SLVSEX0A March 2019 – July 2019
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3 Input and Output Capacitor Selection
The output capacitor is mainly selected to meet the requirements for output ripple and loop stability. This ripple voltage is related to the capacitor’s capacitance and its equivalent series resistance (ESR). Assuming a ceramic capacitor with zero ESR, the minimum capacitance needed for a given ripple can be calculated by:
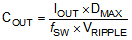
where
- DMAX = maximum switching duty cycle
- VRIPPLE = peak to peak output voltage ripple
The ESR impact on the output ripple must be considered if tantalum or aluminum electrolytic capacitors are used.
Take care when evaluating the derating of a ceramic capacitor under DC bias, aging, and AC signal. For example, the DC bias can significantly reduce capacitance. A ceramic capacitor can lose more than 50% of its capacitance at its rated voltage. Therefore, always leave margin on the voltage rating to ensure adequate capacitance at the required output voltage.
TI recommends using the output capacitor with effective capacitance in the range of 3.3 µF to 10 µF for 600-kHz configuration. TI also recommends placing a small 1 µF capacitor right across the rectifier diode cathode to the GND pin of the TLV61048 to reduce the high RMS current loop's inductance. The output capacitor affects the small signal control loop stability of the boost regulator. If the output capacitor is below the range, the boost regulator can potentially become unstable. Increasing the output capacitor makes the output voltage ripple smaller in PWM mode. Table 3 lists the recommended capacitor for the TLV61048.
Table 3. Recommended Output Capacitors for the TLV61048
| PART NUMBER | COUT (µF) | RATING | PACKAGE | VENDOR(1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMK316BLD106KL | 10 | 25 V, X5R | 1206 | Taiyo Yuden |
| CC1206KKX5R8BB106 | 10 | 25 V, X5R | 1206 | Yageo |
For input capacitor, a ceramic capacitor with more than 1 µF is enough for most applications.