SLVAFE7 September 2022 LM51551
3.5 Overload Protection
Figure 3-11 through Figure 3-14 show the output overload protection when one of the outputs goes overload.
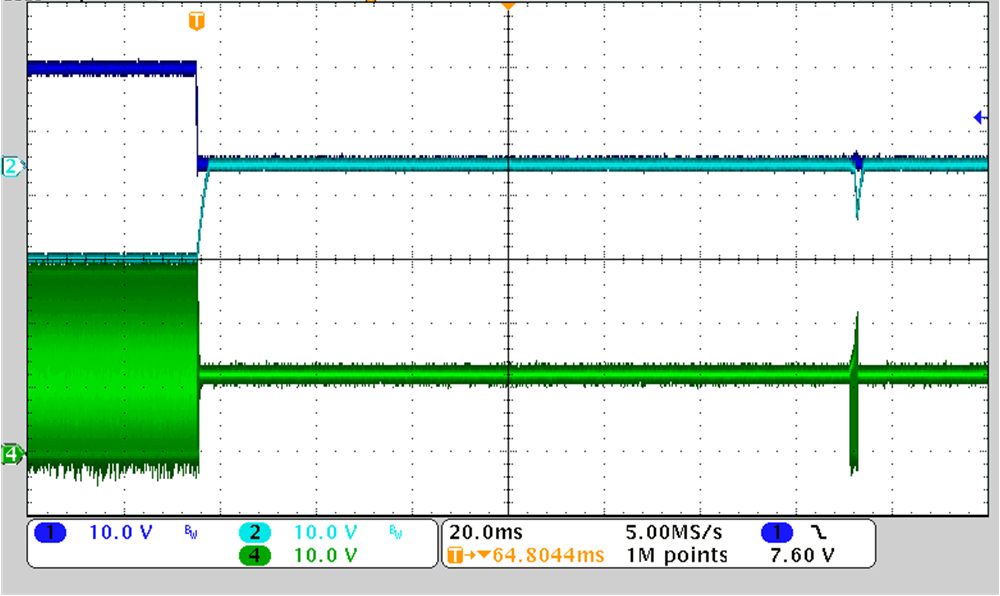
CH1: VOUT1, CH2: VOUT2, CH4: VSW
Figure 3-11 12-V Input, ±15 V, 10 mA, Output1 Overload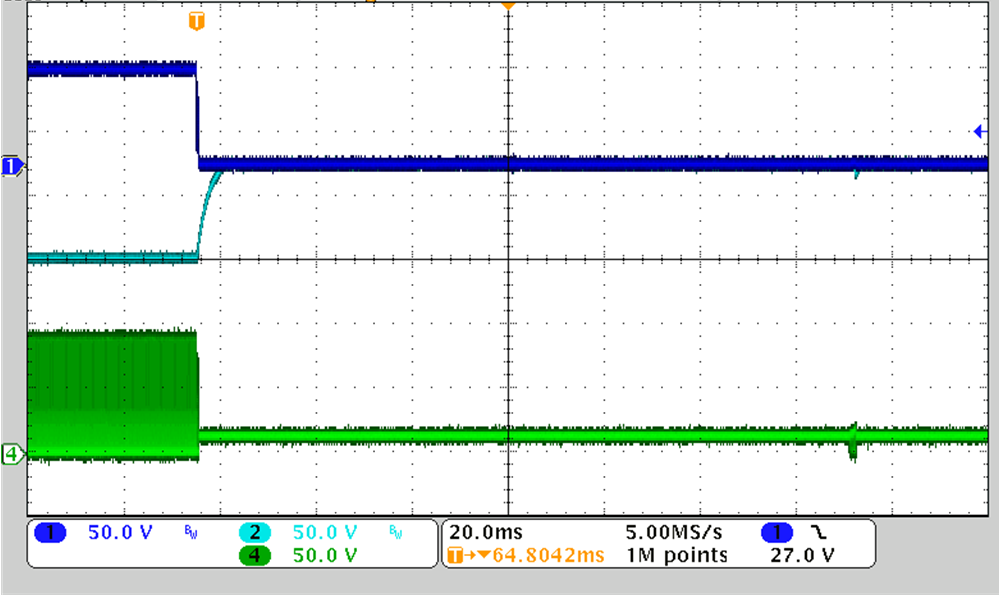
