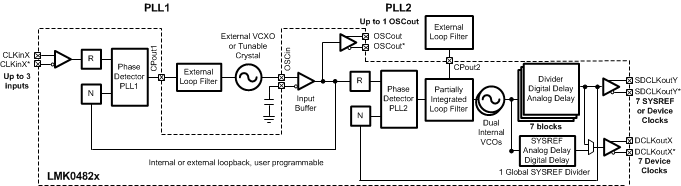
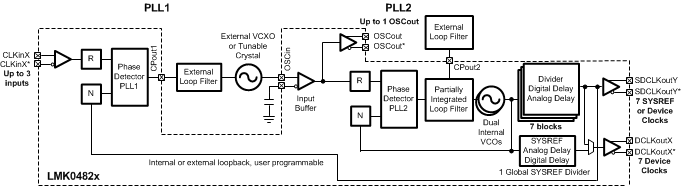
SNAS605AS March 2013 – May 2020 LMK04821 , LMK04826 , LMK04828
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1
Overview
- 9.1.1 Jitter Cleaning
- 9.1.2 JEDEC JESD204B Support
- 9.1.3 Three PLL1 Redundant Reference Inputs
- 9.1.4 VCXO/Crystal Buffered Output
- 9.1.5 Frequency Holdover
- 9.1.6 PLL2 Integrated Loop Filter Poles
- 9.1.7 Internal VCOs
- 9.1.8 External VCO Mode
- 9.1.9 Clock Distribution
- 9.1.10 Zero-Delay
- 9.1.11 Status Pins
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6 Register Maps
- 9.7
Device Register Descriptions
- 9.7.1 System Functions
- 9.7.2
(0x100 - 0x138) Device Clock and SYSREF Clock Output Controls
- 9.7.2.1 CLKoutX_Y_ODL, CLKoutX_Y_IDL, DCLKoutX_DIV
- 9.7.2.2 DCLKoutX_DDLY_CNTH, DCLKoutX_DDLY_CNTL
- 9.7.2.3 DCLKoutX_ADLY, DCLKoutX_ADLY_MUX, DCLKout_MUX
- 9.7.2.4 DCLKoutX_HS, SDCLKoutY_MUX, SDCLKoutY_DDLY, SDCLKoutY_HS
- 9.7.2.5 SDCLKoutY_ADLY_EN, SDCLKoutY_ADLY
- 9.7.2.6 DCLKoutX_DDLY_PD, DCLKoutX_HSg_PD, DCLKout_ADLYg_PD, DCLKout_ADLY_PD, DCLKoutX_Y_PD, SDCLKoutY_DIS_MODE, SDCLKoutY_PD
- 9.7.2.7 SDCLKoutY_POL, SDCLKoutY_FMT, DCLKoutX_POL, DCLKoutX_FMT
- 9.7.3
SYSREF, SYNC, and Device Config
- 9.7.3.1 VCO_MUX, OSCout_MUX, OSCout_FMT
- 9.7.3.2 SYSREF_CLKin0_MUX, SYSREF_MUX
- 9.7.3.3 SYSREF_DIV[12:8], SYSREF_DIV[7:0]
- 9.7.3.4 SYSREF_DDLY[12:8], SYSREF_DDLY[7:0]
- 9.7.3.5 SYSREF_PULSE_CNT
- 9.7.3.6 PLL2_NCLK_MUX, PLL1_NCLK_MUX, FB_MUX, FB_MUX_EN
- 9.7.3.7 PLL1_PD, VCO_LDO_PD, VCO_PD, OSCin_PD, SYSREF_GBL_PD, SYSREF_PD, SYSREF_DDLY_PD, SYSREF_PLSR_PD
- 9.7.3.8 DDLYdSYSREF_EN, DDLYdX_EN
- 9.7.3.9 DDLYd_STEP_CNT
- 9.7.3.10 SYSREF_CLR, SYNC_1SHOT_EN, SYNC_POL, SYNC_EN, SYNC_PLL2_DLD, SYNC_PLL1_DLD, SYNC_MODE
- 9.7.3.11 SYNC_DISSYSREF, SYNC_DISX
- 9.7.3.12 Fixed Registers (0x145, 0x171 - 0x172)
- 9.7.4 (0x146 - 0x149) CLKin Control
- 9.7.5 RESET_MUX, RESET_TYPE
- 9.7.6
(0x14B - 0x152) Holdover
- 9.7.6.1 LOS_TIMEOUT, LOS_EN, TRACK_EN, HOLDOVER_FORCE, MAN_DAC_EN, MAN_DAC[9:8]
- 9.7.6.2 MAN_DAC[9:8], MAN_DAC[7:0]
- 9.7.6.3 DAC_TRIP_LOW
- 9.7.6.4 DAC_CLK_MULT, DAC_TRIP_HIGH
- 9.7.6.5 DAC_CLK_CNTR
- 9.7.6.6 CLKin_OVERRIDE, HOLDOVER_PLL1_DET, HOLDOVER_LOS_DET, HOLDOVER_VTUNE_DET, HOLDOVER_HITLESS_SWITCH, HOLDOVER_EN
- 9.7.6.7 HOLDOVER_DLD_CNT[13:8], HOLDOVER_DLD_CNT[7:0]
- 9.7.7
(0x153 - 0x15F) PLL1 Configuration
- 9.7.7.1 CLKin0_R[13:8], CLKin0_R[7:0]
- 9.7.7.2 CLKin1_R[13:8], CLKin1_R[7:0]
- 9.7.7.3 CLKin2_R[13:8], CLKin2_R[7:0]
- 9.7.7.4 PLL1_N
- 9.7.7.5 PLL1_WND_SIZE, PLL1_CP_TRI, PLL1_CP_POL, PLL1_CP_GAIN
- 9.7.7.6 PLL1_DLD_CNT[13:8], PLL1_DLD_CNT[7:0]
- 9.7.7.7 PLL1_R_DLY, PLL1_N_DLY
- 9.7.7.8 PLL1_LD_MUX, PLL1_LD_TYPE
- 9.7.8
(0x160 - 0x16E) PLL2 Configuration
- 9.7.8.1 PLL2_R[11:8], PLL2_R[7:0]
- 9.7.8.2 PLL2_P, OSCin_FREQ, PLL2_XTAL_EN, PLL2_REF_2X_EN
- 9.7.8.3 PLL2_N_CAL
- 9.7.8.4 PLL2_FCAL_DIS, PLL2_N
- 9.7.8.5 PLL2_WND_SIZE, PLL2_CP_GAIN, PLL2_CP_POL, PLL2_CP_TRI
- 9.7.8.6 SYSREF_REQ_EN, PLL2_DLD_CNT
- 9.7.8.7 PLL2_LF_R4, PLL2_LF_R3
- 9.7.8.8 PLL2_LF_C4, PLL2_LF_C3
- 9.7.8.9 PLL2_LD_MUX, PLL2_LD_TYPE
- 9.7.9
(0x16F - 0x1FFF) Misc Registers
- 9.7.9.1 PLL2_PRE_PD, PLL2_PD
- 9.7.9.2 VCO1_DIV
- 9.7.9.3 OPT_REG_1
- 9.7.9.4 OPT_REG_2
- 9.7.9.5 RB_PLL1_LD_LOST, RB_PLL1_LD, CLR_PLL1_LD_LOST
- 9.7.9.6 RB_PLL2_LD_LOST, RB_PLL2_LD, CLR_PLL2_LD_LOST
