SNOA951 June 2016 LDC1312 , LDC1312-Q1 , LDC1314 , LDC1314-Q1 , LDC1612 , LDC1612-Q1 , LDC1614 , LDC1614-Q1
- Inductive Sensing Touch-On-Metal Buttons Design Guide
3.1.1.2 Metal Thickness
Using thinner metal sheets allows higher deformation at a given force than using thicker sheets, as illustrated in Figure 3. For example, with a 20-mm diameter button of aluminum and a force of 1 N, the 0.25-mm thick sheet has a peak deflection of 27 µm, whereas a 1-mm thick sheet only has a deflection of 0.42 µm.
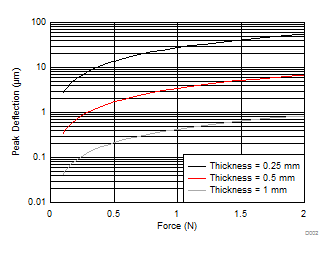 Figure 7. Force vs Peak Deflection for an Example Sheet of Al-6061-T6
Figure 7. Force vs Peak Deflection for an Example Sheet of Al-6061-T6