SNIU028D February 2016 – September 2020 UCD3138 , UCD3138064 , UCD3138064A , UCD3138128 , UCD3138A , UCD3138A64
- 1 Introduction
-
2 Digital Pulse Width Modulator (DPWM)
- 2.1 DPWM Block Diagram
- 2.2 Introduction to DPWM (DPWM Multi-Mode, Open Loop)
- 2.3 DPWM Normal Mode
- 2.4 DPWM Phase Shift Mode
- 2.5 DPWM Multiple Output Mode (Multi Mode)
- 2.6 DPWM Resonant Mode
- 2.7 Triangular Mode
- 2.8 DPWM Leading Edge Mode
- 2.9 Sync FET Ramp and IDE Calculation
- 2.10 Automatic Mode Switching
- 2.11 DPWMC, Edge Generation, IntraMax
- 2.12 Time Resolution of Various DPWM Registers
- 2.13 PWM Counter and Clocks
- 2.14 DPWM Registers - Overview
- 2.15
DPWM Control Register 0 (DPWMCTRL0)
- 2.15.1 DPWM Auto Config Mid and Max Registers
- 2.15.2 Intra Mux
- 2.15.3 Cycle by Cycle Current Limit Enable
- 2.15.4 Multi Mode On/Off
- 2.15.5 Minimum Duty Mode
- 2.15.6 Master Sync Control Select
- 2.15.7 Master Sync Slave Enable
- 2.15.8 D Enable
- 2.15.9 Resonant Mode Fixed Duty Enable
- 2.15.10 DPWM A and B Fault Priority
- 2.15.11 Blank Enable
- 2.15.12 DPWM Mode
- 2.15.13 DPWM Invert
- 2.15.14 1.15.14 Filter Enable (CLA_EN)
- 2.15.15 DPWM Enable
- 2.16
DPWM Control Register 1
- 2.16.1 Period Counter Preset Enable
- 2.16.2 Sync FET Ramp Enable
- 2.16.3 Burst Mode Enable
- 2.16.4 Current/Flux Balancing Duty Adjust
- 2.16.5 1.16.5 Sync Out Divisor Selection
- 2.16.6 FIlter Scale
- 2.16.7 External Sync Enable
- 2.16.8 Cycle By Cycle B Side Active Enable
- 2.16.9 Auto Mode Switching Enable
- 2.16.10 1.16.10 Event Update Select
- 2.16.11 Check Override
- 2.16.12 Global Period Enable
- 2.16.13 Using DPWM Pins as General Purpose I/O
- 2.16.14 High Resolution enable/disable
- 2.16.15 Asynchronous Protection Disable
- 2.16.16 Single Frame Enable
- 2.17 DPWM Control Register 2
- 2.18 Period and Event Registers
- 2.19 Phase Trigger Registers
- 2.20 Cycle Adjust Registers
- 2.21 Resonant Duty Register
- 2.22 DPWM Fault Control Register
- 2.23 DPWM Overflow Register
- 2.24 DPWM Interrupt Register
- 2.25 DPWM Counter Preset Register
- 2.26 Blanking Registers
- 2.27 DPWM Adaptive Sample Register
- 2.28 DPWM Fault Status Register
- 2.29 DPWM Auto Switch Registers
- 2.30 DPWM Edge PWM Generation Register
- 2.31
DPWM 0-3 Registers Reference
- 2.31.1 DPWM Control Register 0 (DPWMCTRL0)
- 2.31.2 DPWM Control Register 1 (DPWMCTRL1)
- 2.31.3 DPWM Control Register 2 (DPWMCTRL2)
- 2.31.4 DPWM Period Register (DPWMPRD)
- 2.31.5 DPWM Event 1 Register (DPWMEV1)
- 2.31.6 DPWM Event 2 Register (DPWMEV2)
- 2.31.7 DPWM Event 3 Register (DPWMEV3)
- 2.31.8 DPWM Event 4 Register (DPWMEV4)
- 2.31.9 DPWM Sample Trigger 1 Register (DPWMSAMPTRIG1)
- 2.31.10 DPWM Sample Trigger 2 Register (DPWMSAMPTRIG2)
- 2.31.11 DPWM Phase Trigger Register (DPWMPHASETRIG)
- 2.31.12 DPWM Cycle Adjust A Register (DPWMCYCADJA)
- 2.31.13 DPWM Cycle Adjust B Register (DPWMCYCADJB)
- 2.31.14 DPWM Resonant Duty Register (DPWMRESDUTY)
