SLVSC16B August 2013 – July 2016
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
Buck Controllers: Normal Mode PWM Operation
- 7.4.1.1 Frequency Selection and External Synchronization
- 7.4.1.2 Enable Inputs
- 7.4.1.3 Feedback Inputs
- 7.4.1.4 Soft-Start Inputs
- 7.4.1.5 Current-Mode Operation
- 7.4.1.6 Current Sensing and Current Limit With Foldback
- 7.4.1.7 Slope Compensation
- 7.4.1.8 Power-Good Outputs and Filter Delays
- 7.4.1.9 Light-Load PFM Mode
- 7.4.1
Buck Controllers: Normal Mode PWM Operation
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Boost Component Selection
- 8.2.2.2 Boost Maximum Input Current IIN_MAX
- 8.2.2.3 Boost Inductor Selection, L
- 8.2.2.4 Inductor Ripple Current, IRIPPLE
- 8.2.2.5 Peak Current in Low-Side FET, IPEAK
- 8.2.2.6 Right Half-Plane Zero RHP Frequency, fRHP
- 8.2.2.7 Output Capacitor, COUTx
- 8.2.2.8 Bandwidth of Boost Converter, fC
- 8.2.2.9 Output Ripple Voltage Due to Load Transients, ∆VOUTx
- 8.2.2.10 Selection of Components for Type II Compensation
- 8.2.2.11 Input Capacitor, CIN
- 8.2.2.12 Output Schottky Diode D1 Selection
- 8.2.2.13 Low-Side MOSFET (BOT_SW3)
- 8.2.2.14 BuckA Component Selection
- 8.2.2.15 Inductor Selection L
- 8.2.2.16 Inductor Ripple Current IRIPPLE
- 8.2.2.17 Output Capacitor COUTA
- 8.2.2.18 Bandwidth of Buck Converter fC
- 8.2.2.19 Selection of Components for Type II Compensation
- 8.2.2.20 Resistor Divider Selection for Setting VOUTA Voltage
- 8.2.2.21 BuckB Component Selection
- 8.2.2.22 Resistor Divider Selection for Setting VOUT Voltage
- 8.2.2.23 BuckX High-Side and Low-Side N-Channel MOSFETs
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 System Examples
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
10.1.1 Boost Converter
- The path formed from the input capacitor to the inductor and BOT_SW3 with the low-side current-sense resistor must have short leads and PC trace lengths. The same applies for the trace from the inductor to Schottky diode D1 to the COUT1 capacitor. Connect the negative terminal of the input capacitor and the negative terminal of the sense resistor together with short trace lengths.
- The overcurrent-sensing shunt resistor requires noise filtering, and the filter capacitor must be close to the IC pin.
10.1.2 Buck Converter
- Connect the drain of TOP_SW1 and TOP_SW2 together with the positive terminal of input capacitor COUT1. The trace length between these terminals must be short.
- Connect a local decoupling capacitor between the drain of TOP_SWx and the source of BOT_SWx.
- The Kelvin-current sensing for the shunt resistor has traces with minimum spacing, routed in parallel with each other. Place any filtering capacitors for noise near the IC pins.
- The resistor divider for sensing the output voltage connects between the positive terminal of itherespective output capacitor and COUTA or COUTB and the IC signal ground. Do not locate these components and their traces near any switching nodes or high-current traces.
10.1.3 Other Considerations
- Short PGNDx and AGND to the thermal pad. Use a star-ground configuration if connecting to a non-ground plane system. Use tie-ins for the EXTSUP capacitor, compensation-network ground, and voltage-sense feedback ground networks to this star ground.
- Connect a compensation network between the compensation pins and IC signal ground. Connect the oscillator resistor (frequency setting) between the RT pin and IC signal ground. These sensitive circuits must not be located near nodes showing high dv/dt; these include the gate-drive outputs, phase pins, and boost circuits (bootstrap).
