SNVS820B APRIL 2013 – December 2016
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 6.7 Recommended External Clock Source Conditions
- 6.8 I2C Timing Requirements (SDA, SCL)
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: Current Consumption
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: LED Output
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 LED Drivers Operational Description
- 7.3.2 Direct I2C Register PWM Control Example
- 7.3.3 Program Execution Engines
- 7.3.4 Power-Save Mode
- 7.3.5 External Clock
- 7.3.6 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.7 Logic Interface Operational Description
- 7.3.8 I/O Levels
- 7.3.9 ADDR_SEL0, ADDR_SEL1 Pins
- 7.3.10 CLK_32 Pin
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Enable Register (Enable) (Address = 00h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.2 Operation Mode Register (OP Mode) (address = 01h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.3 B LED Output PWM Control Register (B_PWM) (address = 02h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.4 G LED Output PWM Control Register (G_PWM) (address = 03h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.5 R LED Output PWM Control Register (R_PWM) (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.6 B LED Output Current Control Register (B_CURRENT)(address = 05h) [reset = AFh]
- 7.6.7 G LED Output Current Control Register (G_CURRENT)(address = 06h) [reset = AFh]
- 7.6.8 R LED Output Current Control Register (R_CURRENT) (address = 07h) [reset = AFh]
- 7.6.9 Configuration Control Register (CONFIG) (address = 08h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.10 Engine 1 Program Counter Value Register (Engine 1 PC) (address = 09h) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.11 Engine 2 Program Counter Value Register (Engine 2 PC) (address = 0Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.12 Engine 3 Program Counter Value Register (Engine 3 PC) (address = 0Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.13 STATUS/INTERRUPT Register (address = 0Ch) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.14 RESET Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.15 WLED Output PWM Control Register (W_PWM) (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 7.6.16 W LED Output Current Control Register (W_CURRENT) (address = 0Fh) [reset = AFh]
- 7.6.17 LED Mapping Register (LED Map) (address = 70h) [reset = 39h]
- 7.6.18 Program Memory (address = 10h - 6Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendation
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V (VDD, VEN/VCC, R, G, B, W) | −0.3 | 6 | V | |
| Voltage on pins | −0.3 | VDD + 0.3 with 6 V maximum | V | |
| Continuous power dissipation(2) | Internally limited | |||
| Junction temperature, TJ-MAX | 125 | °C | ||
| Maximum lead temperature (soldering) | See(3) | |||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | −65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) Internal thermal shutdown circuitry protects the device from permanent damage. Thermal shutdown engages at TJ = 150°C (typical) and disengages at TJ = 130°C (typical).
(3) For detailed soldering specifications and information, refer to Texas Instruments Application Note AN-1112 : DSBGA Wafer Level Chip Scale Package.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±1000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±250 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | 2.7 | 5.5 | V | ||
| VEN/VCC | 1.65 | VDD | V | ||
| Junction temperature, TJ | −40 | 125 | °C | ||
| Ambient temperature, TA(1) | −40 | 85 | °C | ||
(1) In applications where high power dissipation and/or poor package thermal resistance is present, the maximum ambient temperature may have to be derated. Maximum ambient temperature (TA-MAX) is dependent on the maximum operating junction temperature
(TJ-MAX-OP = 125°C), the maximum power dissipation of the device in the application (PD-MAX), and the junction-to ambient thermal resistance of the part/package in the application (RθJA), as given by the equation: TA-MAX = TJ-MAX-OP – (RθJA × PD-MAX).
(TJ-MAX-OP = 125°C), the maximum power dissipation of the device in the application (PD-MAX), and the junction-to ambient thermal resistance of the part/package in the application (RθJA), as given by the equation: TA-MAX = TJ-MAX-OP – (RθJA × PD-MAX).
