SLOA198A September 2014 – December 2021 DRV2665 , DRV2667 , DRV2700 , DRV8662
- Trademarks
- 1 Boost Converter Basics
- 2 DRV8662, DRV2700, DRV2665, and DRV2667 Boost Converter
- 3 Configuring the Boost Converter
- 4 Boost Converter Output Voltage
- 5 Calculating the Load Current
- 6 Selecting an Inductor
- 7 Calculate the Maximum Boost Current
- 8 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9 Input Capacitor Selection
- 10PCB Layout
- 11Examples
- 12Revision History
6.3 Thermal Current Rating
The thermal current rating is typically measured as the RMS current that causes some fixed rise in temperature (typically 20 – 30°C). Do not exceed this RMS current value.
Calculate the RMS current through the inductor using Equation 6. This is an approximation based on a triangular RMS waveform.
Equation 6. 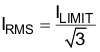
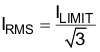
| Symbol | Description | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| IRMS | Inductor RMS Current | – | ARMS |
| ILIMIT | Peak current limit set by the DRVxxxx REXT resistor | – | Ap |