SNIA054 January 2023 TMP61
2 Problems of NTC Thermistors in Air Conditioners
In air conditioners, temperature sensors are usually made in the form of probes for temperature detection convenience. NTC thermistor is made of metals and their oxides, with low cost and good stability, and is widely used in air conditioning systems, but it also has some problems:
- Non-linearity leads to material
management problems
The relationship between the resistance of the NTC and the temperature is nonlinear, resulting in low resistance resolution in high temperature range. Therefore, NTCs with different resistance are suitable for different temperature ranges. In the air-conditioning system, the temperature ranges are different for evaporator coil, condenser coil and the compressor exhaust, in order to ensure higher temperature resolution for all above locations, their NTC thermistors should be different. Figure 2-1 is a diagram of the R-T relationship of NTCs with different resistance. This also complicates material management as multiple types of NTC thermistors are required.
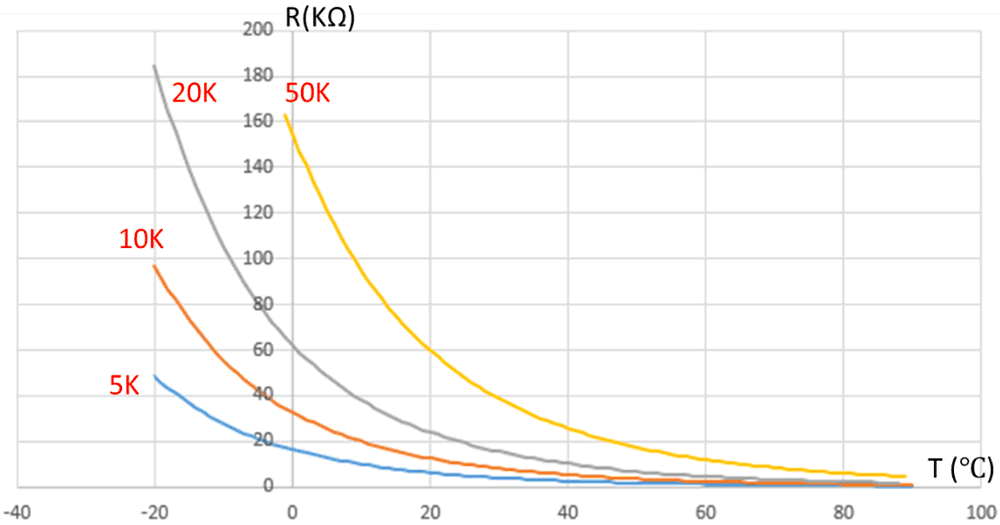 Figure 2-1 Diagram of NTC R-T Relationship
With Different Resistance Values
Figure 2-1 Diagram of NTC R-T Relationship
With Different Resistance Values - Slow response time
NTC thermistor has slow response due to their material, but fast response is very important for good system performance. For example, when the air conditioner is refrigerating, the sensor detects that the temperature of the evaporator coil is 3°C, the actual temperature may already be lower than 3°C. The lag of temperature control increases the working time of the air conditioner compressor, and even causes the evaporator to frost. Therefore, an excessively slow response time increases the energy consumption and reduces the cooling efficiency of the air conditioner.
- Complex software processing
The traditional NTC thermistor uses R-T look-up table and interpolation fitting to estimate the temperature corresponding to different resistance. The R-T look-up table occupies the ROM space of the MCU. However, each NTCs require a corresponding R-T tables, resulting in the occupation of more MCU ROM resources. To save some ROM resources, the interval of the R-T table for interpolation fitting is usually 1°C, which reduces the temperature detection accuracy.
- NTC resistance tolerance and drift
The resistance tolerance of conventional NTC thermistors away from 25°C is usually much larger than specified in the device-specific data sheet, and in some cases the resistance tolerance can be increased from ±1% of 25°C to ±4% of – 40 ~150°C. In addition, due to the long life of the air-conditioning system and the large drift of the NTC thermistor, system temperature detection error will further increase for long-term operation.