SBAS453G July 2009 – August 2016 ADS1146 , ADS1147 , ADS1148
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 ADC Input and Multiplexer
- 9.3.2 Low-Noise PGA
- 9.3.3 Clock Source
- 9.3.4 Modulator
- 9.3.5 Digital Filter
- 9.3.6 Voltage Reference Input
- 9.3.7 Internal Voltage Reference
- 9.3.8 Excitation Current Sources
- 9.3.9 Sensor Detection
- 9.3.10 Bias Voltage Generation
- 9.3.11 General-Purpose Digital I/O
- 9.3.12 System Monitor
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 Digital Interface
- 9.5.2 Data Format
- 9.5.3
Commands
- 9.5.3.1 WAKEUP (0000 000x)
- 9.5.3.2 SLEEP (0000 001x)
- 9.5.3.3 SYNC (0000 010x)
- 9.5.3.4 RESET (0000 011x)
- 9.5.3.5 RDATA (0001 001x)
- 9.5.3.6 RDATAC (0001 010x)
- 9.5.3.7 SDATAC (0001 011x)
- 9.5.3.8 RREG (0010 rrrr, 0000 nnnn)
- 9.5.3.9 WREG (0100 rrrr, 0000 nnnn)
- 9.5.3.10 SYSOCAL (0110 0000)
- 9.5.3.11 SYSGCAL (0110 0001)
- 9.5.3.12 SELFOCAL (0110 0010)
- 9.5.3.13 NOP (1111 1111)
- 9.5.3.14 Restricted Command (1111 0001)
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 ADS1146 Register Map
- 9.6.2
ADS1146 Detailed Register Definitions
- 9.6.2.1 BCS—Burn-out Current Source Register (offset = 00h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.2.2 VBIAS—Bias Voltage Register (offset = 01h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.2.3 MUX—Multiplexer Control Register (offset = 02h) [reset = x0h]
- 9.6.2.4 SYS0—System Control Register 0 (offset = 03h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.2.5 OFC—Offset Calibration Coefficient Registers (offset = 04h, 05h, 06h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.2.6 FSC—Full-Scale Calibration Coefficient Registers (offset = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 9.6.2.7 ID—ID Register (offset = 0Ah) [reset = x0h]
- 9.6.3 ADS1147 and ADS1148 Register Map
- 9.6.4
ADS1147 and ADS1148 Detailed Register Definitions
- 9.6.4.1 MUX0—Multiplexer Control Register 0 (offset = 00h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.4.2 VBIAS—Bias Voltage Register (offset = 01h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.4.3 MUX1—Multiplexer Control Register 1 (offset = 02h) [reset = x0h]
- 9.6.4.4 SYS0—System Control Register 0 (offset = 03h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.4.5 OFC—Offset Calibration Coefficient Register (offset = 04h, 05h, 06h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.4.6 FSC—Full-Scale Calibration Coefficient Register (offset = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 9.6.4.7 IDAC0—IDAC Control Register 0 (offset = 0Ah) [reset = x0h]
- 9.6.4.8 IDAC1—IDAC Control Register 1 (offset = 0Bh) [reset = FFh]
- 9.6.4.9 GPIOCFG—GPIO Configuration Register (offset = 0Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.4.10 GPIODIR—GPIO Direction Register (offset = 0Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.4.11 GPIODAT—GPIO Data Register (offset = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1
Application Information
- 10.1.1 Serial Interface Connections
- 10.1.2 Analog Input Filtering
- 10.1.3 External Reference and Ratiometric Measurements
- 10.1.4 Establishing a Proper Common-Mode Input Voltage
- 10.1.5 Isolated (or Floating) Sensor Inputs
- 10.1.6 Unused Inputs and Outputs
- 10.1.7 Pseudo Code Example
- 10.1.8 Channel Multiplexing Example
- 10.1.9 Power-Down Mode Example
- 10.2 Typical Applications
- 10.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 10.1
Application Information
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
See(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power-supply voltage | AVDD to AVSS | –0.3 | 5.5 | V |
| AVSS to DGND | –2.8 | 0.3 | ||
| DVDD to DGND | –0.3 | 5.5 | ||
