SLVAFE7 September 2022 LM51551
3.4 Load Transient Test
Figure 3-9 and Figure 3-10 show the waveforms of output AC ripples at load transient. The high current level is full load for 10 ms; the low current level is half load for 10 ms, with a slew rate of 0.1 A/μs. As the load on the positive output remains stable, the load on the negative increases from 5 mA to 10 mA, the voltage drops are 151 mV and 367 mV with the output 15 V and 75 V, respectively.
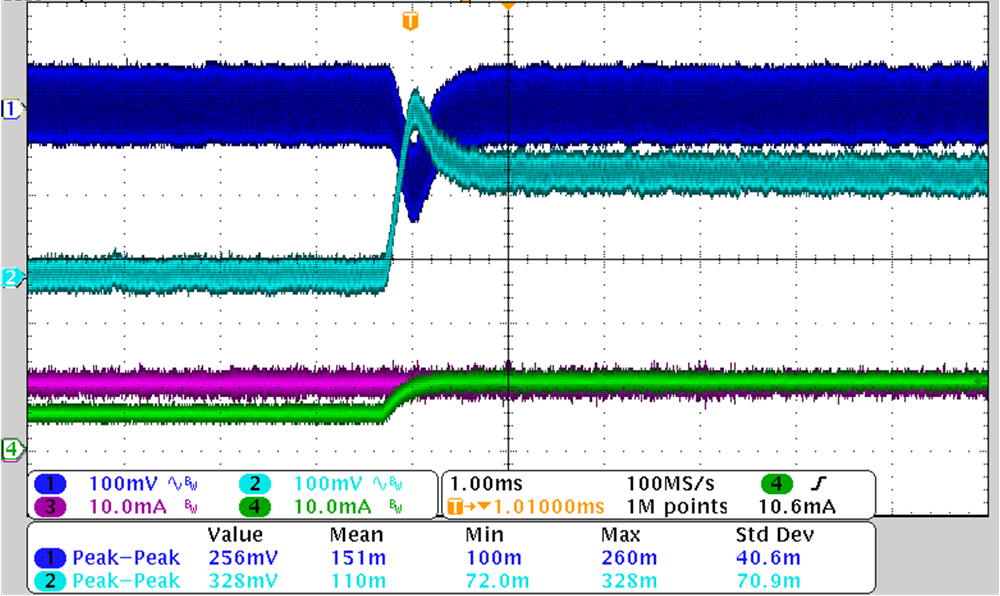
CH1: VOUT1, CH2: VOUT2, CH3: IOUT1, CH4: –IOUT2
Figure 3-9 12-V Input, 15 V, 10 mA, –15 V, 5 mA to 10 mA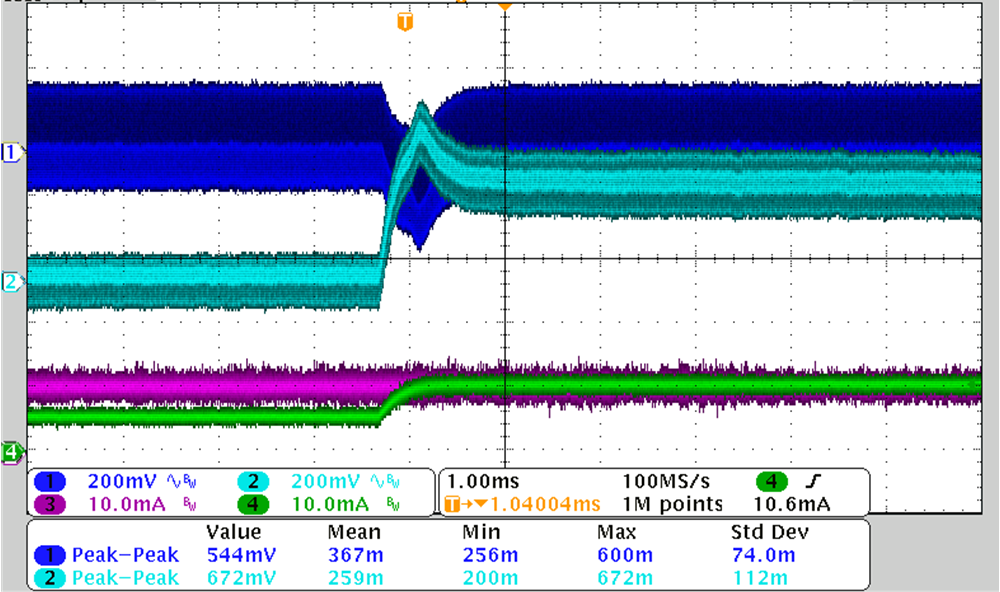
CH1: VOUT1, CH2: VOUT2, CH3: IOUT1, CH4: –IOUT2
Figure 3-10 12-V Input, 75 V, 10 mA, –75 V, 5 mA to 10 mA