- 2.31.15 DPWM Fault Control Register (DPWMFLTCTRL)
- 2.31.16 DPWM Overflow Register (DPWMOVERFLOW)
- 2.31.17 DPWM Interrupt Register (DPWMINT)
- 2.31.18 DPWM Counter Preset Register (DPWMCNTPRE)
- 2.31.19 DPWM Blanking A Begin Register (DPWMBLKABEG)
- 2.31.20 DPWM Blanking A End Register (DPWMBLKAEND)
- 2.31.21 DPWM Blanking B Begin Register (DPWMBLKBBEG)
- 2.31.22 DPWM Blanking B End Register (DPWMBLKBEND)
- 2.31.23 DPWM Minimum Duty Cycle High Register (DPWMMINDUTYHI)
- 2.31.24 DPWM Minimum Duty Cycle Low Register (DPWMMINDUTYLO)
- 2.31.25 DPWM Adaptive Sample Register (DPWMADAPTIVE)
- 2.31.26 DPWM Fault Status (DPWMFLTSTAT)
- 2.31.27 DPWM Auto Switch High Upper Thresh Register (DPWMAUTOSWHIUPTHRESH)
- 2.31.28 DPWM Auto Switch High Lower Thresh Register (DPWMAUTOSWHILOWTHRESH)
- 2.31.29 DPWM Auto Switch Low Upper Thresh Register (DPWMAUTOSWLOUPTHRESH)
- 2.31.30 DPWM Auto Switch Low Lower Thresh Register (DPWMAUTOSWLOLOWTHRESH)
- 2.31.31 DPWM Auto Config Max Register (DPWMAUTOMAX)
- 2.31.32 DPWM Auto Config Mid Register (DPWMAUTOMID)
- 2.31.33 DPWM Edge PWM Generation Control Register (DPWMEDGEGEN)
- 2.31.34 DPWM Filter Duty Read Register (DPWMFILTERDUTYREAD)
- 2.31.35 DPWM BIST Status Register (DPWMBISTSTAT)
-
3 Front End
- 3.1 Error ADC and Front End Gain
- 3.2 Front End DAC
- 3.3 Ramp Module
- 3.4 Successive Approximation Mode
- 3.5 Absolute Value Without SAR
- 3.6 EADC Modes
- 3.7
Front End Control Registers
- 3.7.1 Ramp Control Register (RAMPCTRL)
- 3.7.2 Ramp Status Register (RAMPSTAT)
- 3.7.3 Ramp Cycle Register (RAMPCYCLE)
- 3.7.4 EADC DAC Value Register (EADCDAC)
- 3.7.5 Ramp DAC Ending Value Register (RAMPDACEND)
- 3.7.6 DAC Step Register (DACSTEP)
- 3.7.7 DAC Saturation Step Register (DACSATSTEP)
- 3.7.8 EADC Trim Register (EADCTRIM) – (For Factory Test Use Only)
- 3.7.9 EADC Control Register (EADCCTRL)
- 3.7.10 Analog Control Register (ACTRL) (For Test Use Only)
- 3.7.11 Pre-Bias Control Register 0 (PREBIASCTRL0)
- 3.7.12 Pre-Bias Control Register 1 (PREBIASCTRL1)
- 3.7.13 SAR Control Register (SARCTRL)
- 3.7.14 SAR Timing Register (SARTIMING)
- 3.7.15 EADC Value Register (EADCVALUE)
- 3.7.16 EADC Raw Value Register (EADCRAWVALUE)
- 3.7.17 DAC Status Register (DACSTAT)
-
4 Filter
- 4.1 Filter Math Details
- 4.2 Filter Status Register
- 4.3
Filter Control Register
- 4.3.1 Filter Enable
- 4.3.2 Use CPU Sample
- 4.3.3 Force Start
- 4.3.4 Kp Off, Kd Off, Ki Off
- 4.3.5 Kd Stall, Ki Stall
- 4.3.6 Nonlinear Mode
- 4.3.7 Output Scaling
- 4.3.8 Output Multiplier Select
- 4.3.9 Switching Period as Output Multiplier
- 4.3.10 KComp as Output Multiplier
- 4.3.11 Feed Forward as Output Multiplier
- 4.3.12 Period Multiplier Select
- 4.3.13 Ki Adder Mode
- 4.4 XN, YN Read and Write Registers
- 4.5 Coefficient Configuration Register
- 4.6 Kp, Ki, and Kd Registers
- 4.7 Alpha Registers
- 4.8 Filter Nonlinear Limit Registers
- 4.9 Clamp Registers
