SLUUC72A September 2020 – October 2021 TPS542A50
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Description
- 3TPS542A50EVM-059 Bottom Circuit
- 4TPS542A50EVM-059 Top Circuit (Small layout area design)
- 5TPS542A50EVM-059 PCB Layout
- 6List of Materials
- 7Revision History
4.1.1 Output Voltage Setpoint
The output voltage is set by the resistor divider network of R5_2 and R10_2, as shown in Figure 4-1. The divider is connected between SREF and AGND pins, where the mid-point of the divider is tapped to the VSET pin. Unlike many converters, the output voltage is not set by connecting a resistor divider directly to the output node. This allows the use of a differential remote sense for improved output voltage accuracy.
It is recommended to use R5_2 and R10_2 in the range of 1 kΩ to 100 kΩ, and the total impedance must be greater than 10 kΩ. A footprint for a small capacitor, C22_2, has been added for high frequency noise filtering, but is typically not necessary and is not populated by default..
The value of R5_2 for a desired output voltage, VOUT, can be calculated using Equation 2.
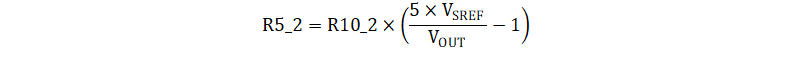
VSREF = 1.2 V
R10_2 = 20.0 kΩ
Note that for Vout below 1 V, the value of R10_2 should be reduced to keep R5_2 and R10_2 between 1 kΩ and 100 kΩ, while still maintaining a total impedance greater than 10 kΩ.
Using I2C, the TPS542A50 output voltage can be adjusted in 0.25% increments from -20% to +10% of the set output voltage. This allows the tolerance of the resistors used to set the output voltage to be completely eliminated, and gives an output voltage accuracy of -0.5% to +0.5% across the entire temperature range. Note that this adjustment to the output voltage over I2C can only be performed after PGOOD goes high.