| Analog input voltage | AINx, REFPx, REFNx, VREFOUT, VREFCOM, IEXC1, IEXC2 | AVSS – 0.3 | AVDD + 0.3 | V |
| Digital input voltage | SCLK, DIN, DOUT/DRDY, DRDY, CS, START, RESET, CLK | DGND – 0.3 | DVDD + 0.3 | V |
| Input current | Continuous, any pin except power supply pins | –10 | 10 | mA |
| Momentary, any pin except power supply pins | –100 | 100 | ||
| Temperature | Junction, TJ | 150 | °C | |
| Storage, Tstg | –60 | 150 | ||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±750 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
Over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| Analog power supply | AVDD to AVSS | 2.7 | 5.25 | V | ||
| AVSS to DGND | –2.65 | 0.1 | ||||
| AVDD to DGND | 2.25 | 5.25 | ||||
| Digital power supply | DVDD to DGND | 2.7 | 5.25 | V | ||
| ANALOG INPUTS(2) | ||||||
| VIN | Differential input voltage | V(AINP) – V(AINN)(1) | –VREF / Gain | VREF / Gain | V | |
| VCM | Common-mode input voltage | (V(AINP) + V(AINN)) / 2 | See Equation 3 | |||
| VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUTS(3) | ||||||
| VREF | Differential reference input voltage | V(REFPx) – V(REFNx) | 0.5 | (AVDD – AVSS) – 1 | V | |
| V(REFNx) | Absolute negative reference voltage | AVSS – 0.1 | V(REFPx) – 0.5 | V | ||
| V(REFPx) | Absolute positive reference voltage | V(REFNx) + 0.5 | AVDD + 0.1 | V | ||
| EXTERNAL CLOCK INPUT(4) | ||||||
| fCLK | External clock frequency | 1 | 4.5 | MHz | ||
| External clock duty cycle | 25% | 75% | ||||
| GENERAL-PURPOSE INPUTS AND OUTPUTS (GPIO) | ||||||
| GPIO input voltage | AVSS | AVDD | V | |||
| DIGITAL INPUTS | ||||||
| Digital input voltage | DGND | DVDD | V | |||
| TEMPERATURE RANGE | ||||||
| TA | Operating ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | ||
| Specified ambient temperature | –40 | 105 | °C | |||
(1) For VREF > 2.7 V, the differential input voltage must not exceed 2.7 V / Gain.
(2) AINP and AINN denote the positive and negative inputs of the PGA.
(3) REFPx and REFNx denote the differential reference input pair (ADS1146, ADS1147), or one of the two available differential reference input pairs (ADS1148).
(4) External clock only required if the internal oscillator is not used.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | ADS1146 | ADS1147 | ADS1148 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW (TSSOP) | PW (TSSOP) | PW (TSSOP) | RHB (VQFN) | |||
| 16 PINS | 20 PINS | 28 PINS | 32 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 95.2 | 87.4 | 74.2 | 32.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 28.9 | 21.7 | 20.2 | 23.9 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 41 | 39.6 | 31.8 | 6.6 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 40.4 | 38.9 | 31.3 | 6.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | — | — | 1.6 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
Minimum and maximum specifications apply from TA = –40°C to +105°C. Typical specifications are at TA = 25°C.All specifications are at AVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3.3 V, AVSS = 0 V, VREF = 2.048 V, and fCLK = 4.096 MHz (unless otherwise noted).
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANALOG INPUTS | ||||||
| Differential input current | 100 | pA | ||||
| Absolute input current | See Table 4 | |||||
| PGA | ||||||
| PGA gain settings | 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 | V/V | ||||
| SYSTEM PERFORMANCE | ||||||
| Resolution | No missing codes | 16 | Bits | |||
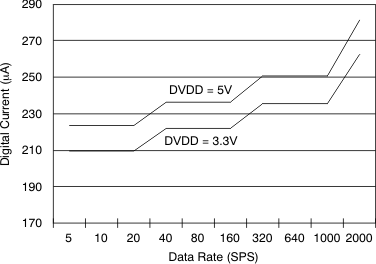
| DR | Data rate | 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 320, 640, 1000, 2000 | SPS | |||
| ADC conversion time | Single-cycle settling | See Table 10 | ||||
