SFFS476 June 2022 ADS131M02-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the ADS131M02-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality. |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality. |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation. |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance. |
Figure 4-1 shows the ADS131M02-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the ADS131M02-Q1 data sheet.
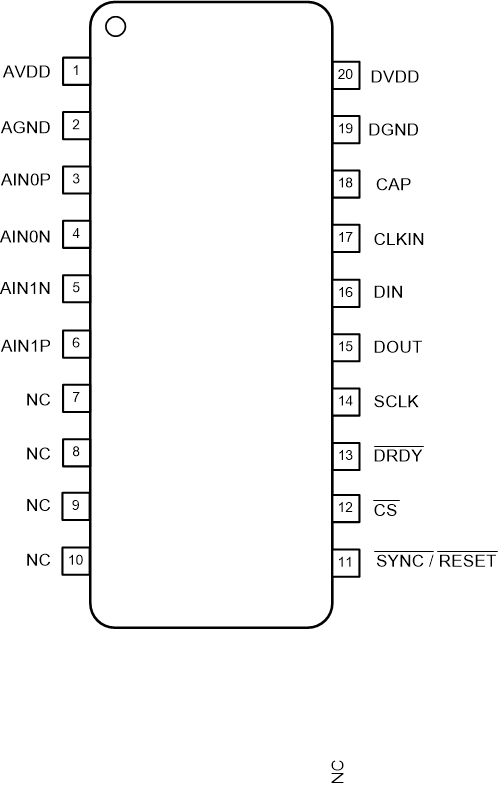 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- AVDD and DVDD use the same 3.3-V supply voltage.
- Short-circuit to supply means short AVDD to DVDD.
- Short-circuit to ground means short AGND to DGND.
- Differential RC filters on every
ADC channel.
Series resistors are sized to limit the input currents into the analog inputs to <10 mA in all circumstances (for example, if the device is unpowered and an input signal is applied). - The device is the only peripheral on the SPI bus.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD | 1 | The device is unpowered and not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| AGND | 2 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| AIN0P | 3 | AIN0P is stuck low. VIN0 = VAIN0P – VAIN0N = AGND – VAIN0N. The conversion results of ADC0 are incorrect. | B |
| AIN0N | 4 | AIN0N is stuck low. VIN0 = VAIN0P – VAIN0N = VAIN0P – AGND. The conversion results of ADC0 are incorrect. | B |
| AIN1N | 5 | AIN1N is stuck low. VIN1 = VAIN1P – VAIN1N = VAIN1P – AGND. The conversion results of ADC1 are incorrect. | B |
| AIN1P | 6 | AIN1P is stuck low. VIN1 = VAIN1P – VAIN1N = AGND – VAIN1N. The conversion results of ADC1 are incorrect. | B |
| NC | 7 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 8 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 9 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 10 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| SYNC/RESET | 11 | SYNC/RESET is stuck low. The device is held in reset. | B |
| CS | 12 | CS is stuck low. Normal operation when trying to communicate with the ADS131M02-Q1. | B |
| DRDY | 13 | DRDY is stuck low. No data-ready indication through the DRDY pin to the host is possible. An increase in supply current occurs when DRDY tries to drive high if the DRDY_HiZ bit = 0b. Device damage is plausible if DRDY drives high for an extended period of time. | A |
| SCLK | 14 | SCLK is stuck low. No SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| DOUT | 15 | DOUT is stuck low. No SPI communication back to the host is possible. An increase in supply current occurs when DOUT tries to drive high. Device damage plausible if DOUT drives high for an extended period of time. | A |
| DIN | 16 | DIN is stuck low. No SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| CLKIN | 17 | CLKIN is stuck low. No clock is provided to the device. The device is not functional, but SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| CAP | 18 | The device is unpowered and not functional. | B |
| DGND | 19 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| DVDD | 20 | The device is unpowered and not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD | 1 | Device functionality is undetermined. The device is unpowered and not functional if all external analog pins are held low. The device can power up through the internal ESD diodes to AVDD if voltages above the device power-on reset threshold are present on any of the analog pins. | B |
| AGND | 2 | Device functionality is undetermined. The device can be unpowered or connected to ground internally through an alternate pin ESD diode and power up. | B |
| AIN0P | 3 | The state of the AIN0P input is undetermined. The conversion results of ADC0 are undetermined. | B |
| AIN0N | 4 | The state of the AIN0N input is undetermined. The conversion results of ADC0 are undetermined. | B |
| AIN1N | 5 | The state of the AIN1N input is undetermined. The conversion results of ADC1 are undetermined. | B |
| AIN1P | 6 | The state of the AIN1P input is undetermined. The conversion results of ADC1 are undetermined. | B |
| NC | 7 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 8 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 9 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 10 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| SYNC/RESET | 11 | The state of the SYNC/RESET input is undetermined. Device functionality is undetermined. The device can operate normally or be held in reset. | B |
| CS | 12 | The state of the CS input is undetermined. SPI communication is corrupted. | B |
| DRDY | 13 | The state of the DRDY output is undetermined. No data-ready indication through the DRDY pin to the host is possible. | B |
| SCLK | 14 | The state of the SCLK input is undetermined. No SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| DOUT | 15 | The state of the DOUT output is undetermined. No SPI communication back to the host is possible. | B |
| DIN | 16 | The state of the DIN input is undetermined. No SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| CLKIN | 17 | The state of the CLKIN input is undetermined. No clock is provided to the device. The device is not functional, but SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| CAP | 18 | The internal digital LDO is unstable. Device functionality is undetermined. | B |
| DGND | 19 | Device functionality is undetermined. The device can be unpowered or connected to ground internally through an alternate pin ESD diode and power up. | B |
