SBOA564A December 2022 – August 2024 TRF0206-SP
- 1
- Single-Event Effects Test Report of the TRF0206-SP 6.5-GHz Differential Amplifier
- Trademarks
- 1 Overview
- 2 Single-Event Effects
- 3 Test Device and Evaluation Board Information
- 4 Irradiation Facility and Setup
- 5 Depth, Range, and LETEFF Calculation
- 6 Test Set-Up and Procedures
- 7 Single-Event Latch-up (SEL) Results
- 8 Single-Event Transients (SET) Results
- 9 Event Rate Calculations
- 10Summary
- A Total Ionizing Dose from SEE Experiments
- B Confidence Interval Calculations
- C Orbital Environment Estimations
- D References
- E Revision History
4 Irradiation Facility and Setup
The heavy-ion species used for the SEE studies on this product were provided and delivered by the TAMU Cyclotron Radiation Effects Facility [3], using a superconducting cyclotron and advanced electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) ion source. At the fluxes used, ion beams had good flux stability and high-irradiation uniformity over a 1-in diameter circular cross-sectional area for the in-air station. Uniformity is achieved by means of magnetic defocusing. The flux of the beam is regulated over a broad range spanning several orders of magnitude. For the bulk of these studies ion fluxes between 104 and 105 ions/s-cm2 were used to provide a heavy-ion fluences between 106 and 107 ions/cm2.
For these experiments Holmium (165Ho), Praseodymium (141Pr), Silver (108Ag), Krypton (84Kr), Copper (63Cu) and Argon (40Ar) were used. Angles were used to increment the LETEFF, details are provided in Section 5. The 141Pr, 84Kr and 63Cu ions used had a total kinetic energy of 2114, 1259, and 944 MeV in the vacuum, (15-MeV/amu line) respectively. Ion beam uniformity for all tests was in the range of 88 to 97%.
Figure 4-1 shows the TRF0206-SP mounted on the EVM board in front of the beam exit port, as in the heavy-ion characterization. The beam port has a 1-mil Aramica (Kevlar®), 1-in diameter to allow in-air testing while maintaining the vacuum in the accelerator with only minor ion energy losses. The air space between the DUT and beam exit port the was set to 40 mm.
The data recorded in this report was based on finalized EVM boards with optimized component values that follow data sheet recommendations.
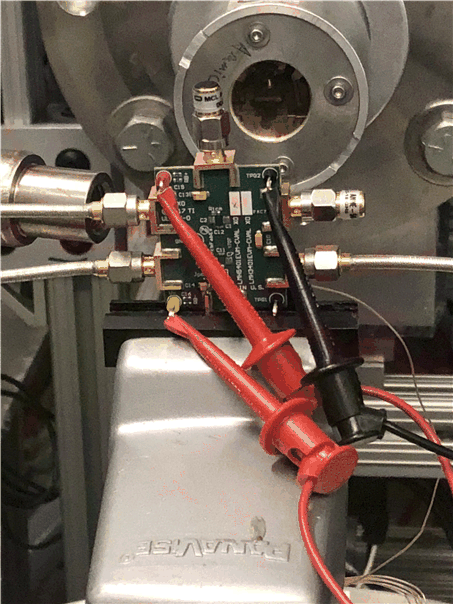 Figure 4-1 TRF0206-SP Evaluation Board Mounted in Front of the Heavy-Ion Beam Exit Port
Figure 4-1 TRF0206-SP Evaluation Board Mounted in Front of the Heavy-Ion Beam Exit Port