SLYA065 October 2022 TMAG5328
4.1 Conducting Diagnostic Tests With TMAG5328EVM and Head-On Linear Displacement 3D Print
This diagnostic technique was tested on the TMAG5328EVM by loading firmware on the EVM's microcontroller that would generate a timer interrupt every 100 ms. In the firmware, the DAC produces a square wave that alternates between 0.68 V (the low state) and 1.04 V (the high state), which creates a BRP,HIGH value of 12 mT and a BOP,LOW value of 8.5 mT. The head-on linear displacement attachment was connected to the TMAG5328 and configured so that the TMAG5328 sees a magnetic field between 8.5 mT to 12 mT.
In the timer interrupt service routine, the TMAG5328 output is first read. If the DAC output voltage is at 1.04 V, the TMAG5328 OUT pin should be high. If the DAC output voltage is currently at 0.68 V, the TMAG5328 OUT pin should be low. If the TMAG5328 OUT pin is not in the correct state, a fault has occurred, which is logged by the microcontroller.
After checking the state of the TMAG5328 OUT pin, the microcontroller configures the DAC to switch to 1.04 V if the TMAG5328 OUT pin is currently at 0.68 V or switch to 0.68 V if the TMAG5328 OUT is currently at 1.04 V. The TMAG5328 output is checked at the next timer interrupt, which gives the TMAG5328 enough time to update its BOP.
Figure 4-2 below shows the expected waveform on the TMAG5328 OUT pin when no faults are present. Due to the OUT pin changing states, the LED connected to the TMAG5328EVM would blink at a frequency equal to the frequency of the DAC square wave (approximately 5 Hz).
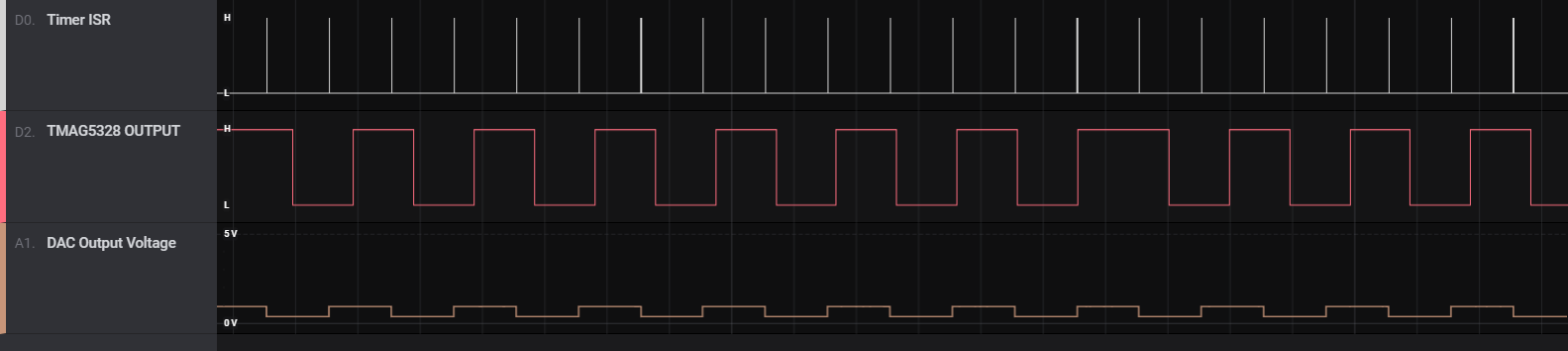 Figure 4-2 Logic Analyzer Screenshot of TMAG5328 OUT Pin
When No Faults Present During Diagnostic Testing.
Figure 4-2 Logic Analyzer Screenshot of TMAG5328 OUT Pin
When No Faults Present During Diagnostic Testing.