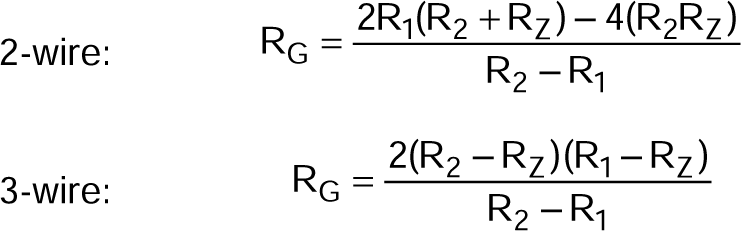
where
- RZ = RTD resistance at TMIN
- R1 = RTD resistance at (TMIN + TMAX) / 2
- R2 = RTD resistance at TMAX
To maintain good accuracy, use at least 1% (or better) resistors for RG. Table 7-1 provides standard 1% RG resistor values for a 3-wire Pt100 RTD connection with linearization.