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LP5562 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| YQE (DSBGA) | |||
| 12 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 85.9 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 1.0 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 15.3 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.6 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 15.4 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified: limits for typical values are for TA = 25°C and minimum and maximum limits apply over the operating ambient temperature range (−40°C < TA < +85°C); VIN = 3.6V, VEN/VCC = 1.8 V.(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CURRENT CONSUMPTION AND OSCILLATOR ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| IVDD | Standby supply current | EN = 0 (pin), CHIP_EN = 0 (bit), external 32 kHz clock running or not running | 0.2 | 2 | µA | |
| EN = 1 (pin), CHIP_EN = 0 (bit), external 32 kHz clock not running |
2 | µA | ||||
| EN = 1 (pin), CHIP_EN = 0 (bit) External 32-kHz clock running |
2.4 | µA | ||||
| Normal mode supply current | LED drivers disabled | 0.25 | mA | |||
| LED drivers enabled | 1 | mA | ||||
| Powersave mode supply current | External 32-kHz clock running | 10 | µA | |||
| Internal oscillator running | 0.25 | mA | ||||
| ƒOSC | Internal oscillator frequency accuracy | TA = 25°C | –4% | 4% | ||
| –7% | 7% | |||||
| LED DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (R, G, B, W OUTPUTS) | ||||||
| ILEAKAGE | R, G, B, W pin leakage current | TA = 25°C | 0.1 | 1 | µA | |
| IMAX | Maximum source current | Outputs R, G, B, W | 25.5 | mA | ||
| IOUT | Accuracy of output current(4) | Output current set to 17.5 mA, VDD = 3.6 V TA = 25°C |
–4% | 4% | ||
| Output current set to 17.5 mA, VDD = 3.6 V | –5% | 5% | ||||
| IMATCH | Matching(4) | Output current set to 17.5 mA, VDD = 3.6V | 1% | 2% | ||
| ƒLED | LED PWM switching frequency | PWM_HF = 1 | 558 | Hz | ||
| PWM_HF = 0 | 256 | |||||
| VSAT | Saturation voltage(5) | Output current set to 17.5 mA TA = 25°C |
60 | 100 | mV | |
(1) The electrical characteristics tables list ensured specifications under the listed recommended conditions except as otherwise modified or specified by the electrical characteristics test conditions and/or notes. Typical specifications are estimations only and are not verified by production testing.
(2) All voltages are with respect to the potential at the GND pins.
(3) Minimum and maximum limits are ensured by design, test, or statistical analysis. Typical numbers are not verified by production, but do represent the most likely norm.
(4) Output current accuracy is the difference between the actual value of the output current and programmed value of this current. Matching is the maximum difference from the average. For the constant current outputs on the part, the following are determined: the maximum output current (MAX), the minimum output current (MIN), and the average output current of all outputs (AVG). Two matching numbers are calculated: (MAX – AVG)/AVG and (AVG – MIN)/AVG. The largest number of the two (worst case) is considered the matching figure. Note that some manufacturers have different definitions in use.
(5) Saturation voltage is defined as the voltage when the LED current has dropped 10% from the set value.
6.6 Logic Interface Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified: limits for typical values are for TA = 25°C and minimum and maximum limits apply over the operating ambient temperature range (−40°C < TA < +85°C); VEN = 1.65 V.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOGIC INPUT EN | ||||||
| VIL | Input low level | 0.5 | V | |||
| VIH | Input high level | 1.2 | V | |||
| II | Logic input current | –1 | 1 | µA | ||
| tDELAY | Input delay(1) | 2 | µs | |||
| LOGIC INPUT SCL, SDA, CLK_32K, ADDR_SEL0, ADDR_SEL1, VEN = 1.8 V | ||||||
| VIL | Input low level | 0.2 × VEN | V | |||
| VIH | Input high level | 0.8 × VEN | V | |||
| II | Input current | –1 | 1 | µA | ||
| ƒCLK_32K | Clock frequency | 32 | kHz | |||
| ƒSCL | Clock frequency | 400 | kHz | |||
| LOGIC OUTPUT SDA | ||||||
| VOL | Output low level | IOUT = 3 mA (pullup current) | 0.3 | 0.5 | V | |
| IL | Output leakage current | 1 | µA | |||
(1) The I2C host should allow at least 1ms before sending data to the LP5562 after the rising edge of the enable line.
6.7 Recommended External Clock Source Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOGIC INPUT CLK_32K | ||||||
| ƒCLK_32K | Clock frequency | 32.7 | kHz | |||
| tCLKH | High time | 6 | µs | |||
| tCLKL | Low time | 6 | µs | |||
| tr | Clock rise time | 10% to 90% | 2 | µs | ||
| tf | Clock fall time | 90% to 10% | 2 | µs | ||
(1) Specification is ensured by design and is not tested in production. VEN = 1.65 V to VDD.
(2) The ideal external clock signal for the LP5562 is a 0 V to VEN 25% to 75% duty-cycle square wave. At frequencies above 32.7 kHz, program execution will be faster and at frequencies below 32.7 kHz program execution will be slower.
6.8 I2C Timing Requirements (SDA, SCL)
See(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ƒSCL | Clock frequency | 400 | kHz | |
| 1 | Hold time (repeated) START condition | 0.6 | µs | |
| 2 | Clock low time | 1.3 | µs | |
| 3 | Clock high time | 600 | ns | |
| 4 | Setup time for a repeated START condition | 600 | ns | |
| 5 | Data hold time | 50 | ns | |
| 6 | Data setup time | 100 | ns | |
| 7 | Rise time of SDA and SCL | 20 + 0.1Cb | 300 | ns |
| 8 | Fall time of SDA and SCL | 15 + 0.1Cb | 300 | ns |
| 9 | Set-up time for STOP condition | 600 | ns | |
| 10 | Bus-free time between a STOP and a START condition | 1.3 | µs | |
| Cb | Capacitive load for each bus line | 10 | 200 | pF |
(1) Specification is ensured by design and is not tested in production. VEN = 1.65 V to VDD.
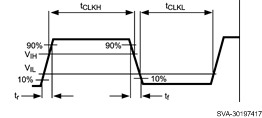 Figure 1. External Clock Timing
Figure 1. External Clock Timing
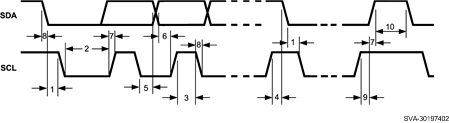 Figure 2. I2C Timing Parameters
Figure 2. I2C Timing Parameters
6.9 Typical Characteristics: Current Consumption
Unless otherwise specified: VDD = 3.6 V, VEN = 3.3 V. Here are presented input current consumption measurements. Current consumption is measured during a LED blink program execution. Program code sets every LED output to full PWM value for 2 seconds and then PWM is set to 0 for 2 seconds. This is looped endlessly. 750 measurements are taken during one measurement cycle.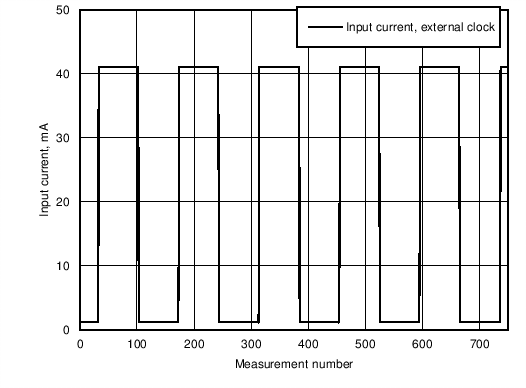 Figure 3. Input Current Consumption in Normal Mode With External Clock Running. 4 LEDs (RGBW) Set as Load. Every LED Driver Current Value Is Set to 10 mA.
Figure 3. Input Current Consumption in Normal Mode With External Clock Running. 4 LEDs (RGBW) Set as Load. Every LED Driver Current Value Is Set to 10 mA.
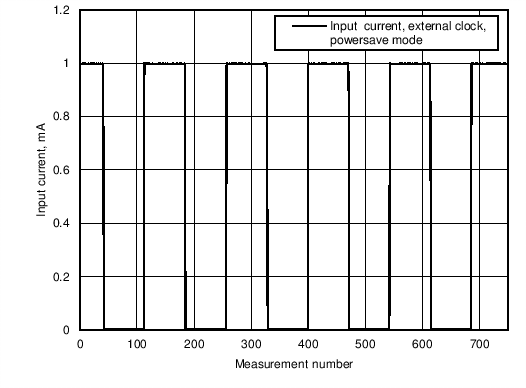 Figure 5. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With External Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. All 4 LED Drivers are Enabled During Program Execution.
Figure 5. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With External Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. All 4 LED Drivers are Enabled During Program Execution.
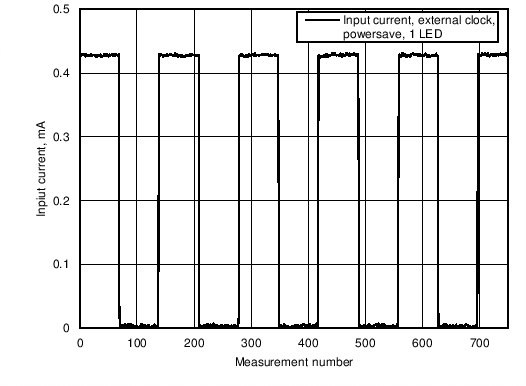 Figure 7. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With External Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. Only 1 LED Driver is Enabled During Program Execution.
Figure 7. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With External Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. Only 1 LED Driver is Enabled During Program Execution.
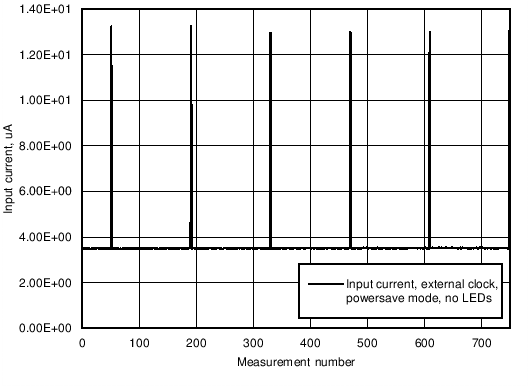 Figure 9. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With External Clock Running, no LEDs as Load and no LED Drivers are Enabled During Program Execution.
Figure 9. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With External Clock Running, no LEDs as Load and no LED Drivers are Enabled During Program Execution.
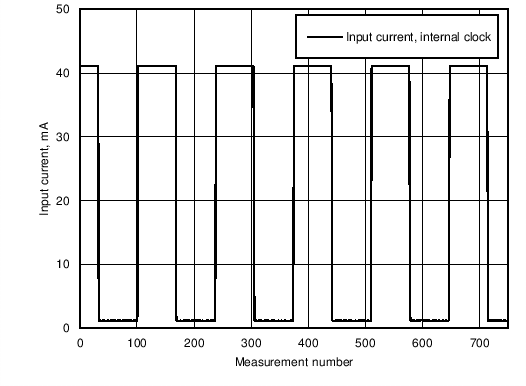 Figure 4. Input Current Consumption in Normal Mode With Internal Clock Running. 4 LEDs (RGBW) set as Load. Every LED Driver Current Value is Set to 10 mA .
Figure 4. Input Current Consumption in Normal Mode With Internal Clock Running. 4 LEDs (RGBW) set as Load. Every LED Driver Current Value is Set to 10 mA .
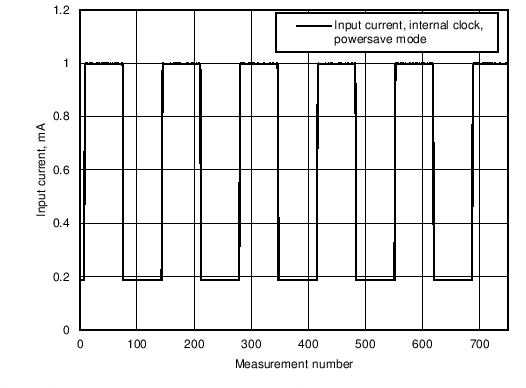 Figure 6. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With Internal Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. All 4 LED Drivers are Enabled During Program Execution.
Figure 6. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With Internal Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. All 4 LED Drivers are Enabled During Program Execution.