- 4.10 Filter Preset Register
- 4.11
Filter Registers Reference
- 4.11.1 Filter Status Register (FILTERSTATUS)
- 4.11.2 Filter Control Register (FILTERCTRL)
- 4.11.3 CPU XN Register (CPUXN)
- 4.11.4 Filter XN Read Register (FILTERXNREAD)
- 4.11.5 Filter KI_YN Read Register (FILTERKIYNREAD)
- 4.11.6 Filter KD_YN Read Register (FILTERKDYNREAD)
- 4.11.7 Filter YN Read Register (FILTERYNREAD)
- 4.11.8 Coefficient Configuration Register (COEFCONFIG)
- 4.11.9 Filter KP Coefficient 0 Register (FILTERKPCOEF0)
- 4.11.10 Filter KP Coefficient 1 Register (FILTERKPCOEF1)
- 4.11.11 Filter KI Coefficient 0 Register (FILTERKICOEF0)
- 4.11.12 Filter KI Coefficient 1 Register (FILTERKICOEF1)
- 4.11.13 Filter KD Coefficient 0 Register (FILTERKDCOEF0)
- 4.11.14 Filter KD Coefficient 1 Register (FILTERKDCOEF1)
- 4.11.15 Filter KD Alpha Register (FILTERKDALPHA)
- 4.11.16 Filter Nonlinear Limit Register 0 (FILTERNL0)
- 4.11.17 Filter Nonlinear Limit Register 1 (FILTERNL1)
- 4.11.18 Filter Nonlinear Limit Register 2 (FILTERNL2)
- 4.11.19 Filter KI Feedback Clamp High Register (FILTERKICLPHI)
- 4.11.20 Filter KI Feedback Clamp Low Register (FILTERKICLPLO)
- 4.11.21 Filter YN Clamp High Register (FILTERYNCLPHI)
- 4.11.22 Filter YN Clamp Low Register (FILTERYNCLPLO)
- 4.11.23 Filter Output Clamp High Register (FILTEROCLPHI)
- 4.11.24 Filter Output Clamp Low Register (FILTEROCLPLO)
- 4.11.25 Filter Preset Register (FILTERPRESET)
-
5 Loop Mux
- 5.1 Front End Control Muxes (FECTRL0MUX, FECTRL1MUX, FECTRL2MUX)
- 5.2 Sample Trigger Control (SAMPTRIGCTRL)
- 5.3 External DAC Control (EXTDACCTRL)
- 5.4 Filter Mux Register (FILTERMUX)
- 5.5 Filter KComp Registers (FILTERKCOMPx)
- 5.6 DPWM Mux Register (DPWMMUX)
- 5.7 Global Enable Register (GLBEN)
- 5.8 PWM Global Period Register (PWMGLBPRD)
- 5.9 Sync Control (SYNCCTRL)
- 5.10 Light Load (Burst) Mode
- 5.11 Constant Current / Constant Power
- 5.12 Analog Peak Current Mode
- 5.13 Automatic Cycle Adjustment
- 5.14
Loop Mux Registers Reference
- 5.14.1 Front End Control 0 Mux Register (FECTRL0MUX)
- 5.14.2 Front End Control 1 Mux Register (FECTRL1MUX)
- 5.14.3 Front End Control 2 Mux Register (FECTRL2MUX)
- 5.14.4 Sample Trigger Control Register (SAMPTRIGCTRL)
- 5.14.5 External DAC Control Register (EXTDACCTRL)
- 5.14.6 Filter Mux Register (FILTERMUX)
- 5.14.7 Filter KComp A Register (FILTERKCOMPA)
- 5.14.8 Filter KComp B Register (FILTERKCOMPB)
- 5.14.9 DPWM Mux Register (DPWMMUX)
- 5.14.10 Constant Power Control Register (CPCTRL)
- 5.14.11 Constant Power Nominal Threshold Register (CPNOM)
- 5.14.12 Constant Power Max Threshold Register (CPMAX)
- 5.14.13 Constant Power Configuration Register (CPCONFIG)
- 5.14.14 Constant Power Max Power Register (CPMAXPWR)
- 5.14.15 Constant Power Integrator Threshold Register (CPINTTHRESH)
- 5.14.16 Constant Power Firmware Divisor Register (CPFWDIVISOR)
- 5.14.17 Constant Power Status Register (CPSTAT)
