SLAA457B September 2013 – October 2018 MSP430F5500 , MSP430F5501 , MSP430F5502 , MSP430F5503 , MSP430F5504 , MSP430F5505 , MSP430F5506 , MSP430F5507 , MSP430F5508 , MSP430F5509 , MSP430F5510 , MSP430F5513 , MSP430F5514 , MSP430F5515 , MSP430F5517 , MSP430F5519 , MSP430F5521 , MSP430F5522 , MSP430F5524 , MSP430F5525 , MSP430F5526 , MSP430F5527 , MSP430F5528 , MSP430F5529 , MSP430F5630 , MSP430F5631 , MSP430F5632 , MSP430F5633 , MSP430F5634 , MSP430F5635 , MSP430F5636 , MSP430F5637 , MSP430F5638 , MSP430F5658 , MSP430F5659 , MSP430F6630 , MSP430F6631 , MSP430F6632 , MSP430F6633 , MSP430F6634 , MSP430F6635 , MSP430F6636 , MSP430F6637 , MSP430F6638 , MSP430F6658 , MSP430F6659 , MSP430FG6425 , MSP430FG6426 , MSP430FG6625 , MSP430FG6626
5.1 How to Choose a USB Device Class
Tradeoffs between the three device classes are shown in Table 5. (Plain text indicates advantages or neutral comments, and italic text indicates possible disadvantages.)
Table 5. Device Class Tradeoffs
| Characteristic | CDC
(Communications Device Class) |
HID
(Human Interface Device Class) |
MSC
(Mass Storage Class) |
|---|---|---|---|
| The interface generated on the host |
|
|
|
| Industry expertise for this interface |
|
|
Storage volumes are common in the industry; widely-supported and well-understood |
| Installation on the host |
|
|
|
| How the end user interacts with it |
|
|
|
| Driver certification needs |
|
|
|
| Code footprint and complexity |
|
|
|
| Throughput |
|
|
|
| Good for point-to-point communication between host and device |
|
|
|
| Good for bulk data transfer |
|
|
|
Sometimes the choice of device class is clear. In other cases, the application can be considered general purpose, giving the developer options. Although there are many ways to approach this decision, one way is shown in Figure 11.
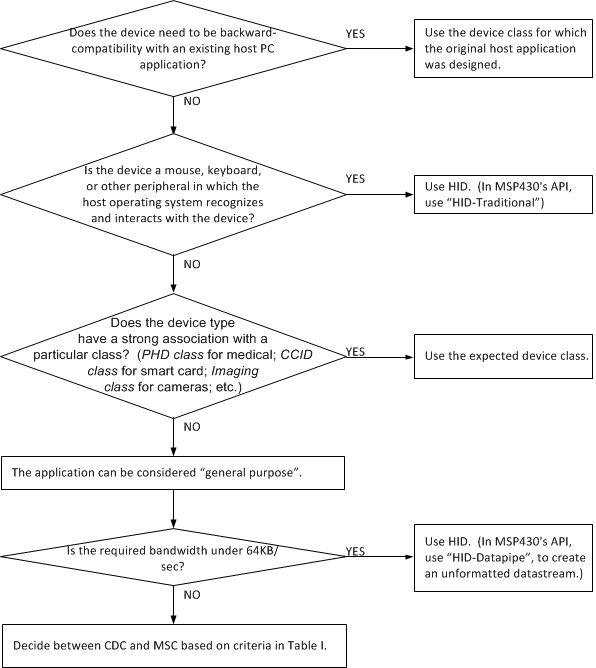 Figure 11. Example Process for Deciding on a USB Device Class
Figure 11. Example Process for Deciding on a USB Device Class For general-purpose use, HID-Datapipe should be considered, because of its combination of silent loading on the host (easy for the end user) and its small footprint and simplicity on the MSP430 MCUs, which speeds development. Coding of a corresponding host application is made easier with the MSP430 Java HID Demo App.