SBOA523 July 2021 TMP390 , TMP392
1 Temperature Switch Introduction
The ability to detect and react to thermal events within a system is not only a paramount aspect of safety, but also a strong factor in being able to optimize system performance. There are many applications in which thermal management is important, including DC/AC inverters, DC/DC converters, temperature transmitters, environmental control systems (ECS), power tools, power banks, and wireless infrastructure. The simplest solution is to create a temperature switch that toggles based on certain thresholds that the user sets, and will alert the user should the temperature exceed the set thresholds. Figure 1-1 shows an example of the desired operation of a temperature switch.
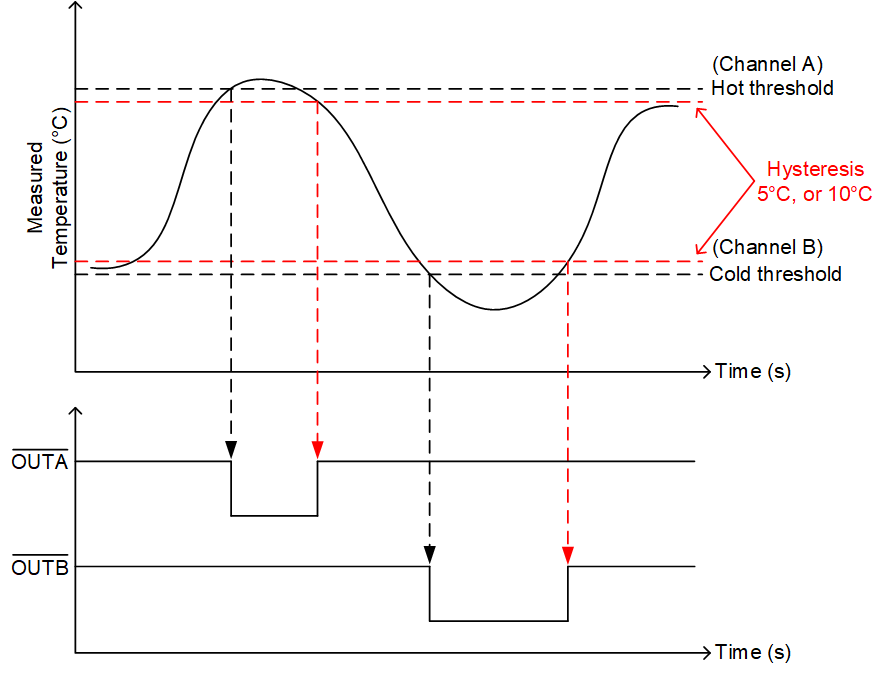 Figure 1-1 Temperature Switch Output With Hot or Cold Thresholds and Hysteresis
Figure 1-1 Temperature Switch Output With Hot or Cold Thresholds and HysteresisThere are two outputs that both have active low logic. Each output corresponds to a channel and each channel corresponds to a threshold. In this example, Channel A corresponds to the hot threshold while channel B corresponds to the cold threshold, both of which can be specified by the user. In addition, there is an option of hysteresis of either 5°C or 10°C. This behavior is recreated with the three subsequent designs presented in this report.