SLUUBM0D May 2017 – October 2020 TPS92518 , TPS92518-Q1 , TPS92518HV , TPS92518HV-Q1
- Trademarks
- 1Description
- 2Performance Specifications
- 3Performance Data and Typical Characteristic Curves
- 4Schematic, PCB Layout, and Bill of Materials
- 5Software
- 6Use of LEDSPIMCUEVM-879 Microcontroller Board for SPI Communications with the TPS92518
- 7Revision History
3.3 Current Sharing
The TPS92518 device can be set up to share current with both channels driving a single load.
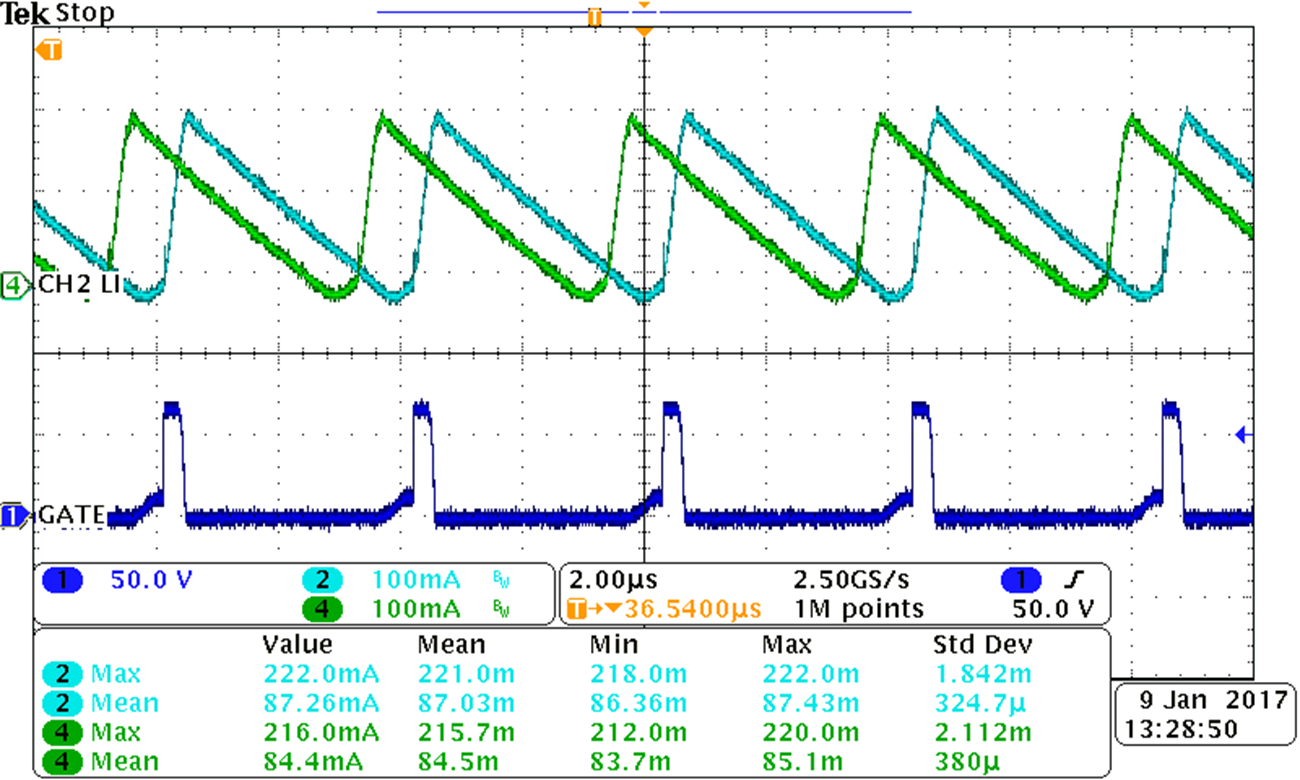
VIN = 65 V, driving 1 LED for a VLED of 3.0062 V, with a peak threshold = 45 to get approximately a 225-mA LED current, showing max and mean inductor currents on channels 1 and 2
Figure 3-9 Current Sharing