| DVDD | 20 | Device functionality is undetermined. The device is unpowered and not functional if all external digital pins are held low. The device can power up through the internal ESD diodes to DVDD if voltages above the device power-on reset threshold are present on any of the digital pins. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD | 1 | AGND | The device is unpowered and not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| AGND | 2 | AIN0P | AIN0P is stuck low. VIN0 = VAIN0P – VAIN0N = AGND – VAIN0N. The conversion results of ADC0 are incorrect. | B |
| AIN0P | 3 | AIN0N | VIN0 = VAIN0P – VAIN0N = 0 V. The conversion results of ADC0 are approximately 0 V. | B |
| AIN0N | 4 | AIN1N | The conversion results of ADC0 and ADC1 are undetermined. | B |
| AIN1N | 5 | AIN1P | VIN1 = VAIN1P – VAIN1N = 0 V. The conversion results of ADC1 are approximately 0 V. | B |
| AIN1P | 6 | NC | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 7 | NC | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 8 | NC | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 9 | NC | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 10 | SYNC/RESET | Not considered. Corner pin. | D |
| SYNC/RESET | 11 | CS | The device behavior is dependent on the drive strength of the control signals driving the CS and SYNC/RESET pins. If the SYNC/RESET control signal can overdrive the CS control signal, then CS is stuck high or SPI communication is corrupted. No SPI communication with the device is possible. If the CS control signal can overdrive the SYNC/RESET control signal, then the device synchronizes conversions every time CS transitions high. Conversion results are valid, but data ready is indicated outside the expected time window. If the SYNC/RESET pin is held low for longer than the reset time period, a device reset occurs. | B |
| CS | 12 | DRDY | SPI communication is corrupted. No SPI communication with the device is possible. An increase in supply current is possible when DRDY tries to drive low when CS is driven high and vice versa. Device damage plausible if this condition exists for an extended period of time. | A |
| DRDY | 13 | SCLK | SPI communication is corrupted. No SPI communication with the device is possible. An increase in supply current is possible when DRDY tries to drive low when SCLK is driven high and vice versa. Device damage plausible if this condition exists for an extended period of time. | A |
| SCLK | 14 | DOUT | SPI communication is corrupted. No SPI communication with the device is possible. An increase in supply current is possible when DOUT tries to drive low when SCLK is driven high and vice versa. Device damage plausible if this condition exists for an extended period of time. | A |
| DOUT | 15 | DIN | SPI communication is corrupted. No SPI communication with the device is possible. An increase in supply current is possible when DOUT tries to drive low when DIN is driven high and vice versa. Device damage plausible if this condition exists for an extended period of time. | A |
| DIN | 16 | CLKIN | SPI communication is corrupted. No SPI communication with the device is possible. The CLKIN signal is corrupted. Device behavior is undetermined. | B |
| CLKIN | 17 | CAP | Device behavior is undetermined. Device damage is plausible when the CLKIN pin drives the digital core LDO output on the CAP pin to >1.8 V. | A |
| CAP | 18 | DGND | The device is unpowered and not functional. | B |
| DGND | 19 | DVDD | The device is unpowered and not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| DVDD | 20 | AVDD | Not considered. Corner pin. | D |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVDD | 1 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| AGND | 2 | The device is unpowered and not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| AIN0P | 3 | AIN0P is stuck high. VIN0 = VAIN0P – VAIN0N = AVDD – VAIN0N. The conversion results of ADC0 are incorrect. | B |
| AIN0N | 4 | AIN0N is stuck high. VIN0 = VAIN0P – VAIN0N = VAIN0P – AVDD. The conversion results of ADC0 are incorrect. | B |
| AIN1N | 5 | AIN1N is stuck high. VIN1 = VAIN1P – VAIN1N = VAIN1P – AVDD. The conversion results of ADC1 are incorrect. | B |
| AIN1P | 6 | AIN1P is stuck high. VIN1 = VAIN1P – VAIN1N = AVDD – VAIN1N. The conversion results of ADC1 are incorrect. | B |
| NC | 7 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 8 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 9 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| NC | 10 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| SYNC/RESET | 11 | No effect. Normal operation. The device cannot be reset or synchronized using the SYNC/RESET pin anymore. | B |
| CS | 12 | CS is stuck high. No SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| DRDY | 13 | DRDY is stuck high. No data-ready indication through the DRDY pin to the host is possible. An increase in supply current occurs when DRDY tries to drive low. Device damage plausible if DRDY drives low for an extended period of time. | A |
| SCLK | 14 | SCLK is stuck high. No SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| DOUT | 15 | DOUT is stuck high. No SPI communication back to the host is possible. An increase in supply current occurs when DOUT tries to drive low. Device damage plausible if DOUT drives low for an extended period of time. | A |
| DIN | 16 | DIN is stuck high. No SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| CLKIN | 17 | CLKIN is stuck high. No clock is provided to the device. The device is not functional, but SPI communication with the device is possible. | B |
| CAP | 18 | The device may operate normally, but permanent device damage within a short period of time is very plausible. The device is not functional anymore in case of damage. | A |
| DGND | 19 | The device is unpowered and not functional. Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for all pins of the device are met, otherwise device damage may be plausible. | A |
| DVDD | 20 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |