SLLSE75B May 2011 – July 2016 TLK10002
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 10-Gbps Power Characteristics - 1.0 V
- 7.6 10-Gbps Power Characteristics - 1.5 V
- 7.7 10-Gbps Power Characteristics - 1.8 V
- 7.8 Transmitter and Receiver Characteristics
- 7.9 MDIO Timing Requirements
- 7.10 JTAG Timing Requirements
- 7.11 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 High-Speed Side Receiver Jitter Tolerance
- 8.3.2 Lane Alignment Scheme
- 8.3.3 Lane Alignment Components
- 8.3.4 Lane Alignment Operation
- 8.3.5 Channel Synchronization
- 8.3.6 Line Rate, SERDES PLL Settings, and Reference Clock Selection
- 8.3.7 Clocking Architecture
- 8.3.8 Loopback Modes
- 8.3.9 Deep Remote Loopback
- 8.3.10 Shallow Remote Loopback and Serial Retime
- 8.3.11 Deep Local Loopback
- 8.3.12 Shallow Local Loopback
- 8.3.13 Test Pattern Generation and Verification
- 8.3.14 Latency Measurement Function
- 8.3.15 Power-Down Mode
- 8.3.16 High Speed CML Output
- 8.3.17 High Speed Receiver
- 8.3.18 Loss of Signal Indication (LOS)
- 8.3.19 MDIO Management Interface
- 8.3.20 MDIO Protocol Timing
- 8.3.21 Clause 22 Indirect Addressing
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The TLK10002 device can be used to support 10-Gbps data transmission over a backplane, for example, between a network processor or MAC and switch ASIC located on separate cards within a router chassis. A block diagram of this application is shown in Figure 33.
9.2 Typical Application
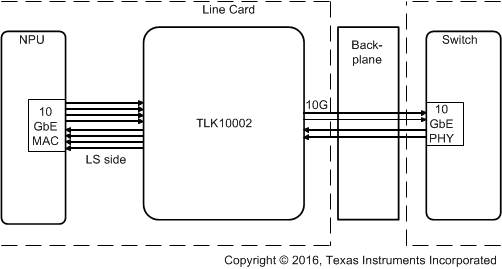 Figure 33. Typical Application Circuit
Figure 33. Typical Application Circuit
9.2.1 Design Requirements
Table 62 lists the design parameters of this example.
Table 62. Design Parameters
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Signaling | 9.8304 Gbps |
| Encoding | 8b/10b |
| REFCLK | 122.88 MHz |
| AC-coupling caps | 0.1 µF |
| Swing | 1260 mVpp |
| Total jitter (max) | 0.298 UI |
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The TLK10031 must be powered through a 1-V (nominal) supply on the VDDD, VDDA, DVDD, VDDT, and VPP rails, and by a 1.5-V or 1.8-V (nominal) supply on the VDDR and VDDO rails. The power supply accuracy must be 5% or better, and the user must be careful that resistive losses across the application PCB’s power distribution network do not cause the voltage present at the TLK10002 BGA balls to be below specification. If a switched-mode power supply is used, take care to ensure low supply ripple.
Table 63. Device Configuration
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Mode | 4:1 |
| PRE | –5 |
| POST1 | –10 |
| POST2 | –7.5 |
9.2.3 Application Curve
 Figure 34. Clean TX Output from TLK10002
Figure 34. Clean TX Output from TLK10002
9.3 Initialization Setup
The following sequence must be performed to initialize and ensure proper operation of the TLK10002 device. This procedure is optimized for electrical connection on HS serial side.
9.3.1 4:1 Mode (9.8304 Gbps on HS Side, 2.4576 Gbps Per Lane on LS Side)
Note: Assume both channel A and channel B have the same setup.
REFCLK frequency = 122.88 MHz, Mode = Transceiver, 4 to 1 serialization on LS side inputs and 1 to 4 deserialization on HS side inputs.
- Device Pin Setting(s) – Pin settings allow for maximum software configurability.
- Ensure PD_TRXA_N input pin is High.
- Ensure PD_TRXB_N input pin is High.
- Ensure PRBSEN input pin is Low.
- Ensure REFCLKA_SEL input pin is Low to enable software control.
- Ensure REFCLKB_SEL input pin is Low to enable software control.
- Reset Device
- Issue a hard or soft reset (RESET_N asserted for at least 10 µs -or- Write 1’b1 to 0.15 GLOBAL_RESET) after power supply stabilization.
- Enable MDIO global write so that each MDIO write affects both channels to shorten provisioning time
- Write 1’b1 to 0.11 GLOBAL_WRITE
- Clock Configuration and Mode control
- Write 1’b1 to 1.9 RX_DEMUX_SEL to select 1 to 4 on the receive side
- Write 1’b1 to 1.8 TX_MUX_SEL to select 4 to 1 on the transmit side
- Select respective Channel SERDES REFCLK input (Default = REFCLK0P/N)
- If REFCLK0P/N used – Write 1’b0 to 1.1 REFCLK_ SEL
- If REFCLK1P/N used – Write 1’b1 to 1.1 REFCLK_ SEL
- HS/LS Data Rate Setting (Refer to Table 3 for more CPRI/OBSAI Rates)
- Write 4’b1101 to 2.3:0 HS_PLL_MULT[3:0], write 2’b00 to 3.9:8 HS_RATE_RX[1:0], write 2’b00 to 3.1:0 HS_RATE_TX[1:0], to select FULL rate and 20x MPY on HS side (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 = 0x811D, HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA444).
- Write 4’b0101 to 6.3:0 LS_MPY[3:0], write 2’b00 to 7.9:8 LS_IN_RATE[1:0], write 2’b00 to 7.1:0 LS_OUT_RATE [1:0], to select FULL rate and 10x MPY on LS side (LS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 = 0xF115, LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xDC04).
- HS Serial Configuration Changed
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- 2.9:8 (HS_LOOP_BANDWIDTH[1:0]), 2.6 (HS_VRANGE)
- 3.15:12 (HS_SWING[3:0]), 3.7:6 (HS_AGCCTRL[1:0])
- 3.5:4 (HS_AZCAL[1:0]), 4.14:12 (HS_EQPRE[2:0])
- 4.11:10 (HS_CDRFMULT[1:0]), 4.9:8 (HS_CDRTHR[1:0]), 4.5 (H1CDRMODE)
- 4.4:0 (HS_TWCRF[4:0]), 5.12:8 (HS_TWPOST1[4:0])
- 5.7:4 (HS_TWPRE[3:0]), 5.3:0 (HS_TWPOST2[3:0])
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- LS Serial Configuration
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- 7.14:12 (LS_SWING[2:0]), 7.7:4 (LS_DE[3:0])
- 8.11:8 (LS_EQ [3:0]), 8.6:4 (LS_CDR [2:0])
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- Toggle HS_ENRX
- Write 1'b0 to 3.2 (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA440)
- Write 1'b1 to 3.2 (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA444)
- Wait 10ms
- Check SERDES PLL Status for Locked State
- Poll F.1 LS_PLL_LOCK (per channel) until it is asserted (high)
- Poll F.0 HS_PLL_LOCK (per channel) until it is asserted (high)
- Issue Data path Reset
- Write 1’b1 to E.3 DATAPATH_RESET
- Clear Latched Registers
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 to clear (per channel)
- Device provisioning has completed at this point
- Periodically Check Device Operational Mode Status (Non-Errored Read Values Shown Below):
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 and verify the following bits:
- F.14 LA_SLAVE_STATUS (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.13 HS_LOS (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.12 HS_AZ_DONE (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.11 HS_AGC_LOCKED (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.10 HS_CHANNEL_SYNC (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.8 HS_DECODE_INVALID (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.7 TX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.6 TX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.5 RX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.4 RX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.3 RX_LS_OK (1’b1) (per channel).
- F.2 TX_LS_OK (1’b1) (per channel).
- F.1 LS_PLL_LOCK (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.0 HS_PLL_LOCK (1’b1) (per channel)
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 and verify the following bits:
9.3.2 2:1 Mode (9.8304 Gbps on HS Side, 4.9152 Gbps Per Lane on LS Side, Only Lanes 0 and 1 on LS Side Active)
Note: Assume both channel A and channel B have the same setup.
REFCLK frequency = 122.88MHz, Mode = Transceiver, 2 to 1 serialization on LS side inputs and 1 to 2 deserialization on HS side inputs.
- Device Pin Setting(s) – Pin settings allow for maximum software configurability.
- Ensure PD_TRXA_N input pin is High.
- Ensure PD_TRXB_N input pin is High.
- Ensure PRBSEN input pin is Low.
- Ensure REFCLKA_SEL input pin is Low to enable software control.
- Ensure REFCLKB_SEL input pin is Low to enable software control.
- Reset Device
- Issue a hard or soft reset (RESET_N asserted for at least 10 µs -or- Write 1’b1 to 0.15 GLOBAL_RESET) after power supply stabilization.
- Enable MDIO global write so that each MDIO write affects both channels to shorten provisioning time
- Write 1’b1 to 0.11 GLOBAL_WRITE
- Clock Configuration and Mode control
- Write 1’b0 to 1.9 RX_DEMUX_SEL to select 1 to 2 on the receive side
- Write 1’b0 to 1.8 TX_MUX_SEL to select 2 to 1 on the transmit side
- Select respective Channel SERDES REFCLK input (Default = REFCLK0P/N)
- If REFCLK0P/N used – Write 1’b0 to 1.1 REFCLK_ SEL
- If REFCLK1P/N used – Write 1’b1 to 1.1 REFCLK_ SEL
- HS/LS Data Rate Setting (Refer to Table 3 for more CPRI/OBSAI Rates)
- Write 4’b1101 to 2.3:0 HS_PLL_MULT[3:0], write 2’b00 to 3.9:8 HS_RATE_RX[1:0], write 2’b00 to 3.1:0 HS_RATE_TX[1:0], to select FULL rate and 20x MPY on HS side (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 = 0x811D, HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA444).
- Write 1'b1 to 9.9 HS_PEAK_DISABLE (HS_OVERLAY_CONTROL = 0x0B00)
- Write 4’b1001 to 6.3:0 LS_MPY[3:0], write 2’b00 to 7.9:8 LS_IN_RATE[1:0], write 2’b00 to 7.1:0 LS_OUT_RATE [1:0], to select FULL rate and 20x MPY on LS side (LS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 = 0XF119, LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xDC04).
- HS Serial Configuration
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- 2.9:8 (HS_LOOP_BANDWIDTH[1:0]), 2.6 (HS_VRANGE)
- 3.15:12 (HS_SWING[3:0]), 3.7:6 (HS_AGCCTRL[1:0])
- 3.5:4 (HS_AZCAL[1:0]), 4.14:12 (HS_EQPRE[2:0])
- 4.11:10 (HS_CDRFMULT[1:0]), 4.9:8 (HS_CDRTHR[1:0])
- 4.4:0 (HS_TWCRF[4:0]), 5.12:8 (HS_TWPOST1[4:0])
- 5.7:4 (HS_TWPRE[3:0]), 5.3:0 (HS_TWPOST2[3:0])
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- LS Serial Configuration
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- 7.14:12 (LS_SWING[2:0]), 7.7:4 (LS_DE[3:0])
- 8.11:8 (LS_EQ [3:0]), 8.6:4 (LS_CDR [2:0])
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- Toggle HS_ENRX
- Write 1'b0 to 3.2 (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA440)
- Write 1'b1 to 3.2 (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA444)
- Wait 10ms
- Check SERDES PLL Status for Locked State
- Poll F.1 LS_PLL_LOCK (per channel) until it is asserted (high)
- Poll F.0 HS_PLL_LOCK (per channel) until it is asserted (high)
- Issue Data path Reset
- Write 1’b1 to E.3 DATAPATH_RESET
- Clear Latched Registers
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 to clear (per channel)
- Device provisioning has completed at this point
- Periodically Check Device Operational Mode Status (Non-Errored Read Values Shown Below):
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 and verify the following bits:
- F.14 LA_SLAVE_STATUS (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.13 HS_LOS (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.12 HS_AZ_DONE (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.11 HS_AGC_LOCKED (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.10 HS_CHANNEL_SYNC (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.8 HS_DECODE_INVALID (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.7 TX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.6 TX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.5 RX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.4 RX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.3 RX_LS_OK (1’b1) (per channel).
- F.2 TX_LS_OK (1’b1) (per channel).
- F.1 LS_PLL_LOCK (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.0 HS_PLL_LOCK (1’b1) (per channel)
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 and verify the following bits:
9.3.3 1:1 Mode (4.9152 Gbps on HS Side, 4.9152Gbps on LS side, Only Lane 0 on LS Side Active)
Note: Assume both channel A and channel B have the same setup.
REFCLK frequency = 122.88 MHz, Mode = Transceiver, 1 to 1 serialization on LS side inputs and 1 to 1 deserialization on HS side inputs.
- Device Pin Setting(s) – Pin settings allow for maximum software configurability.
- Ensure PD_TRXA_N input pin is High.
- Ensure PD_TRXB_N input pin is High.
- Ensure PRBSEN input pin is Low.
- Ensure REFCLKA_SEL input pin is Low to enable software control.
- Ensure REFCLKB_SEL input pin is Low to enable software control.
- Reset Device
- Issue a hard or soft reset (RESET_N asserted for at least 10 µs -or- Write 1’b1 to 0.15 GLOBAL_RESET) after power supply stabilization.
- Enable MDIO global write so that each MDIO write affects both channels to shorten provisioning time
- Write 1’b1 to 0.11 GLOBAL_WRITE
- Clock Configuration and Mode control
- Write 1’b1 to 1.13 RX_MODE_SEL to select 1 to 1 on the receive side
- Write 1’b1 to 1.12 TX_MODE_SEL to select 2 to 1 on the transmit side
- Select respective Channel SERDES REFCLK input (Default = REFCLK0P/N)
- If REFCLK0P/N used – Write 1’b0 to 1.1 REFCLK_ SEL
- If REFCLK1P/N used – Write 1’b1 to 1.1 REFCLK_ SEL
- HS/LS Data Rate Setting (Refer to Table 2 for more CPRI/OBSAI Rates)
- Write 4’b1101 to 2.3:0 HS_PLL_MULT[3:0], write 2’b01 to 3.9:8 HS_RATE_RX[1:0], write 2’b01 to 3.1:0 HS_RATE_TX[1:0], to select HALF rate and 20x MPY on HS side (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 = 0x811D, HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA545).
- Write 4’b1001 to 6.3:0 LS_MPY[3:0], write 2’b00 to 7.9:8 LS_IN_RATE[1:0], write 2’b00 to 7.1:0 LS_OUT_RATE [1:0], to select FULL rate and 20x MPY on LS side (LS_SERDES_CONTROL_1 = 0xF119, LS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xDC04).
- HS Serial Configuration
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- 2.9:8 (HS_LOOP_BANDWIDTH[1:0]), 2.6 (HS_VRANGE)
- 3.15:12 (HS_SWING[3:0]), 3.7:6 (HS_AGCCTRL[1:0])
- 3.5:4 (HS_AZCAL[1:0]), 4.14:12 (HS_EQPRE[2:0])
- 4.11:10 (HS_CDRFMULT[1:0]), 4.9:8 (HS_CDRTHR[1:0])
- 4.4:0 (HS_TWCRF[4:0]), 5.12:8 (HS_TWPOST1[4:0])
- 5.7:4 (HS_TWPRE[3:0]), 5.3:0 (HS_TWPOST2[3:0])
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- LS Serial Configuration
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- 7.14:12 (LS_SWING[2:0]), 7.7:4 (LS_DE[3:0])
- 8.11:8 (LS_EQ [3:0]), 8.6:4 (LS_CDR [2:0])
- Configure the following bits per the desired application:
- Toggle HS_ENRX
- Write 1'b0 to 3.2 (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA449)
- Write 1'b1 to 3.2 (HS_SERDES_CONTROL_2 = 0xA44D)
- Wait 10ms
- Check SERDES PLL Status for Locked State
- Poll F.1 LS_PLL_LOCK (per channel) until it is asserted (high)
- Poll F.0 HS_PLL_LOCK (per channel) until it is asserted (high)
- Issue Data path Reset
- Write 1’b1 to E.3 DATAPATH_RESET
- Clear Latched Registers
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 to clear (per channel)
- Device provisioning has completed at this point
- Periodically Check Device Operational Mode Status (Non-Errored Read Values Shown Below):
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 and verify the following bits:
- F.13 HS_LOS (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.12 HS_AZ_DONE (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.11 HS_AGC_LOCKED (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.7 TX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.6 TX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.5 RX_FIFO_UNDERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.4 RX_FIFO_OVERFLOW (1’b0) (per channel)
- F.1 LS_PLL_LOCK (1’b1) (per channel)
- F.0 HS_PLL_LOCK (1’b1) (per channel)
- Read 0x0F CHANNEL_STATUS_1 and verify the following bits: