SLAA889A March 2019 – July 2021 MSP430FR6041 , MSP430FR6043 , MSP430FR60431 , MSP430FR6045 , MSP430FR6047 , MSP430FR60471
2 Algorithms for Ultrasonic Water Flow Metering
In both of the methods described in Section 1.1.1 and Section 1.1.2 the knowledge of the differential TOF as given in Equation 3 is required. There are two techniques for differential TOF measurement:
- Zero-crossing based using a time-to-digital converter (TDC): This technique uses an initial threshold crossing for the signal, followed by zero crossings of the signal
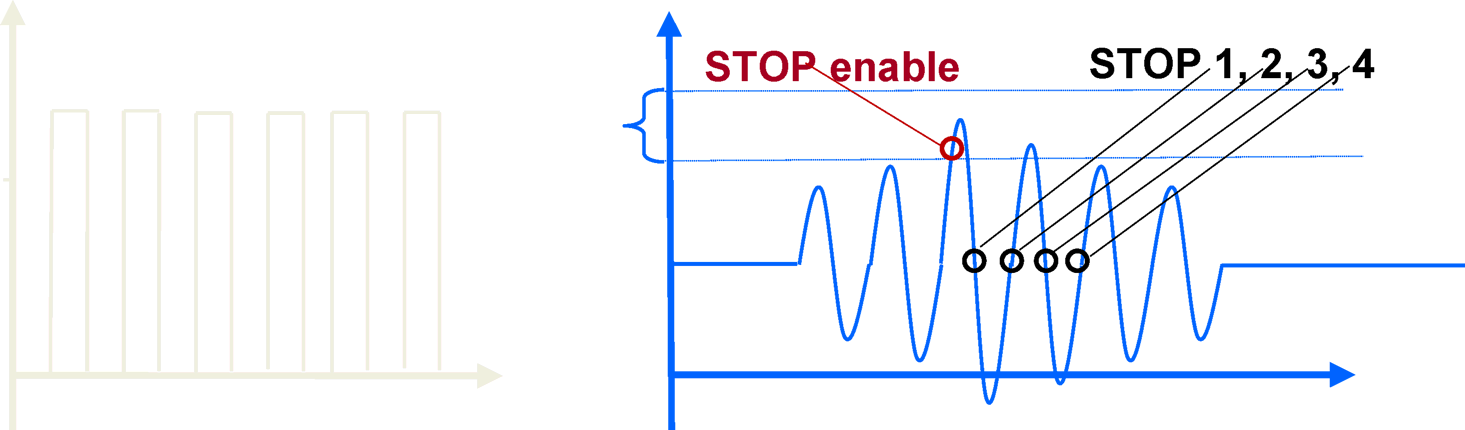 Figure 2-1 Zero-Crossing Based Time-to-Digital Converter
Figure 2-1 Zero-Crossing Based Time-to-Digital Converter - Correlation based using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC): In this technique the whole waveform is captured using ADC and stored for the up/dn stream and then post processing is done on the waveform to derive the differential time of flight.
This document describes the ADC-based technique for ultrasonic flow metering. This approach was chosen because of the following advantages over TDC techniques:
- Performance: The correlation acts as a digital filter to suppress noise (implemented efficiently on the low energy accelerator (LEA) on the MSP430FR6047 MCU). This results in 3 to 4 times lower noise standard deviation. The correlation filter also suppresses other interference like line noise.
- Robustness to signal amplitude variations: The algorithm is insensitive to the received signal amplitude as can occur with high flow rates, transducer-to-transducer variation, and temperature variation.
- The envelope of the signal is obtained naturally in ADC-based processing: This enables tuning to the transducer frequencies because slow variations in the envelope across time can be used to detect aging of transducers or meters.