SLUS829G August 2008 – February 2020 UCC2897A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.2 Soft Start
Once RON is defined, the charge current of the soft-start capacitor is calculated with Equation 13.
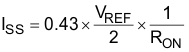
During soft start, CSS charges from 0 to 5 V by the calculated ISS current. The actual control range of the soft-start capacitor voltage is between 2.5 and 4.5 V. Therefore, the soft-start capacitor value must be based on this narrower control range and the required startup time (tSS) according to Equation 14.
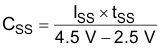
Note that tSS defines a time interval to reach the maximum-current capability of the converter and not the time required to ramp the output voltage from 0 V to the nominal regulated level. Using an open-loop start-up scheme does not allow accurate control over the ramp-up time of the output voltage. In addition to the ISS and CSS values, the time required to reach the nominal output voltage of the converter is a function of the maximum-output current (current limit), the output capacitance of the converter and the actual load conditions. If it is critical to implement a tightly-controlled ramp-up time at the output of the converter, the soft start must be implemented using a closed-loop technique. Closed-loop soft-start implements with the error amplifier of the voltage regulation loop when the voltage reference is ramped from 0 V to the final steady-state value during the required tSS startup-time interval.