SLUS772G March 2008 – June 2020 TPS40210 , TPS40211
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Soft Start
- 7.3.2 BP Regulator
- 7.3.3 Shutdown (DIS/ EN Pin)
- 7.3.4 Minimum On-Time and Off-Time Considerations
- 7.3.5 Setting the Oscillator Frequency
- 7.3.6 Synchronizing the Oscillator
- 7.3.7 Current Sense and Overcurrent
- 7.3.8 Current Sense and Subharmonic Instability
- 7.3.9 Current Sense Filtering
- 7.3.10 Control Loop Considerations
- 7.3.11 Gate Drive Circuit
- 7.3.12 TPS40211
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
12-V to 24-V Nonsynchronous Boost Regulator
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.1.2.3 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.7 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.1.2.8 Current Sense Filter
- 8.2.1.2.9 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.1.2.10 Feedback Divider Resistors
- 8.2.1.2.11 Error Amplifier Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.12 RC Oscillator
- 8.2.1.2.13 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.14 Regulator Bypass
- 8.2.1.2.15 Bill of Materials
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 12-V Input, 700-mA LED Driver, Up to 35-V LED String
- 8.2.1
12-V to 24-V Nonsynchronous Boost Regulator
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.6 Synchronizing the Oscillator
The TPS40210 and TPS40211 can be synchronized to an external clock source. Figure 7-4 shows the functional diagram of the oscillator. When synchronizing the oscillator to an external clock, the RC pin must be pulled below 150 mV for 20 ns or more. The external clock frequency must be higher than the free running frequency of the converter as well. When synchronizing the controller, if the RC pin is held low for an excessive amount of time, erratic operation can occur. The maximum amount of time that the RC pin should be held low is 50% of a nominal output pulse, or 10% of the period of the synchronization frequency. If the external clock signal cannot operate with a low enough duty cycle to limit the amount of time the RC pin is held low, a resistor and capacitor can be added at the gate of the synchronization MOSFET. The capacitor should be added in series with the gate of the MOSFET to AC couple the rising edge of the synchronization signal. The resistor should be added from the gate of the MOSFET to ground to turn off the MOSFET. Typical values for the resistor and capacitor are 220 pF and 1 kΩ.
Under circumstances where the duty cycle is less than 50%, a Schottky diode connected from the RC pin to an external clock can be used to synchronize the oscillator. The cathode of the diode is connected to the RC pin. The trip point of the oscillator is set by an internal voltage divider to be 1/20 of the input voltage. The clock signal must have an amplitude higher than this trip point. When the clock goes low, it allows the reset current to restart the RC ramp, synchronizing the oscillator to the external clock. This provides a simple, single-component method for clock synchronization.
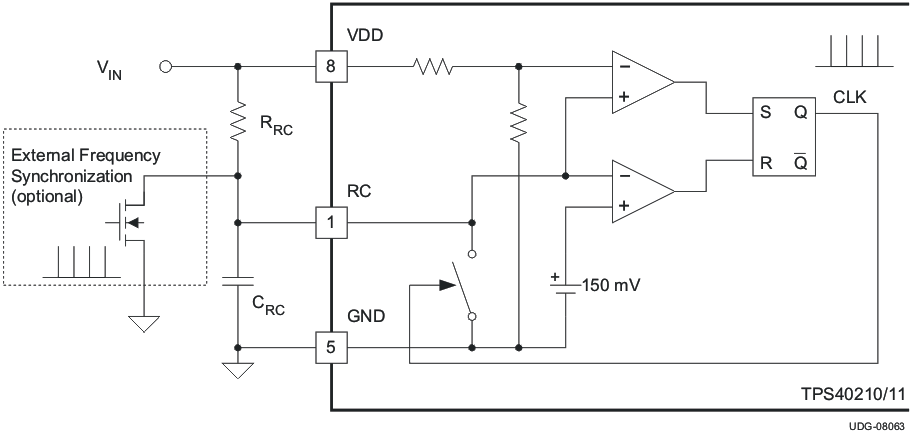 Figure 7-4 Oscillator Functional Diagram
Figure 7-4 Oscillator Functional Diagram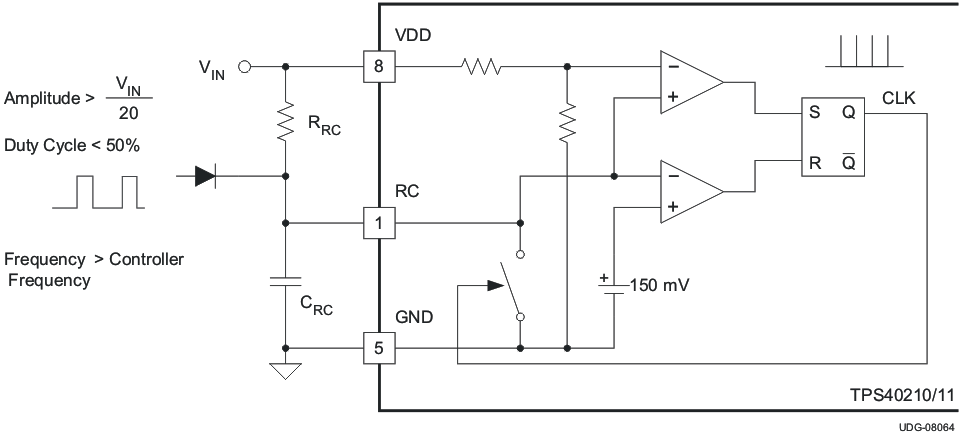 Figure 7-5 Diode Connected Synchronization
Figure 7-5 Diode Connected Synchronization