- Reduce the surface area of the high-current-carrying loops to a minimum by ensuring optimal component placement. Locate the bypass capacitors as close as possible to the respective power and ground pins.
10.2 Layout Example
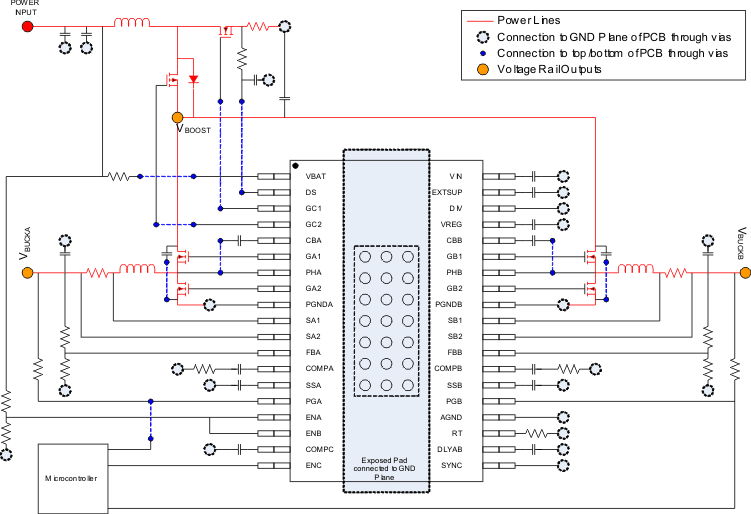 Figure 32. Layout Guidelines Highlighting Critical Paths
Figure 32. Layout Guidelines Highlighting Critical Paths
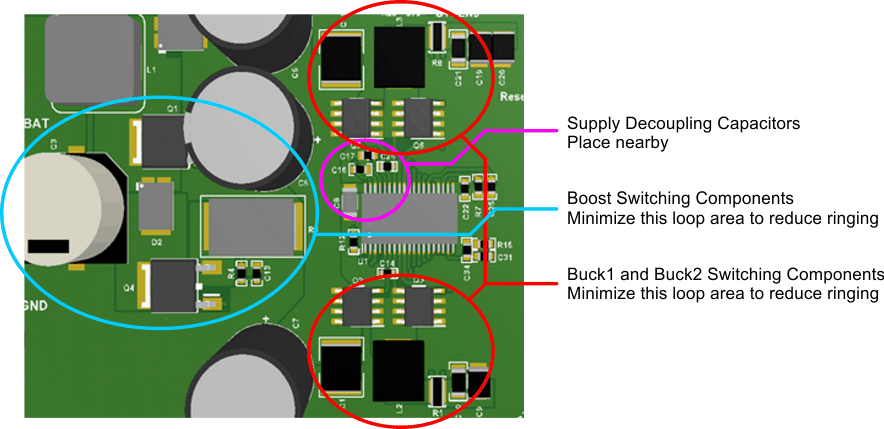 Figure 33. Layout Example and Recommendations
Figure 33. Layout Example and Recommendations
10.3 Power Dissipation Derating Profile, 38-Pin HTTSOP PowerPAD™ Package
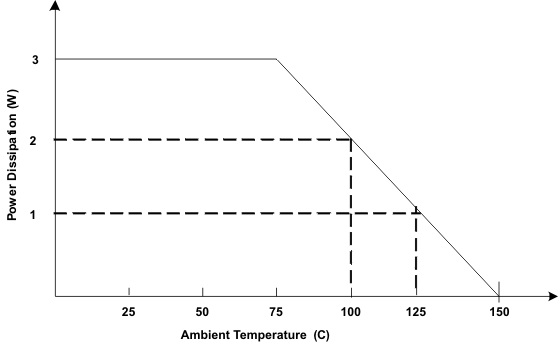 Figure 34. Derating Profile for Power Dissipation Based on High-K JEDEC PCB
Figure 34. Derating Profile for Power Dissipation Based on High-K JEDEC PCB