SLUP409B April 2022 – April 2024 TPS543320 , TPS543620 , TPS543820 , TPS62913 , TPS62916
- 1
- Abstract
- 1 Introduction
- 2 DC/DC Converters are Noisy
- 3 Power-Supply Output Voltage Ripple and Noise Degrade ADC Performance
- 4 Minimizing Low-Frequency Noise Requires Dedicated Low-Noise IC Technologies
- 5 Traditional Approaches to Reducing Ripple
- 6 Using Smaller Capacitors in Parallel
- 7 Larger Inductance
- 8 Adding a Feedthrough Capacitor
- 9 Adding a Ferrite Bead
- 10Layout Techniques
- 11Silicon Solutions
- 12Conclusions
4 Minimizing Low-Frequency Noise Requires Dedicated Low-Noise IC Technologies
Low-frequency noise is not a significant concern for high-speed ADCs, but the noise becomes dominant when powering frequency synthesizers and PLLs where phase noise increases clock jitter. Duty-cycle jitter is very critical, especially at higher clock frequencies, and must be minimized.
To estimate the required low-frequency noise for a DC/DC converter, Figure 4 shows the low-frequency noise of a typical low-noise LDO vs. a DC/DC converter.
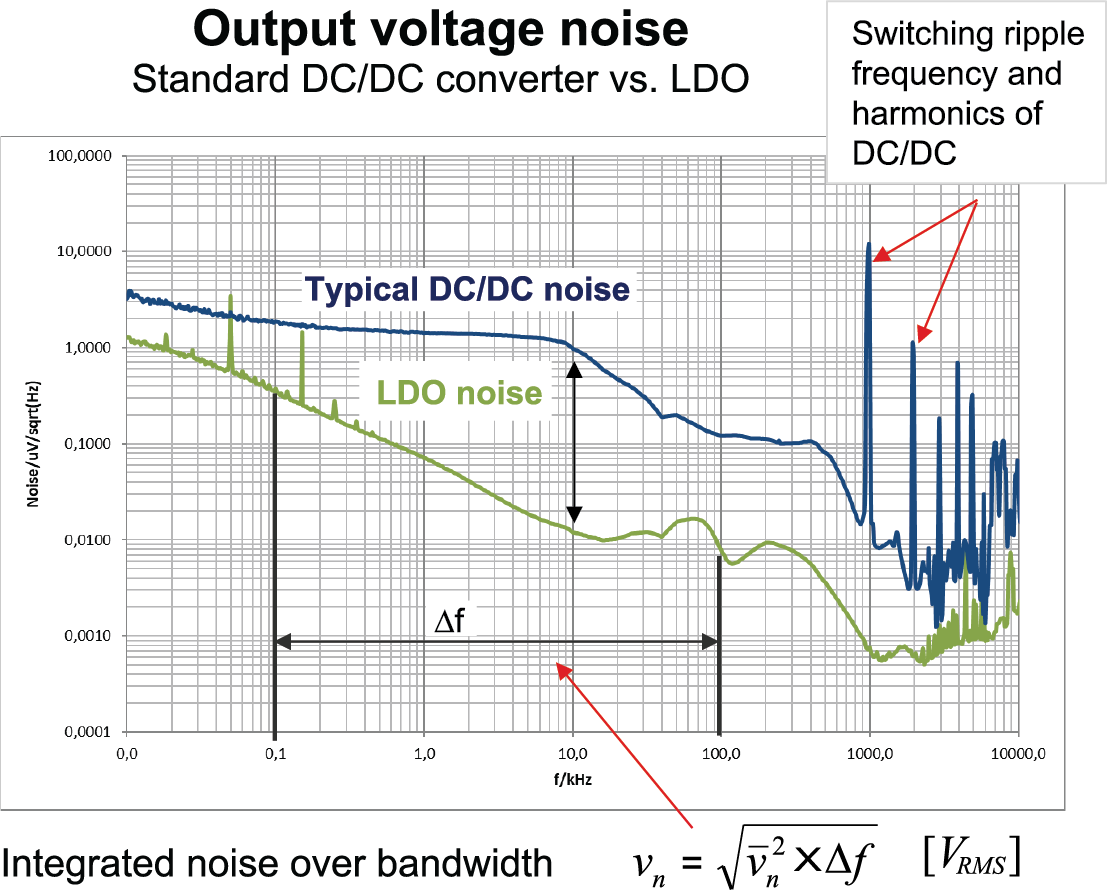 Figure 4 A DC/DC converter generates
three to 10 times more low-frequency noise than a low-noise LDO.
Figure 4 A DC/DC converter generates
three to 10 times more low-frequency noise than a low-noise LDO.Low noise is typically a concern in the range of 100 Hz to 100 kHz; interference with the PLL loop is the most sensitive over this frequency range. Equation 3 expresses the integration of low-frequency noise over a bandwidth from 100 Hz to 100 kHz:
It is also important to look at the spectral noise density, as shown in Figure 4 and expressed as microvolts per square-root hertz, because the root-mean-square noise level of an LDO can be very low, while the spectral noise density can still be high at a single frequency, causing distortions. Reducing the low-frequency noise of a DC/DC converter requires an internal integrated circuit (IC) design. Filtering the output voltage at such low frequencies requires large external passive filter components with an inductance of approximately 5 mH and a capacitance of approximately 10,000 µF for a filter cutoff frequency <20 Hz. Using IC techniques and filtering the internal DC/DC converter reference can achieve DC/DC converter frequency noise as low as 20 µVRMS.
Using low-noise circuit techniques for the internal IC error amplifier, current-sense circuit and oscillator make further improvements possible. A low-noise target of 20 µVRMS showed no degradation in phase noise by characterizing TI’s LMX2592 and LMX2594 frequency synthesizers and LMK04616 jitter cleaner, which are popular in high-speed systems. Low-noise and low ripple design is described in the last section of this document, but first, how to better understand the complexity of achieving a low-output voltage ripple in a DC/DC converter will be discussed in the next section.