- 5.14.18 Cycle Adjustment Control Register (CYCADJCTRL)
- 5.14.19 Cycle Adjustment Limit Register (CYCADJLIM)
- 5.14.20 Cycle Adjustment Status Register (CYCADJSTAT)
- 5.14.21 Global Enable Register (GLBEN)
- 5.14.22 PWM Global Period Register (PWMGLBPRD)
- 5.14.23 Sync Control Register (SYNCCTRL)
- 5.14.24 Light Load Control Register (LLCTRL)
- 5.14.25 Light Load Enable Threshold Register (LLENTHRESH)
- 5.14.26 Light Load Disable Threshold Register (LLDISTHRESH)
- 5.14.27 Peak Current Mode Control Register (PCMCTRL)
- 5.14.28 Analog Peak Current Mode Control Register (APCMCTRL)
- 5.14.29 Loop Mux Test Register (LOOPMUXTEST) (Test Use Only)
-
6 Fault Mux
- 6.1 Analog Comparator Configuration
- 6.2 Analog Comparator Ramp
- 6.3 Digital Comparator Configuration
- 6.4 Fault Pin Configuration
- 6.5 Analog Peak Current
- 6.6 Fault Status Registers
- 6.7 Fault Mux Control Registers
- 6.8 DPWM Fault Action
- 6.9 IDE / DCM Detection Control
- 6.10 Oscillator Failure Detection
- 6.11
Fault Mux Registers Reference
- 6.11.1 Analog Comparator Control 0 Register (ACOMPCTRL0)
- 6.11.2 Analog Comparator Control 1 Register (ACOMPCTRL1)
- 6.11.3 Analog Comparator Control 2 Register (ACOMPCTRL2)
- 6.11.4 Analog Comparator Control 3 Register (ACOMPCTRL3)
- 6.11.5 External Fault Control Register (EXTFAULTCTRL)
- 6.11.6 Fault Mux Interrupt Status Register (FAULTMUXINTSTAT)
- 6.11.7 Fault Mux Raw Status Register (FAULTMUXRAWSTAT)
- 6.11.8 Comparator Ramp Control 0 Register (COMPRAMP0)
- 6.11.9 Digital Comparator Control 0 Register (DCOMPCTRL0)
- 6.11.10 Digital Comparator Control 1 Register (DCOMPCTRL1)
- 6.11.11 Digital Comparator Control 2 Register (DCOMPCTRL2)
- 6.11.12 Digital Comparator Control 3 Register (DCOMPCTRL3)
- 6.11.13 Digital Comparator Counter Status Register (DCOMPCNTSTAT)
- 6.11.14 DPWM 0 Current Limit Control Register (DPWM0CLIM)
- 6.11.15 DPWM 0 Fault AB Detection Register (DPWM0FLTABDET)
- 6.11.16 DPWM 0 Fault Detection Register (DPWM0FAULTDET)
- 6.11.17 DPWM 1 Current Limit Control Register (DPWM1CLIM)
- 6.11.18 DPWM 1 Fault AB Detection Register (DPWM1FLTABDET)
- 6.11.19 DPWM 1 Fault Detection Register (DPWM1FAULTDET)
- 6.11.20 DPWM 2 Current Limit Control Register (DPWM2CLIM)
- 6.11.21 DPWM 2 Fault AB Detection Register (DPWM2FLTABDET)
- 6.11.22 DPWM 2 Fault Detection Register (DPWM2FAULTDET)
- 6.11.23 DPWM 3 Current Limit Control Register (DPWM3CLIM)
- 6.11.24 DPWM 3 Fault AB Detection Register (DPWM3FLTABDET)
- 6.11.25 DPWM 3 Fault Detection Register (DPWM3FAULTDET)
- 6.11.26 HFO Fail Detect Register (HFOFAILDET)
- 6.11.27 LFO Fail Detect Register (LFOFAILDET)
- 6.11.28 IDE Control Register (IDECTRL)
-
7 GIO Module
- 7.1 Fault IO Direction Register (FAULTDIR)
- 7.2 Fault Input Register (FAULTIN)
- 7.3 Fault Output Register (FAULTOUT)
- 7.4 Fault Interrupt Enable Register (FAULTINTENA)
- 7.5 Fault Interrupt Polarity Register (FAULTINTPOL)
