SLUS772G March 2008 – June 2020 TPS40210 , TPS40211
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Soft Start
- 7.3.2 BP Regulator
- 7.3.3 Shutdown (DIS/ EN Pin)
- 7.3.4 Minimum On-Time and Off-Time Considerations
- 7.3.5 Setting the Oscillator Frequency
- 7.3.6 Synchronizing the Oscillator
- 7.3.7 Current Sense and Overcurrent
- 7.3.8 Current Sense and Subharmonic Instability
- 7.3.9 Current Sense Filtering
- 7.3.10 Control Loop Considerations
- 7.3.11 Gate Drive Circuit
- 7.3.12 TPS40211
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
12-V to 24-V Nonsynchronous Boost Regulator
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Duty Cycle Estimation
- 8.2.1.2.3 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.2.1.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.7 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 8.2.1.2.8 Current Sense Filter
- 8.2.1.2.9 Switching MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.1.2.10 Feedback Divider Resistors
- 8.2.1.2.11 Error Amplifier Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.12 RC Oscillator
- 8.2.1.2.13 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.14 Regulator Bypass
- 8.2.1.2.15 Bill of Materials
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 12-V Input, 700-mA LED Driver, Up to 35-V LED String
- 8.2.1
12-V to 24-V Nonsynchronous Boost Regulator
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.2 BP Regulator
The TPS40210 and TPS40211 have an on-board linear regulator that supplies power to the internal circuitry of the controller, including the gate driver. This regulator has a nominal output voltage of 8 V and must be bypassed with a 1-μF capacitor. If the voltage at the VDD pin is less than 8 V, the voltage on the BP pin will also be less and the gate drive voltage to the external FET is reduced from the nominal 8 V. This should be considered when choosing a FET for the converter.
Connecting external loads to this regulator can be done, but care must be taken to ensure that the thermal rating of the device is observed since there is no thermal shutdown feature in this controller. Exceeding the thermal ratings causes out of specification behavior and can lead to reduced reliability. The controller dissipates more power when there is an external load on the BP pin and is tested for dropout voltage for up to 5-mA load. When the controller is in the disabled state, the BP pin regulator also shuts off so loads connected there power down as well. When the controller is disabled with the DIS/ EN pin, this regulator is turned off.
The total power dissipation in the controller can be calculated as follows. The total power is the sum of PQ, PG, and PE.
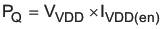
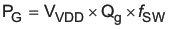
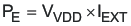
where
- PQ is the quiescent power of the device in W
- VDD is the VDD pin voltage in V
- IDD(en) is the quiescent current of the controller when enabled but not switching in A
- PG is the power dissipated by driving the gate of the FET in W
- Qg is the total gate charge of the FET at the voltage on the BP pin in C
- fSW is the switching frequency in Hz
- PE is the dissipation caused be external loading of the BP pin in W
- IEXT is the external load current in A