SLVU277A January 2009 – October 2021 TPS54232
2.9 Powering Up
The start-up waveforms are shown in Figure 2-9 and Figure 2-10. In Figure 2-9, the top trace shows VOUT , and the bottom trace shows VIN. In Figure 2-10 , the top trace shows VOUT whereas the bottom trace shows the slow start voltage . In Figure 2-10, the input voltage is initially applied and the output is inhibited by using a jumper at J2 to tie EN to GND. When the jumper is removed, EN is released. When the EN voltage reaches the enable-threshold voltage of 1.25 V, the start-up sequence begins and the output ramps up at the externally set rate toward the set value of 2.5 V. The input voltage for these plots is 12 V and there is no load.
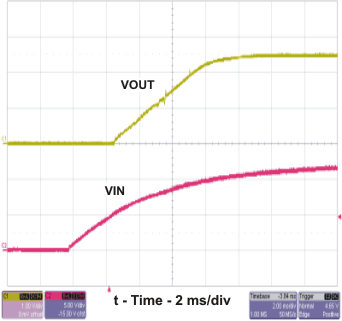 Figure 2-9 TPS54232EVM-415 Start-Up Relative to VIN
Figure 2-9 TPS54232EVM-415 Start-Up Relative to VIN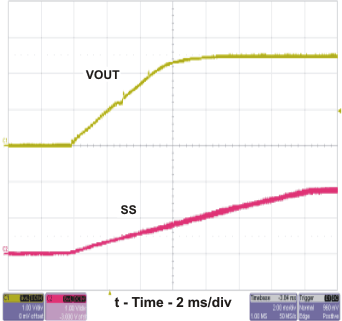 Figure 2-10 TPS54232EVM-415 Start-Up Relative to Enable
Figure 2-10 TPS54232EVM-415 Start-Up Relative to Enable