- 7.6 Fault Interrupt Pending Register (FAULTINTPEND)
- 7.7 External Interrupt Direction Register (EXTINTDIR)
- 7.8 External Interrupt Input Register (EXTINTIN)
- 7.9 External Interrupt Output Register (EXTINTOUT)
- 7.10 External Interrupt Enable Register (EXTINTENA)
- 7.11 External Interrupt Polarity Register (EXTTINTPOL)
- 7.12 External Interrupt Pending Register (EXTINTPEND)
- 7.13 References
-
8 ADC12 Overview
- 8.1 ADC12 Input Impedance Model
- 8.2 ADC12 Impedance vs. Sampling Frequency Data
- 8.3 Effect of External Capacitance
- 8.4 Channel to Channel Crosstalk
- 8.5 Impedance Roll-Off Due to Crosstalk
- 8.6 ADC12 Control FSM
- 8.7 Conversion
- 8.8 Sequencing
- 8.9 Digital Comparators
- 8.10 ADC Averaging
- 8.11 Temperature Sensor
- 8.12 Temp Sensor Control Register (TEMPSENCTRL)
- 8.13 PMBus Addressing
- 8.14 Dual Sample and Hold
- 8.15 Usage of Sample and Hold Circuitry for High Impedance Measurement
- 8.16 ADC Configuration Examples
- 8.17 Useful C Language Statement Examples
- 8.18
ADC Registers
- 8.18.1 ADC Control Register (ADCCTRL)
- 8.18.2 ADC Status Register (ADCSTAT)
- 8.18.3 ADC Test Control Register (ADCTSTCTRL)
- 8.18.4 ADC Sequence Select Register 0 (ADCSEQSEL0)
- 8.18.5 ADC Sequence Select Register 1 (ADCSEQSEL1)
- 8.18.6 ADC Sequence Select Register 2 (ADCSEQSEL2)
- 8.18.7 ADC Sequence Select Register 3 (ADCSEQSEL3)
- 8.18.8 ADC Result Registers 0-15 (ADCRESULTx, x=0:15)
- 8.18.9 ADC Averaged Result Registers 0-5 (ADCAVGRESULTx, x=0:15)
- 8.18.10 ADC Digital Compare Limits Register 0-5 (ADCCOMPLIMx, x=0:5)
- 8.18.11 ADC Digital Compare Enable Register (ADCCOMPEN)
- 8.18.12 ADC Digital Compare Results Register (ADCCOMPRESULT)
- 8.18.13 ADC Averaging Control Register (ADCAVGCTRL)
-
9 Advanced Power Management Control Functions
- 9.1 Package ID Information
- 9.2 Brownout
- 9.3 Temperature Sensor Control
- 9.4 I/O Mux Control
- 9.5 Current Sharing Control
- 9.6 Temperature Reference
- 9.7 Power Disable Control or (Clock Gating Control)
- 9.8
Miscellaneous Analog Control Registers
- 9.8.1 Package ID Register (PKGID)
- 9.8.2 Brownout Register (BROWNOUT)
- 9.8.3 Temp Sensor Control Register (TEMPSENCTRL)
- 9.8.4 I/O Mux Control Register (IOMUX)
- 9.8.5 Current Sharing Control Register (CSCTRL)
- 9.8.6 Temperature Reference Register (TEMPREF)
- 9.8.7 Power Disable Control Register (PWRDISCTRL)
- 9.9 GPIO Overview
- 9.10 Interaction with a Single Pin
- 9.11 Interaction with Multiple Pins
- 9.12 Registers
- 9.13 Need to Clear HFO_LN_FILTER_EN Bit
-
10PMBus Interface/I2C Interface
- 10.1 PMBus Register Summary
- 10.2 PMBus Slave Mode Initialization
- 10.3
PMBus Slave Mode Command Examples
- 10.3.1 Write Command (Send Byte), No PEC
- 10.3.2 Other Simple Writes with Auto Acknowledge
- 10.3.3 Quick Command Write
- 10.3.4 Writes of 4 Bytes or More With Full Auto Acknowledge
- 10.3.5 Writes with Less than 3 Bytes Auto-Acknowledged
- 10.3.6 Manual Slave Address ACK for Write.
- 10.3.7 Manual Command ACK
- 10.3.8 Read Messages with Full Automation
- 10.3.9 Simple Read of 4 Bytes with Full Automation
- 10.3.10 Simple Read of More than 4 Bytes with Full Automation
- 10.3.11 Quick Command Read
- 10.3.12 Simple Read with Manual Slave Address ACK
- 10.3.13 Write/Read with Repeated Start
- 10.3.14 Automatic PEC Addition
- 10.4 Avoiding Clock Stretching
- 10.5 PMBus Slave Mode Low Level Timing
- 10.6 Effect of MAN_SLAVE_ACK bit on EOM Handling
- 10.7
Master Mode Operation Reference
- 10.7.1 Quick Command
- 10.7.2 Send Byte
- 10.7.3 Receive Byte
- 10.7.4 Write Byte/Word
- 10.7.5 Read Byte/Read Word
- 10.7.6 Process Call
- 10.7.7 Block Write
- 10.7.8 Block Read
- 10.7.9 Block Write-Block Read Process Call
- 10.7.10 Alert Response
- 10.7.11 Extended Command - Write Byte/Word, Read Byte/Word
- 10.7.12 Group Command
- 10.8 PMBUS Communications Fault Handling
- 10.9 Other Functions of the PMBus Module
- 10.10
PMBus Interface Registers Reference
- 10.10.1 PMBUS Control Register 1 (PMBCTRL1)
- 10.10.2 PMBus Transmit Data Buffer (PMBTXBUF)
- 10.10.3 PMBus Receive Data Register (PMBRXBUF)
- 10.10.4 PMBus Acknowledge Register (PMBACK)
- 10.10.5 PMBus Status Register (PMBST)
- 10.10.6 PMBus Interrupt Mask Register (PMBINTM)
- 10.10.7 PMBus Control Register 2 (PMBCTRL2)
- 10.10.8 PMBus Hold Slave Address Register (PMBHSA)
- 10.10.9 PMBus Control Register 3 (PMBCTRL3)
-
11Timer Module Overview
- 11.1 T24 – 24 Bit Free-Running Timer with Capture and Compare
- 11.2 T24 Clock Source, Prescaler and Counter
- 11.3 T24 Capture Block
- 11.4 T24 Compare Blocks
- 11.5 T24 Interrupts
- 11.6 T16PWMx - 16 Bit PWM Timers
- 11.7 T16PWMx Summary
- 11.8 T16PWMx Prescaler and Counter
- 11.9 T16PWMx Compare Blocks
- 11.10 T16 Shadow Bit
- 11.11 T16 Interrupts
- 11.12 Using the T16 for a Timer Interrupt
- 11.13 Using the T16 for PWM Generation
- 11.14 WD - Watchdog
- 11.15 Watchdog Prescale and Counter
- 11.16 Watchdog Compare Blocks
- 11.17 Watchdog Protect Bit
- 11.18 Watchdog Timer Example
- 11.19 Warnings for Watchdog Status Register
- 11.20 System Fault Recovery Basics
- 11.21
Timer Module Register Reference
- 11.21.1 24-bit Counter Data Register (T24CNTDAT)
- 11.21.2 24-bit Counter Control Register (T24CNTCTRL)
- 11.21.3 24-bit Capture Channel Data Register (T24CAPDAT) or (T24CAPDATx)
- 11.21.4 24-bit Capture Channel Control Register (T24CAPCTRLx or T24CAPCTRL)
- 11.21.5 24-bit Capture I/O Control and Data Register (T24CAPIO)
- 11.21.6 24-bit Output Compare Channel 0 Data Register (T24CMPDAT0)
- 11.21.7 24-bit Output Compare Channel 1 Data Register (T24CMPDAT1)
- 11.21.8 24-bit Output Compare Channel 0 Control Register (T24CMPCTRL0)
- 11.21.9 24-bit Output Compare Channel 1 Control Register (T24CMPCTRL1)
- 11.21.10 PWMx Counter Data Register (T16PWMxCNTDAT)
- 11.21.11 PWMx Counter Control Register (T16PWMxCNTCTRL)
- 11.21.12 PWMx 16-bit Compare Channel 0-1 Data Register (T16PWMxCMPyDAT)
- 11.21.13 PWMx Compare Control Register (T16PWMxCMPCTRL)
- 11.21.14 Watchdog Status (WDST)
- 11.21.15 Watchdog Control (WDCTRL)
-
12UART Overview
- 12.1 UART Frame Format
- 12.2 Asynchronous Timing Mode
- 12.3 UART Interrupts
- 12.4 Transmit Interrupt
- 12.5 Receive Interrupt
- 12.6 Error Interrupts
- 12.7
UART Registers Reference
- 12.7.1 UART Control Register 0 (UARTCTRL0)
- 12.7.2 UART Receive Status Register (UARTRXST)
- 12.7.3 UART Transmit Status Register (UARTTXST)
- 12.7.4 UART Control Register 3 (UARTCTRL3)
- 12.7.5 UART Interrupt Status Register (UARTINTST)
- 12.7.6 UART Baud Divisor High Byte Register (UARTHBAUD)
- 12.7.7 UART Baud Divisor Middle Byte Register (UARTMBAUD)
