SFFS398 September 2024 TPS723-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the TPS723-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality. |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality. |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation. |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance. |
Figure 4-1 shows the TPS723-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the TPS723-Q1 data sheet.
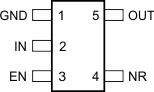 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
• Device contains DBV pin configuration. Device operates at free-air temperatures between -40°C and 125°C.
• Device operates at an input voltage less than -2.7V and more than -10V.
• Device operates according to all recommended operating conditions and does not exceed the absolute maximum ratings.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| IN | 2 | Output voltage is at or near ground. | B |
| EN | 3 | LDO is always off due to EN being grounded. | B |
| NR | 4 | Output voltage is at or near ground. | B |
| OUT | 5 | Output voltage is at or near ground. Device is in current limit. The device can cycle in and out of thermal shutdown depending on power dissipation. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | There is no current loop for internal biasing; device cannot operate. | B |
| IN | 2 | No input to LDO. Output is at or near ground. | B |
| EN | 3 | EN pin voltage floats as the LDO contains no internal pullup or pulldown. LDO is in unknown state. | B |
| NR | 4 | Normal operation. Reference voltage does not have reduced noise. | C |
| OUT | 5 | Device output is unregulated and the load is not powered. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | IN | Output voltage is near or at ground. | B |
| IN | 2 | EN | If EN is positive voltage above the IN absolute maximum rating, IN can be damaged. | A |
| If EN is negative voltage within recommended operating conditions there is no damage to the LDO, but device is always on when IN is powered. | B | |||
| NR | 4 | OUT | Output voltage is at or near ground. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | Output voltage is at or near ground. | B |
| IN | 2 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| EN | 3 | If EN is positive voltage above the IN absolute maximum rating, IN can be damaged. | A |
| If EN is negative voltage within recommended operating conditions there is no damage to the LDO, but device is always on when IN is powered. | B | ||
| NR | 4 | Output voltage follows input voltage (overrides the voltage reference). | B |
| OUT | 5 | Regulation is not possible. The output voltage equals input voltage. | B |