SLVSDV6C November 2017 – November 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.3 Feed-forward Capacitor Selection
A feedforward capacitor (CFF) is recommended in parallel with R1. Equation 5 calculates the CFF value. For the recommended 100k value for R2, a 120 pF feed forward capacitor is used.
space
Equation 5. 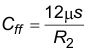
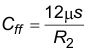
space
Figure 47 and Figure 48 show the results of a frequency domain analysis for both use cases, with and without a feed-forward capacitor. The larger unity gain frequency, caused by the feed forward capacitor, results in a significant improvement of the transient response.
space