SLOS545D November 2008 – December 2014 TLV320AIC3107
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Block Diagram
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Description (Continued)
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Hardware Reset
- 10.3.2 Digital Audio Data Serial Interface
- 10.3.3 Audio Data Converters
- 10.3.4 Audio Analog Inputs
- 10.3.5 Analog Line Output Drivers
- 10.3.6 Analog High Power Output Drivers
- 10.3.7 Input Impedance and VCM Control
- 10.3.8 General Purpose I/O
- 10.3.9 MICBIAS Generation
- 10.3.10 Class-D Speaker Driver
- 10.3.11 Short Circuit Output Protection
- 10.3.12 Jack and Headset Detection
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10.5 Programming
- 10.6 Register Maps
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
11.1 Application Information
The TLV320AIC3107 is a highly integrated low-power stereo audio codec with integrated stereo headphone/line, and mono class D amplifier, as well as multiple inputs and outputs that are programmable in single-ended or fully differential configurations. All the features of the TLV320AIC3107 are accessed by programmable registers. External processor with I2C protocol is required to control the device. It is good practice to perform a hardware reset after initial power up to ensure that all registers are in their default states. Extensive register-based power control is included, enabling stereo 48-kHz DAC playback as low as 14-mW from a 3.3-V analog supply, making it ideal for portable battery-powered audio and telephony applications.
11.2 Typical Application
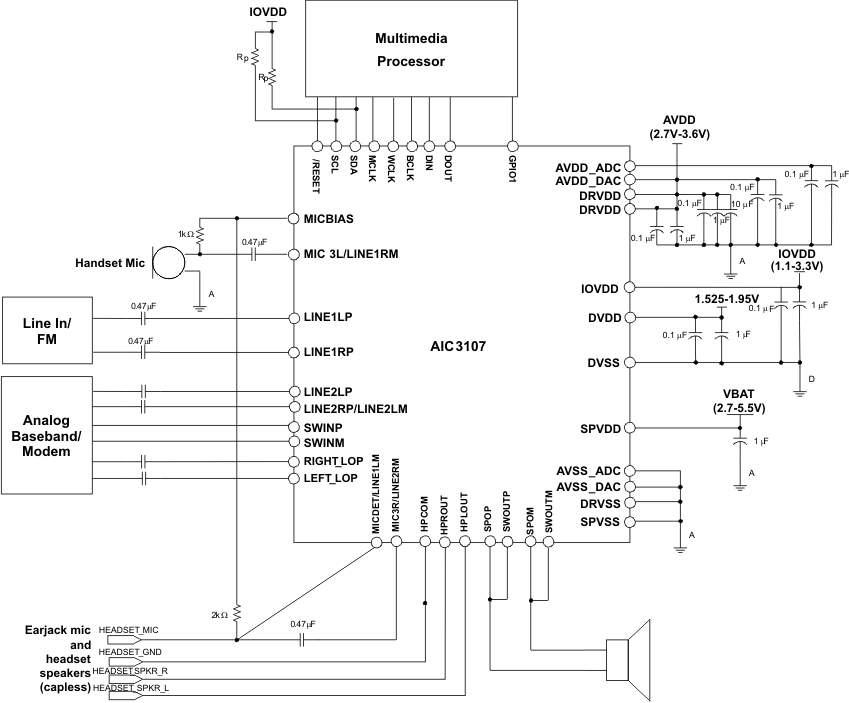 Figure 37. Typical Connections for Capless Headphone and External Speaker Amp
Figure 37. Typical Connections for Capless Headphone and External Speaker Amp
11.2.1 Design Requirements
For this design example, use the parameters shown in Table 7.
Table 7. Design Parameters
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (AVDD, DRVDD) | 3.3 V |
| Supply Voltage (DVDD, IOVDD) | 1.8 V |
| Analog High-Power Output Driver Load | 16 Ω |
| Analog Fully Differential Line Output Driver Load | 10 kΩ |
| Class D Audio Amplifier Load | 18 Ω |
11.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- Use the Typical Application Schematic as a guide, integrate the hardware into the system.
- Following the recommended component placement, schematic layout and routing given in the Figure 41 below, integrate the device and its supporting components into the system PCB.
- For questions and support go to the E2E forums (e2e.ti.com). If it is necessary to deviate from the recommended layout, please visit the E2E forum to request a layout review.
- Determining sample rate and Master clock frequency is required since powering up the device as all internal timing is derived from the master clock. Refer to the Audio Clock Generation section in order to get more information on how to configure correctly the required clocks for the device.
- As the TLV320AIC3107 is designed for low-power applications, when powered up, the device has several features powered down. A correct routing of the TLV320AIC3107 signals is achieved by a correct setting of the device registers, powering up the required stages of the device and configuring the internal switches to follow a desired route.
- For more information of the device configuration and programming, refer to the TLV320AIC3107 technical documents section in ti.com (http://www.ti.com/product/TLV320AIC3105/technicaldocuments).
11.2.3 Application Curves
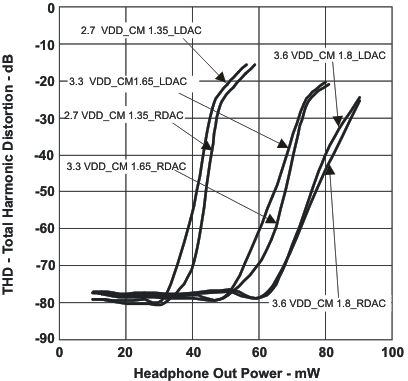 Figure 38. Total Harmonic Distortion vs Headphone Out Power
Figure 38. Total Harmonic Distortion vs Headphone Out Power
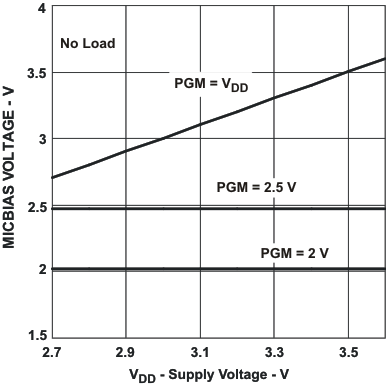 Figure 39. MICBIAS Voltage vs Supply Voltage
Figure 39. MICBIAS Voltage vs Supply Voltage