- 9.7.9.7 RB_DAC_VALUE(MSB), RB_CLKinX_SEL, RB_CLKinX_LOS
- 9.7.9.8 RB_DAC_VALUE
- 9.7.9.9 RB_HOLDOVER
- 9.7.9.10 SPI_LOCK
- 9.1
Overview
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.4.2 Zero-Delay Dual PLL
Figure 19 illustrates the use case of cascaded zero-delay dual-loop mode. This configuration differs from dual-loop mode Figure 18 in that the feedback for PLL2 is driven by a clock output instead of the VCO output. Figure 20 illustrates the use case of nested zero-delay dual-loop mode. This configuration is similar to the dual PLL in Dual PLL, except that the feedback to the first PLL is driven by a clock output. This causes the clock outputs to have deterministic phase relationship with the clock input. Because all the clock outputs can be synchronized together, all the clock outputs can share the same deterministic phase relationship with the clock input signal. The feedback to PLL1 can be connected internally as shown using CLKout6, CLKout8, SYSREF, or externally using FBCLKin (CLKin1).
It is also possible to use an external VCO in place of the PLL2 internal VCO; however, because CLKin1 must be used as Fin for the external VCO, it is unavailable as a reference to PLL1 or as external zero-delay feedback.
LMK04821 includes VCO1 divider on VCO1 output.
Table 6. Cascaded Zero-Delay Dual-Loop Mode Register Configuration
| FIELD | REGISTER
ADDRESS |
FUNCTION | VALUE | SELECTED VALUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLL1_NCLK_MUX | 0x13F | Selects the input to the PLL1 N divider | 0 | OSCin |
| PLL2_NCLK_MUX | 0x13F | Selects the input to the PLL2 N divider | 1 | Feedback mux |
| FB_MUX_EN | 0x13F | Enables the feedback mux. | 1 | Feedback mux enabled |
| FB_MUX | 0x13F | Selects the output of the feedback mux. | 0, 1, or 2 | Select between DCLKout6, DCLKout8, SYSREF |
| OSCin_PD | 0x140 | Powers down the OSCin port. | 0 | Powered up |
| CLKin0_OUT_MUX | 0x147 | Selects where the output of CLKin0 is directed. | 0 | PLL1 |
| CLKin1_OUT_MUX | 0x147 | Selects where the output of CLKin1 is directed. | 0 or 2 | Fin or PLL1 |
| VCO_MUX | 0x138 | Selects the VCO 0, 1 or an external VCO | 0 or 1 | VCO 0 or VCO 1 |
LMK04821 includes the VCO1 divider on the VCO1 output.
Table 7 illustrates nested zero-delay mode. This is the same as cascaded, except the clock out feedback is to PLL1. The CLKin and CLKout have the same deterministic phase relationship, but the VCXO's phase is not deterministic to the CLKin or CLKouts.
Table 7. Nested Zero-Delay Dual-Loop Mode Register Configuration
| FIELD | REGISTER
ADDRESS |
FUNCTION | VALUE | SELECTED VALUE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLL1_NCLK_MUX | 0x13F | Selects the input to the PLL1 N divider | 1 | Feedback mux |
| PLL2_NCLK_MUX | 0x13F | Selects the input to the PLL2 N divider | 0 | PLL2 P |
| FB_MUX_EN | 0x13F | Enables the feedback mux. | 1 | Enabled |
| FB_MUX | 0x13F | Selects the output of the feedback mux. | 0, 1, or 2 | Select between DCLKout6, DCLKout8, SYSREF |
| OSCin_PD | 0x140 | Powers down the OSCin port. | 0 | Powered up |
| CLKin0_OUT_MUX | 0x147 | Selects where the output of CLKin0 is directed. | 2 | PLL1 |
| CLKin1_OUT_MUX | 0x147 | Selects where the output of CLKin1 is directed. | 0 or 2 | Fin or PLL1 |
| VCO_MUX | 0x138 | Selects the VCO 0, 1 or an external VCO | 0 or 1 | VCO 0 or VCO 1 |