SFFS015 April 2021 TPS62816-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) for the pins of the TPS62816-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to Ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to VIN (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the TPS62816-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the TPS62816-Q1datasheet.
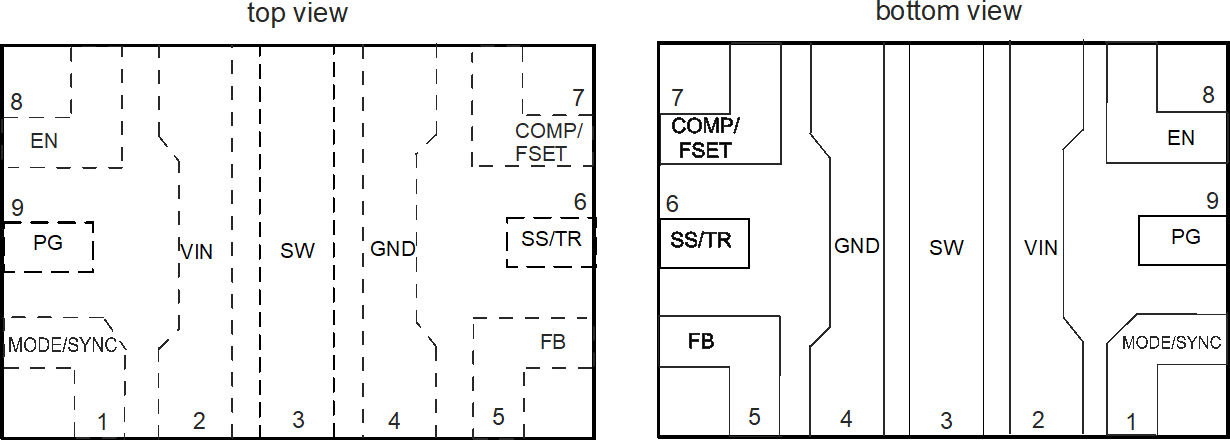 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
Assumption the device is running in the typical application, please refer to the 'Simplified Schematics' on the
1st page in the TPS62816-Q1datasheet.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| MODE/SYNC | 1 | Normal operation | D |
| VIN | 2 | Device does not power up, no output voltage | B |
| SW | 3 | Potential device damage | A |
| GND | 4 | Normal operation | D |
| FB | 5 | 100% duty cycle mode, output voltage follows the input voltage | B |
| SS/TR | 6 | Device does not start properly, no output voltage | B |
| COMP/FSET | 7 | Normal operation | D |
| EN | 8 | Device is disabled, no output voltage | B |
| PG | 9 | Normal operation, no power good indication | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| MODE/SYNC | 1 | Device either operates in forced PWM or power save mode enabled. Output voltage is regulated to its nominal value. | B |
| VIN | 2 | Device does not power up, no output voltage | B |
| SW | 3 | No output voltage | B |
| GND | 4 | Device does not power up, no output voltage | B |
| FB | 5 | 100% or 0% duty cycle operation, no regulated output voltage. Output voltage either follows the input voltage or no output voltage | B |
| SS/TR | 6 | Normal operation | D |
| COMP/FSET | 7 | Normal operation | D |
| EN | 8 | Device is either enabled or disabled. If enabled, output voltage is regulated to its nominal value. If disabled no output voltage | B |
| PG | 9 | Normal operation | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODE/SYNC | 1 | 2 | Normal operation | D |
| VIN | 2 | 3 | Potential device damage | A |
| SW | 3 | 4 | Potential device damage | A |
| GND | 4 | 5 | 100% duty cycle mode, output voltage follows the input voltage | B |
| FB | 5 | 6 | 0% duty cycle mode, no output voltage | B |
| SS/TR | 6 | 7 | Normal operation | D |
| COMP/FSET | 7 | 4 | Normal operation | D |
| EN | 8 | 2 | Normal operation | D |
| EN | 8 | 9 | Device does not power up, no output voltage | B |
| PG | 9 | 1 | Device operates in forced PWM once PG is high impedance. Output voltage is regulated to its nominal value. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| MODE/SYNC | 1 | Normal operation | D |
| VIN | 2 | Normal operation | D |
| SW | 3 | Potential device damage | A |
| GND | 4 | Device does not power up, no output voltage | B |
| FB | 5 | Potential device damage | A |
| SS/TR | 6 | Normal operation | D |
| COMP/FSET | 7 | Normal operation | D |
| EN | 8 | Normal operation | D |
| PG | 9 | Potential device damage |
A |