SLUP408 February 2022 LM25149-Q1 , LM61460-Q1 , LM61495-Q1 , LMQ61460-Q1
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Defining EMI
- 3 What Causes EMI in a Switched-Mode DC/DC Regulator?
- 4 Existing Passive EMI Filtering Techniques
- 5 Passive Filter Limitations
- 6 AEF
- 7 Spread Spectrum
- 8 DRSS
- 9 True Slew-Rate Control
- 10HotRod™ Package Technology
- 11Optimized Package and Pinout
- 12Integrated Capacitors
- 13Conclusions
- 14References
- 15Important Notice
5 Passive Filter Limitations
CF connects to the main power rail and must be rated for the maximum DC voltage. Designs requiring a large CF and a higher DC voltage will necessitate the use of a larger and more expensive capacitor. Similarly, LIN must be rated for the maximum input current (IIN) at minimum input voltages. In higher-power systems, the inductor size and cost will further increase given the larger inductance and DC current requirements. Transients such as load dump and cold crank exacerbate the VIN and IIN requirements.
A second-order effect is that the self-resonant frequency (SRF) decreases as the size of CF increases. At the SRF, the impedance of the equivalent series inductance (ESL) equals that of the capacitance and marks the lowest impedance point over the frequency range. A higher ESL deteriorates the filter’s performance and its ability to attenuate noise at high frequencies.
Figure 5-1 shows two capacitors where the larger capacitor (in blue) is less effective at higher frequencies compared to the smaller capacitor (in black). The figure shows both the impedance and effective capacitance. At frequencies above the SRF, the capacitance rolls off and the parasitic inductance dominates the capacitor impedance. A similar SRF effect can limit LIN in filter performance, where parasitic capacitance dominates the inductor and deteriorates performance at high frequencies.
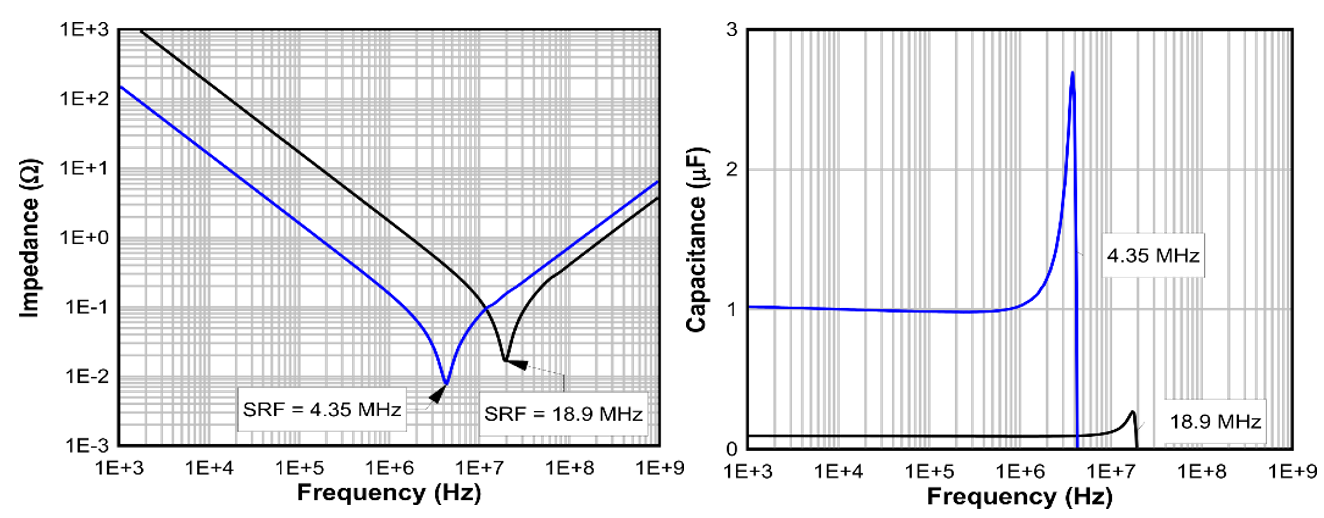 Figure 5-1 Impedance of two different
package and value capacitors: the larger capacitor (blue) is in a larger package
and has a lower SRF, which results in a larger impedance at high frequencies
compared to the smaller-package capacitor (black).
Figure 5-1 Impedance of two different
package and value capacitors: the larger capacitor (blue) is in a larger package
and has a lower SRF, which results in a larger impedance at high frequencies
compared to the smaller-package capacitor (black).