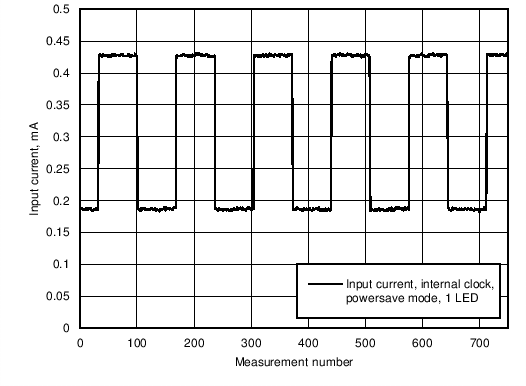 Figure 8. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With Internal Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. Only 1 LED Driver is Enabled During Program Execution.
Figure 8. Input Current Consumption in Power Save Mode With Internal Clock Running, no LEDs as Load. Only 1 LED Driver is Enabled During Program Execution.
6.10 Typical Characteristics: LED Output
LED driver typical performance images.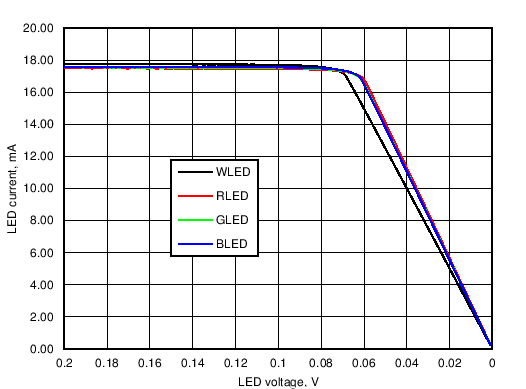 Figure 10. Every LED Driver Saturation Voltage, Current Setting 17.5 mA
Figure 10. Every LED Driver Saturation Voltage, Current Setting 17.5 mA
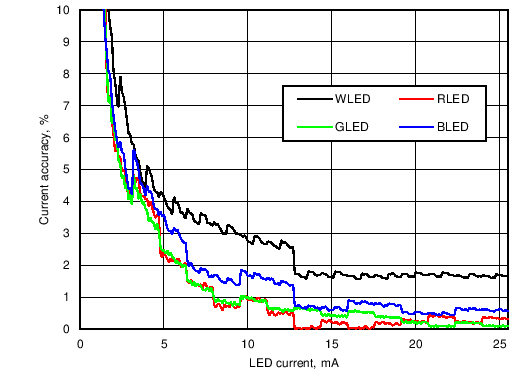 Figure 12. LED Driver Current Accuracy With Different Current Setting
Figure 12. LED Driver Current Accuracy With Different Current Setting
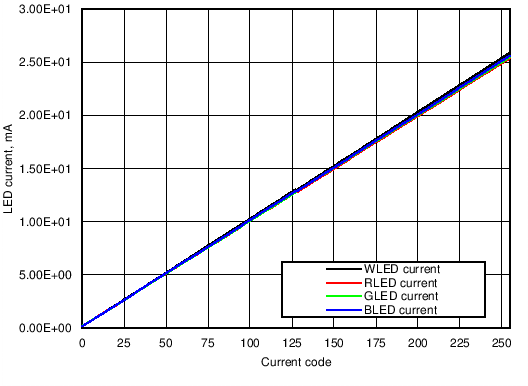 Figure 11. LED Driver Currents Compared to Current Setting Code
Figure 11. LED Driver Currents Compared to Current Setting Code
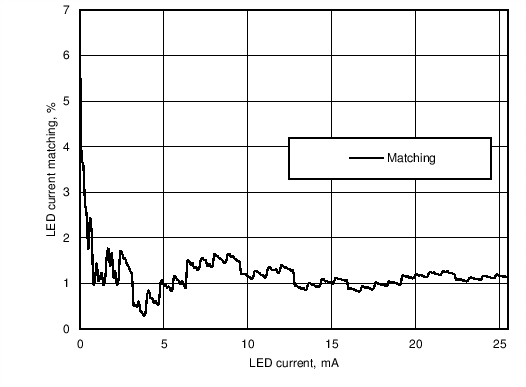 Figure 13. LED Driver Current Matching Between all LED Drivers With Different Current Setting
Figure 13. LED Driver Current Matching Between all LED Drivers With Different Current Setting