ZHCSSK2D October 2006 – October 2024 XTR111
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
6.3.3 External Current Limit
The XTR111 does not provide an internal current limit in case the external FET is forced to a low-impedance state. The internal current source controls the current, but a high current from IS to GND forces an internal voltage clamp between VSP and IS to turn on. This clamp results in a low-resistance path, and the current is only limited by the load impedance and the current capability of the external FET.
Figure 6-5a shows an example of a current-limit circuit. Limit the current to 50mA. The 15Ω resistor (R6) limits the current to approximately 37mA (33mA when hot). Select a PNP transistor that allows a peak current of several hundred milliamperes. Power dissipation is not usually critical because the peak current duration is only a few microseconds. However, observe the leakage current through the transistor from IS to VG. The addition of this current limiting transistor and R6 still require time to discharge the gate of the external MOSFET. R7 and C3 are added for this reason, as well as to limit the steepness of external distortion pulses. Additional EMI and overvoltage protection can be required depending on the application.
Figure 6-5b is a universal and basic current-limiter circuit, using PNP or NPN transistors that can be connected in the source (IS to S) or in the drain output (in series with the current path). This circuit does not contribute to leakage currents. Consider adding an output filter like R7 and C3 in this limiter circuit.
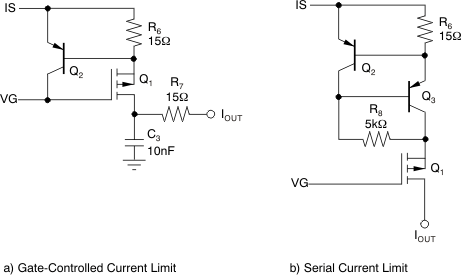 Figure 6-5 External
Current Limit Circuits
Figure 6-5 External
Current Limit Circuits