SLVAFG6B December 2022 – November 2024 TPS25762-Q1 , TPS25763-Q1 , TPS25772-Q1
5.2 Fair Share Power Policy Example
This section provides examples of power sharing between two ports configured with Fair Share Power Policy and when connected to Port Partners that are Good Sinks. When Port Partners are Good Sinks, the power distribution is the same whether Blind Sink Support is enabled or disabled. Table 5-10 shows the SPM Engine parameters used in this section's example. The FSP Parameters shown in Table 5-4 are used in the power distribution method and to achieve FSP between two Sinks.
| SPM Engine Parameters | Configuration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| System Max Power | 75W | Total system power capacity allocated for Port A and B |
| Port A Max Power | 60W | Maximum Port A Power |
| Port B Max Power | 60W | Maximum Port B Power |
| Port A Min Power | 15W | Minimum Port A power |
| Port B Min Power | 15W | Minimum Port B power |
| Shared Mode | Fair Share Power Policy without Blind Sink Support | Port Min Power is guaranteed for each port and remaining power is intelligently distributed |
| Fair Share Power Policy Parameters | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Equally Divided Shared Power | (75-(15+15))/2=22.5W | Equally shared power for each port that can be distributed: (Total VBUS power – Sum of Port A and B's Min Power)/Total number of ports |