- 12.7.8 UART Baud Divisor Low Byte Register (UARTLBAUD)
- 12.7.9 UART Receive Buffer (UARTRXBUF)
- 12.7.10 UART Transmit Buffer (UARTTXBUF)
- 12.7.11 UART I/O Control Register (UARTIOCTRLSCLK, UARTIOCTRLRX, UARTIOCTRLTX)
- 13Boot ROM and Boot Flash
- 14ARM7TDMI-S MPUSS
-
15Memory
- 15.1 Memory Controller – MMC Registers Reference
- 15.2
DEC – Address Manager Registers Reference
- 15.2.1 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 0 (MFBAHR0)
- 15.2.2 Memory Fine Base Address Low Register 0 (MFBALR0)
- 15.2.3 1.1.1 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 1-3,17-19 (MFBAHRx)
- 15.2.4 Memory Fine Base Address Low Register 1-3, 17-19 (MFBALRx)
- 15.2.5 Memory Fine Base Address High Load Differences for Enhanced 3138 Devices
- 15.2.6 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 4 (MFBAHR4)
- 15.2.7 Memory Fine Base Address Low Register 4-16 (MFBALRx)
- 15.2.8 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 5 (MFBAHR5)
- 15.2.9 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 6 (MFBAHR6)
- 15.2.10 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 7 (MFBAHR7)
- 15.2.11 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 8 (MFBAHR8)
- 15.2.12 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 9 (MFBAHR9)
- 15.2.13 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 10 (MFBAHR10)
- 15.2.14 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 11 (MFBAHR11)
- 15.2.15 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 12 (MFBAHR12)
- 15.2.16 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 13 (MFBAHR13)
- 15.2.17 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 14 (MFBAHR14)
- 15.2.18 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 15 (MFBAHR15)
- 15.2.19 Memory Fine Base Address High Register 16 (MFBAHR16)
- 15.2.20 Program Flash Control Register (PFLASHCTRL)
- 15.2.21 Data Flash Control Register (DFLASHCTRL)
- 15.2.22 Flash Interlock Register (FLASHILOCK)
-
16Control System Module
- 16.1
Address Decoder (DEC)
- 16.1.1 Memory Mapping Basics
- 16.1.2 Why Change Memory Map?
- 16.1.3 How do Memory Map Registers Work?
- 16.1.4 RONLY Bit
- 16.1.5 Boot ROM Memory Initialization
- 16.1.6 Erasing the Programming Flash
- 16.1.7 Waiting for Flash Operations to Finish
- 16.1.8 Flash Interlock Register
- 16.1.9 Clearing RDONLY Bit
- 16.1.10 Switching from User Mode to Supervisor Mode
- 16.1.11 Erasing Data Flash
- 16.1.12 Writing to Data Flash
- 16.1.13 Erasing Program Flash
- 16.1.14 Writing to Program Flash
- 16.2 Memory Management Controller (MMC)
- 16.3 System Management (SYS)
- 16.4 Central Interrupt Module (CIM)
- 16.5
SYS – System Module Registers Reference
- 16.5.1 Clock Control Register (CLKCNTL)
- 16.5.2 System Exception Control Register (SYSECR)
- 16.5.3 System Exception Status Register (SYSESR)
- 16.5.4 Abort Exception Status Register (ABRTESR)
- 16.5.5 Global Status Register (GLBSTAT)
- 16.5.6 Device Identification Register (DEV)
- 16.5.7 System Software Interrupt Flag Register (SSIF)
- 16.5.8 System Software Interrupt Request Register (SSIR)
- 16.5.9 References
- 16.1
Address Decoder (DEC)
-
17Flash Memory Programming, Integrity, and Security
- 17.1 Quick Start Summary
- 17.2 Flash Memory Operations
- 17.3 Flash Management for Firmware Development
- 17.4 Flash Management in Production
- 17.5 Firmware Examples
- 18CIM – Central Interrupt Module Registers Reference
- 19Revision History
13.8.2 UCD3138A64 and UCD3138A64A
On the UCD3138 and UCD3138064, the checksum for an area of program flash is calculated as the sum of bytes over the program flash area.
