SLVUB56A July 2017 – September 2021 TPS54424
2.2 Efficiency
Figure 2-1 shows the efficiency for the TPS54424EVM-779 at an ambient temperature of 25°C. The efficiency of this EVM peaks at a load current of about 2 A and then decreases as the load current increases toward full load.
Figure 2-2 shows the efficiency for the TPS54424EVM-779 using a semi-log scale to more easily show efficiency at lower output currents. The TPS54424 operates in continuous conduction mode at light loads in order to keep a fixed frequency and this results in lower efficiency at lower output currents.
Figure 2-3 shows the efficiency for the TPS54424EVM-779 versus input voltage with a fixed load.
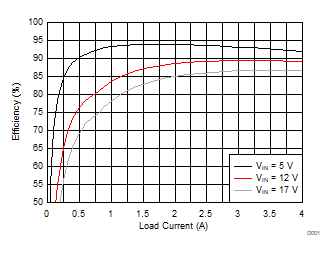 Figure 2-1 TPS54424EVM-779 Efficiency
Figure 2-1 TPS54424EVM-779 Efficiency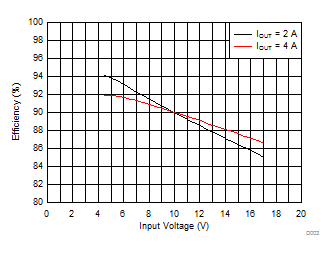 Figure 2-3 TPS54424EVM-779 Efficiency
Figure 2-3 TPS54424EVM-779 Efficiency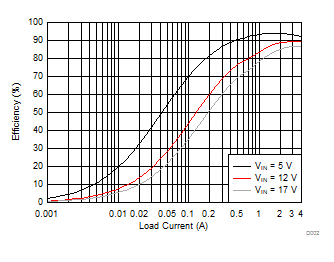 Figure 2-2 TPS54424EVM-779 Low Current Efficiency
Figure 2-2 TPS54424EVM-779 Low Current EfficiencyThe efficiency may be lower at higher ambient temperatures, due to temperature variation in the drain-to-source resistance of the internal MOSFETs.