SLVAET3 October 2021 TPS8802
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2System Architecture
- 3Current Consumption
- 4System Power Calculation and Measurements
- 5Summary
- 6References
3.2.1 Smoke Measurement Current
Taking a smoke measurement generally follows the procedure:
- Enable the photo amplifier and analog multiplexer (AMUX) buffer.
- Take an ADC measurement after the photo amplifier and AMUX settles. This measures the ambient light entering the photo chamber.
- Enable the LED driver.
- Take an ADC measurement after the photo amplifier and AMUX settles. This measures the ambient light and smoke concentration in the photo chamber.
- Disable the LED driver, photo amplifier, and AMUX buffer.
- Process the ADC measurements to determine the smoke concentration.
The power consumed from taking a smoke measurement is dominated by the LED driver current. The average LED current is shown in Equation 3, where ILED is the LED pulse current, TLED is the LED pulse duration, and fMEAS is the measurement frequency.
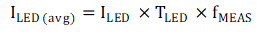
If the LED is supplied by the boost converter, the average LED current is scaled by the boost input-output voltage ratio and efficiency. The average LED current draw from the battery is calculated in Equation 4. Connecting the LED directly to the battery is the most efficient method of powering the LED.
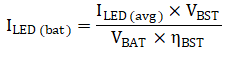
Secondary sources of power dissipation during the smoke measurement are the MCU active current and boost charging current. The MCU active current is drawn during the length of a measurement while the MCU is not in standby. Optimizing measurements for speed is essential to reducing the MCU active current. Boost charging current is caused by charging and discharging the VBST capacitor. Boost charging is further discussed in Section 3.3.1.