For example, to calculate the checksum from start_address to end_address, the Boot ROM program on the UCD3138 and UCD3138064 executes something like the following code:
Uint32 calculate_checksum(register Uint32 start_address, register Uint32 end_address)
{
Uint32 checksum = 0;
Uint8 *addr;
for(addr=(Uint8 *)start_address; (Uint32)addr < end_address; addr++)
{
checksum = checksum + (*addr); // read byte data from flash
}
return checksum;
}For the UCD3138A64 and UCD3138128 (and A versions), the checksum is calculated as the sum of 32-bit words in the program flash area covered by the checksum, rather than the sum of 8-bit bytes. This makes the checksum calculation approximately 4 times faster. It means that the Boot ROM program can verify the checksum for 64kB in around 5ms, while the UCD3138 Boot ROM program takes 10ms to verify 32kB of program flash. Here is the code for calculating the checksum.
void calculate_checksum(register Uint32 *start_address, register Uint32 *end_address)
{
//use local register variable for speed.
register unsigned long long lcs = long_checksum;
while(start_address < end_address)
{
lcs = lcs + *start_address ;
lcs = lcs + (Uint32)*(start_address + 1) ;
start_address = start_address + 2;
}
long_checksum = lcs;
}Two words are added each pass through the loop to increase the execution speed even further.
The checksums for the UCD3138A64 and UCD3138128 are now 8 bytes in length (versus 4 bytes for the UCD3138 and UCD3138064).
The checksums and their locations are shown in Table 13-5.
| Checksum Location | Purpose |
|---|---|
| 0x07F8 | Checksum for 2kB boot in program flash 0 |
| 0x7FF8 | Checksum for 32kB program in program flash 0 |
| 0xFFF8 | Checksum for 64kB program in program flash 0 and 1 |
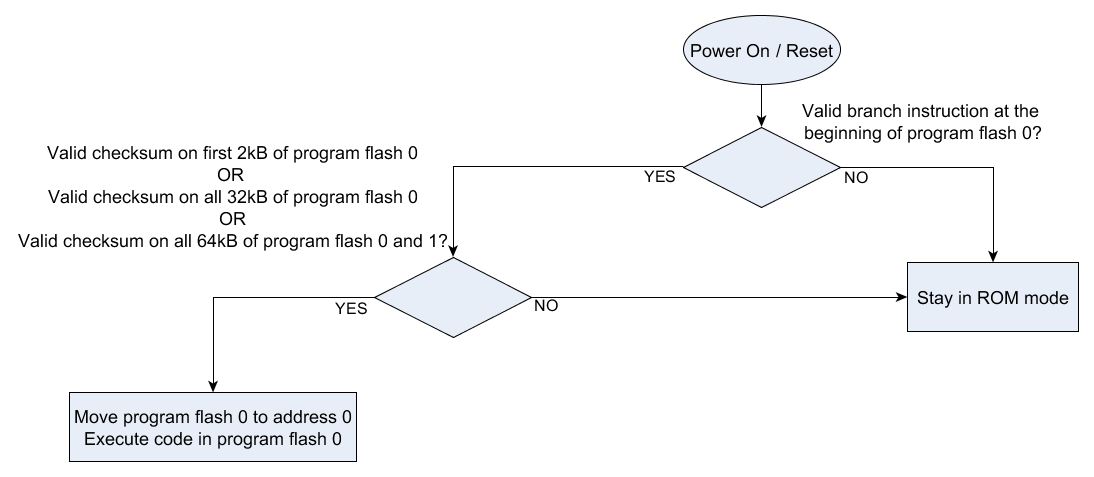 Figure 13-4 UCD3138A64 Boot ROM Execution After Power-on/Reset
Figure 13-4 UCD3138A64 Boot ROM Execution After Power-on/ResetFigure 13-4 is a flowchart showing the order in which the ROM verifies the integrity of the program flash contents using the different checksums.
The branch instruction check at the beginning prevents the checksum program from trying to verify the integrity of an empty block of memory. Otherwise a block filled with zeroes would pass the checksum test.
The UCD3138A64 doesn’t have ROM support for putting 2 separate programs into flash, one in each flash block. This can still be done, however, using a boot flash program. Or the program in block 0 can be a fixed program, which checks the program in block 1 and jumps to it if appropriate.