SLUSDD4B April 2019 – December 2020
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.1 UVLO
The UVLO circuit ensures that VCC is adequate to make the UC1843B-SP fully operational before enabling the output stage. Figure 7-4 shows that the UVLO turnon and turnoff thresholds are fixed internally at 8.4 V and 7.6 V, respectively. The 0.6-V hysteresis prevents VCC oscillations during power sequencing.
Figure 7-5 shows supply current requirements. Start-up current is < 1 mA for efficient bootstrapping from the rectified input of an off-line converter, as shown in Figure 7-6. During normal circuit operation, VCC is developed from auxiliary winding, WAux, with D1 and CIN. However, at start-up, CIN must be charged to 8.4 V through RIN. With a start-up current of 1 mA, RIN can be as large as 100 kΩ and still charge CIN when VAC = 90-V RMS (low line). Power dissipation in RIN would then be less than 350 mW even under high line (VAC = 130-V RMS) conditions.
During UVLO, the output driver is in a low state. While it does not exhibit the same saturation characteristics as normal operation, it can easily sink 1 mA, enough to ensure the MOSFET is held off. For efficient operations, an LDO can take the place of RIN and be disabled during the operation of the device.
 Figure 7-4 UVLO Turnon and Turnoff Threshold
Figure 7-4 UVLO Turnon and Turnoff Threshold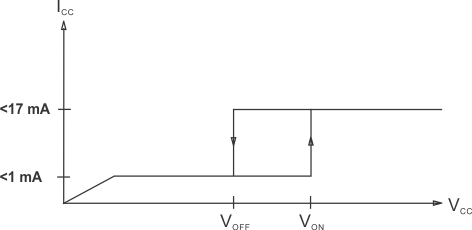
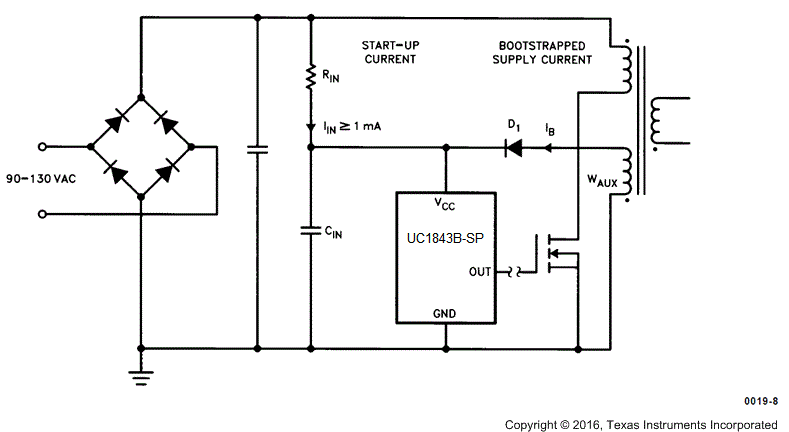 Figure 7-6 Providing Power to the UC1843B-SP
Figure 7-6 Providing Power to the UC1843B-SP