SLAU723A October 2017 – October 2018 MSP432E401Y , MSP432E411Y
- 1
- 7
- 65
- 132
-
167
- 168
-
215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 408
- 415
- 482
- 564
- 643
- 715
- 791
- 841
- 855
- 870
-
917
- 918
- 919
- 920
- 1002
- 1017
-
1021
- 1022
- 1023
- 1024
- 1025
- 1026
- 1027
- 1028
- 1029
- 1030
- 1031
- 1032
- 1033
- 1034
- 1035
- 1036
- 1037
- 1038
- 1039
- 1040
- 1041
- 1042
- 1043
- 1044
- 1045
- 1046
- 1047
- 1048
- 1049
- 1050
- 1051
- 1052
- 1053
- 1054
- 1055
- 1056
- 1057
- 1058
- 1059
- 1060
- 1061
- 1062
- 1063
- 1064
- 1065
- 1066
- 1067
- 1068
- 1069
- 1070
- 1071
- 1072
- 1073
- 1074
- 1075
- 1076
- 1077
- 1078
- 1079
- 1080
- 1081
- 1082
- 1083
- 1084
- 1085
- 1086
- 1087
- 1088
- 1089
- 1090
- 1091
- 1092
- 1093
- 1094
- 1095
- 1125
- 1189
- 1251
- 1304
- 1365
- 1431
- 1478
- 1503
- 1552
- 1569
- 1618
-
1669
- 1670
- 1671
- 1672
- 1723
-
1726
- 1727
- 1728
- 1729
- 1730
- 1731
- 1732
- 1733
- 1734
- 1735
- 1736
- 1737
- 1738
- 1739
- 1740
- 1741
- 1742
- 1743
- 1744
- 1745
- 1746
- 1747
- 1748
- 1749
- 1750
- 1751
- 1752
- 1753
- 1754
- 1755
- 1756
- 1757
- 1758
- 1759
- 1760
- 1761
- 1762
- 1763
- 1764
- 1765
- 1766
- 1767
- 1768
- 1769
- 1770
- 1771
- 1772
- 1773
- 1774
- 1775
- 1776
- 1777
- 1778
- 1779
- 1780
- 1781
- 1782
- 1783
- 1784
- 1785
- 1786
- 1787
- 1788
- 1789
- 1790
- 1791
- 1792
- 1793
- 1794
- 1795
- 1796
- 1797
- 1798
- 1799
- 1800
- 1801
- 1802
- 1803
- 1804
- 1805
- 1806
- 1833
17.3.1.2 Data Register Operation
To aid in the efficiency of software, the GPIO ports allow for the modification of individual bits in the GPIO Data (GPIODATA) register (see Section 17.5.1) by using bits [9:2] of the address bus as a mask. In this manner, software drivers can modify individual GPIO pins in a single instruction without affecting the state of the other pins. This method is more efficient than the conventional method of performing a read-modify-write operation to set or clear an individual GPIO pin. To implement this feature, the GPIODATA register covers 256 locations in the memory map.
During a write, if the address bit associated with that data bit is set, the value of the GPIODATA register is altered. If the address bit is cleared, the data bit is left unchanged.
For example, writing a value of 0xEB to the address GPIODATA + 0x098 has the results shown in Figure 17-3, where u indicates that data is unchanged by the write. This example demonstrates how GPIODATA bits 5, 2, and 1 are written.
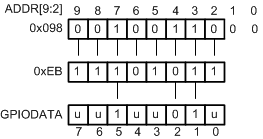 Figure 17-3 GPIODATA Write Example
Figure 17-3 GPIODATA Write Example During a read, if the address bit associated with the data bit is set, the value is read. If the address bit associated with the data bit is cleared, the data bit is read as a zero, regardless of its actual value. For example, reading address GPIODATA + 0x0C4 yields as shown in Figure 17-4. This example shows how to read GPIODATA bits 5, 4, and 0.
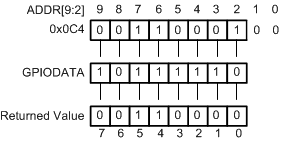 Figure 17-4 GPIODATA Read Example
Figure 17-4 GPIODATA Read Example