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | Differential input, end point fit, Gain = 1, VCM = 2.5 V |
–1 | 0.5 | 1 | LSB |
| Offset error | After calibration | –1 | 1 | LSB | ||
| Offset drift | Gain = 1 | 100 | nV/°C | |||
| Gain = 128 | 15 | nV/°C | ||||
| Gain error | Excluding VREF errors | –0.5% | 0.5% | |||
| Gain drift | Gain = 1, excludes VREF drift | 1 | ppm°C | |||
| Gain = 128, excludes VREF drift | –3.5 | ppm/°C | ||||
| Noise | See Table 1 and Table 2 | |||||
| NMRR | Normal mode rejection | See Table 6 | ||||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection | At DC, Gain = 1 | 90 | dB | ||
| At DC, Gain = 32 | 100 | |||||
| PSRR | Power supply rejection | AVDD, DVDD at DC | 100 | dB | ||
| VOLTAGE REFERENCE INPUTS | ||||||
| Reference input current | 30 | nA | ||||
| INTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE | ||||||
| VREF | Internal reference voltage | 2.038 | 2.048 | 2.058 | V | |
| Reference drift(1) | TA = –40°C to +105°C | 20 | 50 | ppm/°C | ||
| Output current(2) | –10 | 10 | mA | |||
| Load regulation | 50 | µV/mA | ||||
| Start-up time | See Table 7 | |||||
| INTERNAL OSCILLATOR | ||||||
| Internal oscillator frequency | 3.89 | 4.096 | 4.3 | MHz | ||
| EXCITATION CURRENT SOURCES (IDACs) | ||||||
| Output current settings | 50, 100, 250, 500, 750, 1000, 1500 | µA | ||||
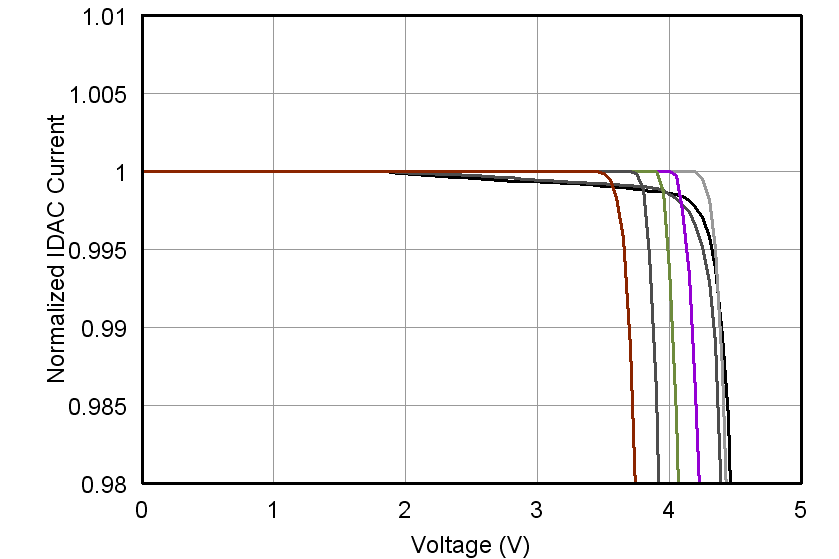
| Compliance voltage | All currents | See Figure 9 and Figure 10 | ||||
| Absolute error | All currents, each IDAC | –6% | ±1% | 6% | ||
| Absolute mismatch | All currents, between IDACs | ±0.2% | ||||
| Temperature drift | Each IDAC | 200 | ppm/°C | |||
| Temperature drift matching | Between IDACs | 10 | ppm/°C | |||
| BURN-OUT CURRENT SOURCES | ||||||
| Burn-out current source settings | 0.5, 2, 10 | µA | ||||
| BIAS VOLTAGE | ||||||
| Bias voltage | (AVDD + AVSS) / 2 | V | ||||
| Bias voltage output impedance | 400 | Ω | ||||
| TEMPERATURE SENSOR | ||||||
| Output voltage | TA = 25°C | 118 | mV | |||
| Temperature coefficient | 405 | µV/°C | ||||
| GENERAL-PURPOSE INPUTS AND OUTPUTS (GPIO) | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | AVSS | 0.3 × AVDD | V | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × AVDD | AVDD | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 1 mA | AVSS | 0.2 × AVDD | V | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = 1 mA | 0.8 × AVDD | V | ||
| DIGITAL INPUTS AND OUTPUTS (OTHER THAN GPIO) | ||||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | DGND | 0.3 × DVDD | V | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.7 × DVDD | DVDD | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 1 mA | DGND | 0.2 × DVDD | V | |
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = 1 mA | 0.8 × DVDD | V | ||
| Input leakage | DGND < VIN < DVDD | –10 | 10 | µA | ||
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| IAVDD | Analog supply current | Power-down mode | 0.1 | µA | ||
| Converting, AVDD = 3.3 V, DR = 20 SPS, external reference |
212 | |||||
| Converting, AVDD = 5 V, DR = 20 SPS, external reference |
225 | |||||
| Additional current with internal reference enabled | 180 | |||||
| IDVDD | Digital supply current | Power-down mode | 0.2 | µA | ||
| Normal operation, DVDD = 3.3 V, DR = 20 SPS, internal oscillator |
210 | |||||
| Normal operation, DVDD = 5 V, DR = 20 SPS, internal oscillator |
230 | |||||
| PD | Power dissipation | AVDD = DVDD = 3.3 V, DR = 20 SPS, internal oscillator, external reference |
1.4 | mW | ||
| AVDD = DVDD = 5 V, DR = 20 SPS, internal oscillator, external reference |
2.3 | |||||
(1) Specified by the combination of design and final production test.