CH1: VOUT1, CH2: VOUT2, CH3: IOUT2, CH4: VSW
Figure 3-13 12-V Input, ±75 V, 10 mA, Output1 Overload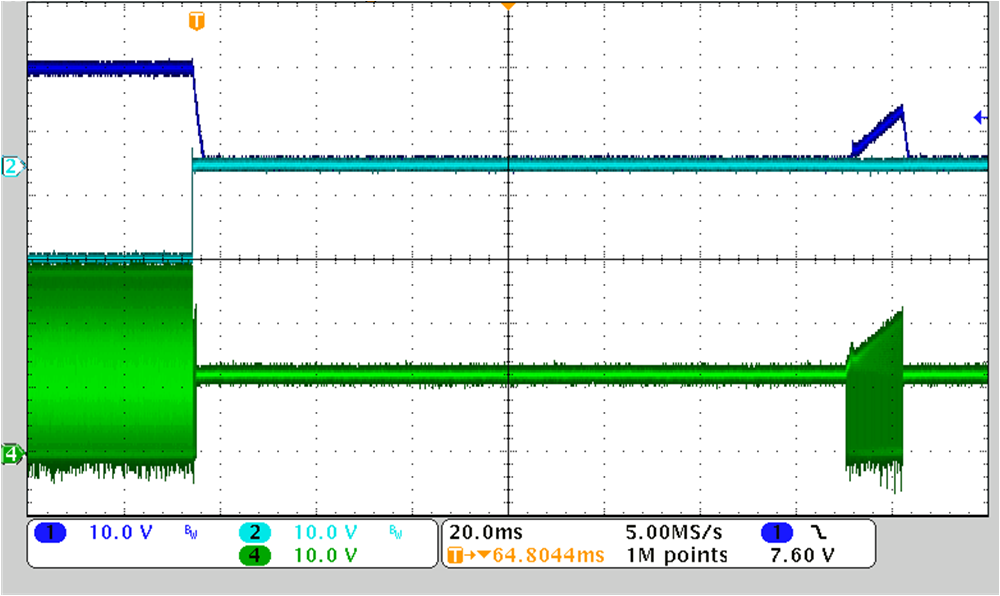
CH1: VOUT1, CH2: VOUT2, CH4: VSW
Figure 3-12 12-V Input, ±75 V, 10 mA, Output2 Overload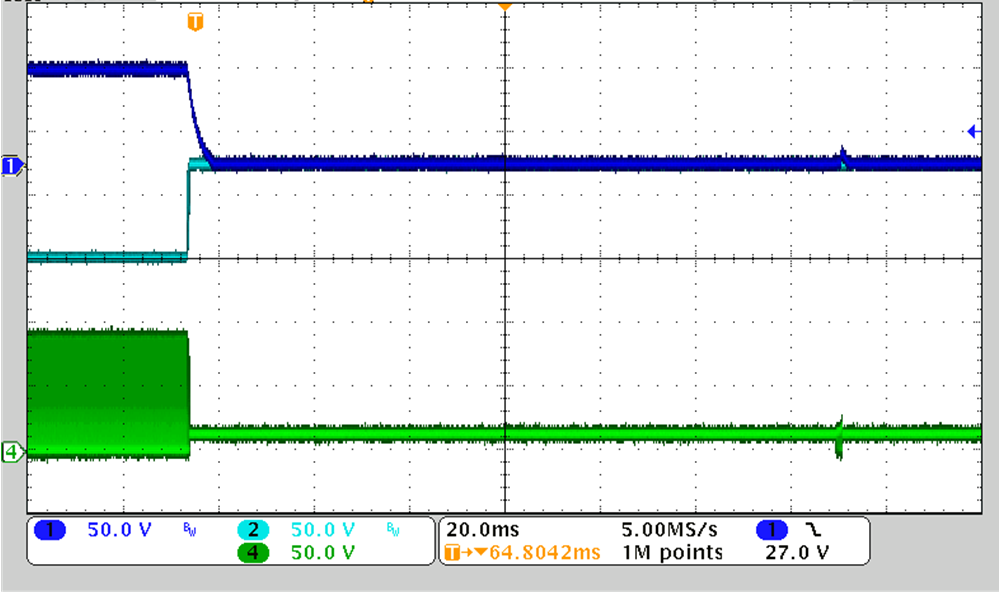
CH1: VOUT1, CH2: VOUT2, CH3: IOUT2, CH4: VSW
Figure 3-14 12-V Input, ±75 V, 10 mA, Output2 Overload