| Per Port Guaranteed FSP | 15+22.5W=37.5W | Guaranteed Shared Power for each port: Equally Divided Shared Power + Port Min Power |
Four example scenarios of Fair Share Power Policy power distribution are concisely summarized in Table 5-5.
| Port A | Port B | |
|---|---|---|
| Initially Allocated | 15W | 15W |
| Scenario 1: Port A connects to a Sink that requires 60W. Port B is unconnected. | ||
| Power Required by Sink | 60W | |
| Power Distributed to Sink | 60W | |
| Scenario 2: Port B connects to a Sink that also requires 60W Sink Cap. | ||
| Power Required by Sink | 60W | 60W |
| Power Distributed to Sinks(1) | 37.5W | 37.5W |
| Scenario 3: Port B changes the requirement to 15W. | ||
| Power Required by Sink | 60W | 15W |
| Power Distributed to Sinks(2) | 60W | 15W |
| Scenario 4: Port B changes the requirement to 25W. | ||
| Power Required by Sink | 60W | 25W |
| Power Distributed to Sinks(3) | 50W | 25W |
Figure 5-3 and Figure 5-4 show the PD negotiation flow following the FSP examples from Scenario 1 and Scenario 2 of Table 5-5, respectively.
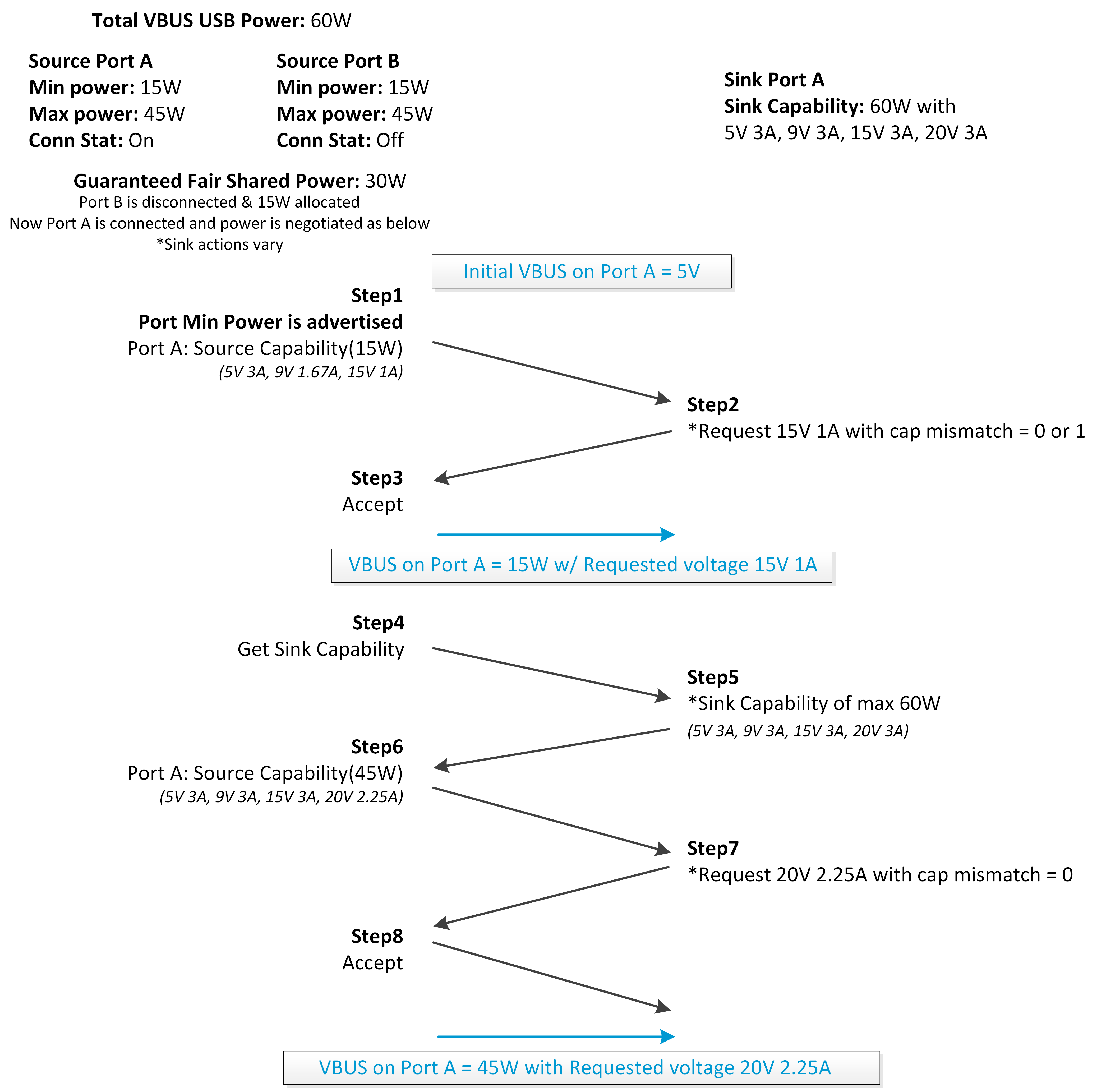 Figure 5-3 FSP Negotiation Flow -
Scenario 1
Figure 5-3 FSP Negotiation Flow -
Scenario 1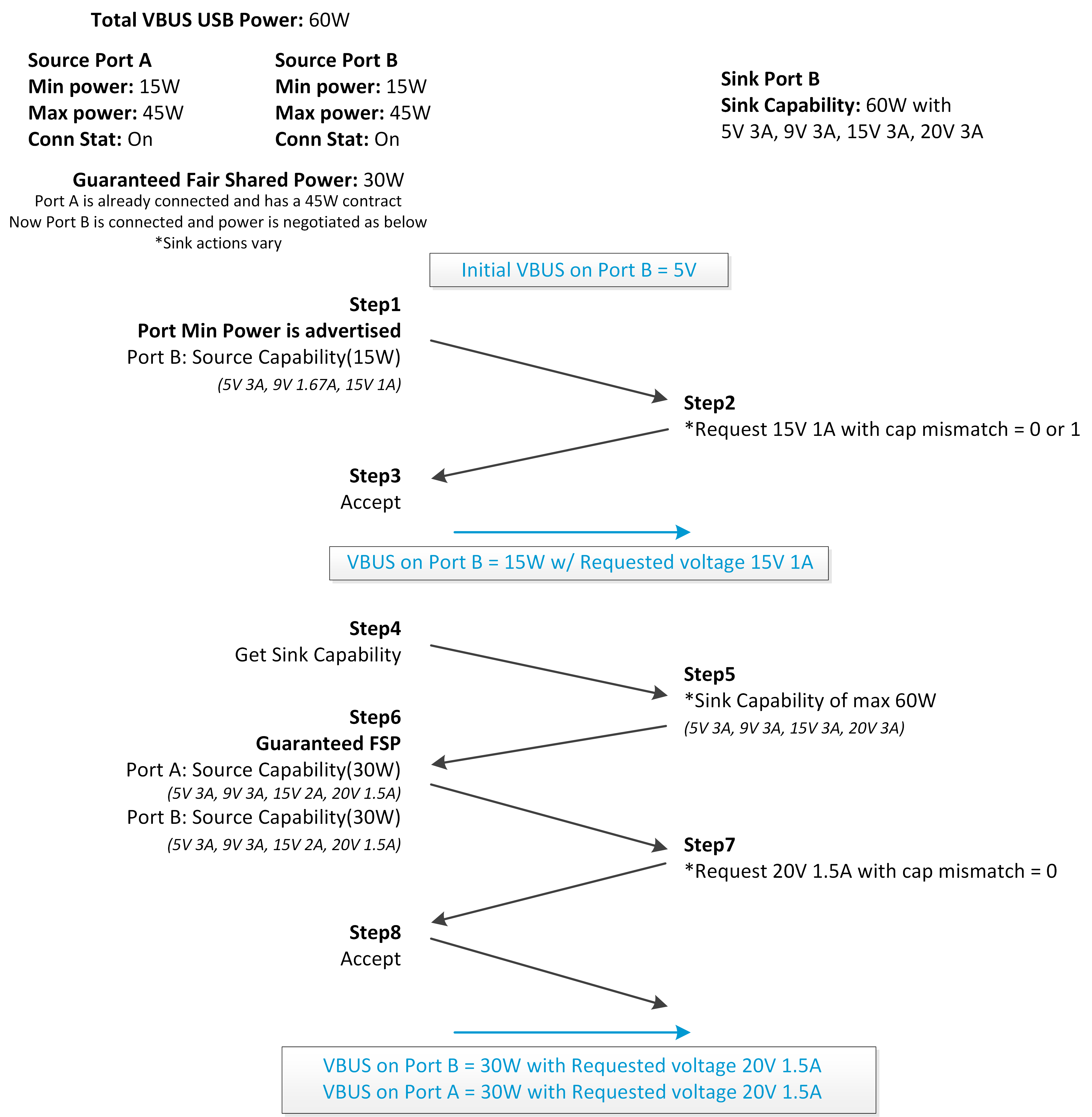 Figure 5-4 FSP Negotiation Flow -
Scenario 2
Figure 5-4 FSP Negotiation Flow -
Scenario 2