(2) Do not exceed this loading on the internal voltage reference.
7.6 Timing Requirements
At TA = –40°C to +105°C and DVDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
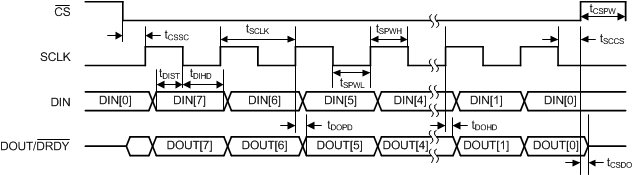
| SERIAL INTERFACE (SEE Figure 1 AND Figure 2) | |||||
| tCSSC | Delay time, first SCLK rising edge after CS falling edge | 10 | ns | ||
| tSCCS | Delay time, CS rising edge after final SCLK falling edge | 7 | tCLK(1) | ||
| tCSPW | Pulse duration, CS high | 5 | tCLK | ||
| tSCLK | SCLK period | 488 | ns | ||
| 64 | Conversions | ||||
| tSPWH | Pulse duration, SCLK high | 0.25 | 0.75 | tSCLK | |
| tSPWL | Pulse duration, SCLK low | 0.25 | 0.75 | tSCLK | |
| tDIST | Setup time, DIN valid before SCLK falling edge | 5 | ns | ||
| tDIHD | Hold time, DIN valid after SCLK falling edge | 5 | ns | ||
| tSTD | Setup time, SCLK low before DRDY rising edge | 5 | tCLK | ||
| tDTS | Delay time, SCLK rising edge after DRDY falling edge | 1 | tCLK | ||
| MINIMUM START TIME PULSE DURATION (SEE Figure 3) | |||||
| tSTART | Pulse duration, START high | 3 | tCLK | ||
| RESET PULSE DURATION, SERIAL INTERFACE COMMUNICATION AFTER RESET (SEE Figure 4) | |||||
| tRESET | Pulse duration, RESET low | 4 | tCLK | ||
| tRHSC | Delay time, SCLK rising edge (start of serial interface communication) after RESET rising edge | 0.6(2) | ms | ||
(1) tCLK = 1 / fCLK. The default clock frequency fCLK = 4.096 MHz.
(2) Applicable only when fCLK = 4.096 MHz, scales proportionally with fCLK frequency.
7.7 Switching Characteristics
At TA = –40°C to +105°C and DVDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V (unless otherwise noted; see Figure 1 and Figure 2)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tDOPD | Propagation delay time, SCLK rising edge to valid new DOUT |
DVDD ≤ 3.6 V | 50 | ns | ||
| DVDD > 3.6 V | 180 | |||||
| tDOHD | DOUT hold time | 0 | ns | |||
| tCSDO | Propagation delay time, CS rising edge to DOUT high impedance |
10 | ns | |||
| tPWH | Pulse duration, DRDY high | 3 | tCLK | |||
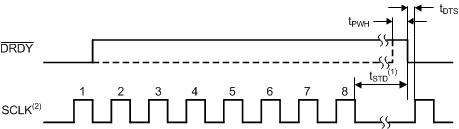
1. This timing diagram is applicable only when the CS pin is low. SCLK does not need to be low during tSTD when CS is high.
2. SCLK must only be sent in multiples of eight during partial retrieval of output data.
Figure 2. Serial Interface Timing to Allow Conversion Result Loading
 Figure 3. Minimum Start Pulse Duration
Figure 3. Minimum Start Pulse Duration
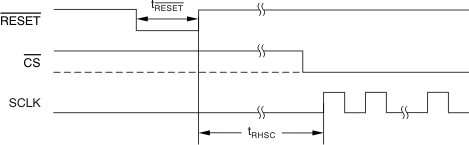 Figure 4. Reset Pulse Duration and Serial Interface Communication After Reset
Figure 4. Reset Pulse Duration and Serial Interface Communication After Reset
7.8 Typical Characteristics
TA = 25°C, AVDD = 5 V, AVSS = 0 V, and VREF = 2.5 V (unless otherwise noted)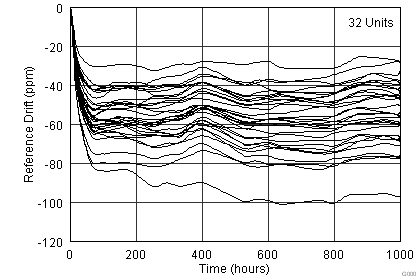 Figure 5. Internal Reference Long-Term Drift
Figure 5. Internal Reference Long-Term Drift
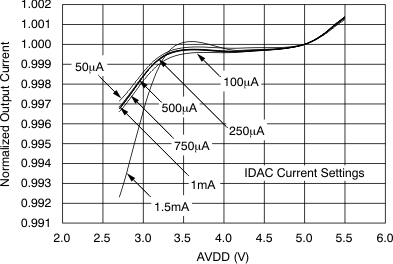 Figure 7. IDAC Line Regulation
Figure 7. IDAC Line Regulation
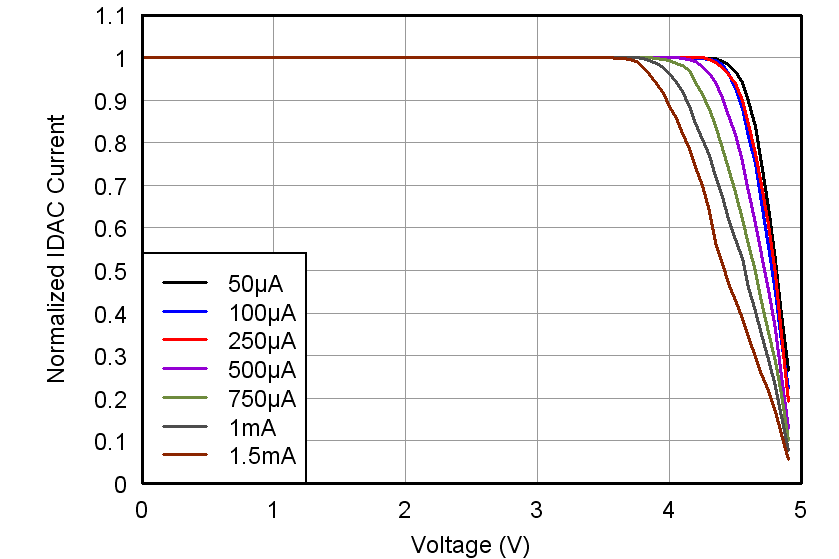 Figure 9. IDAC Voltage Compliance
Figure 9. IDAC Voltage Compliance
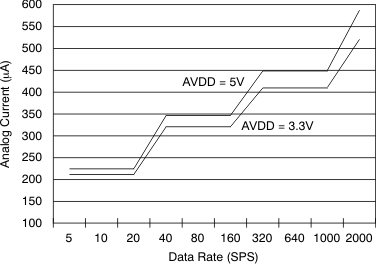 Figure 11. Analog Supply Current vs Data Rate
Figure 11. Analog Supply Current vs Data Rate
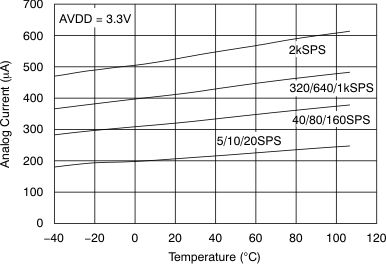
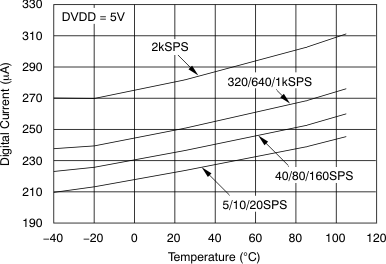
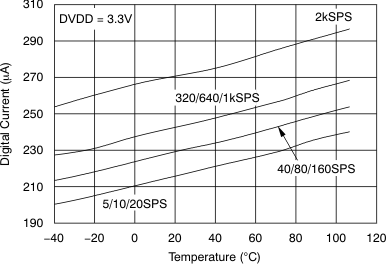
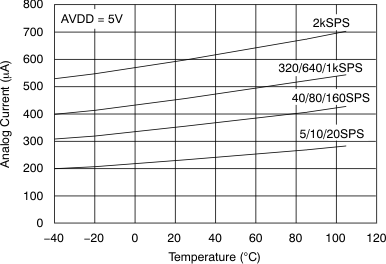 Figure 13. Analog Supply Current vs Temperature
Figure 13. Analog Supply Current vs Temperature